|
Curt Brunnée
Curt Brunnée (24 May 1928 – 14 December 2023) was a German physicist known for his contributions to the field of mass spectrometry instrumentation. Brunnée was born on 24 May 1928. Brunnée married his long time laboratory assistant, Curta, in 1953. He died on 14 December 2023, at the age of 95. Career and research Brunnée grew up in Rostock, his father was a dentist and his grandfather had a factory in Göttingen that produced optical instruments. During the war, his childhood home was destroyed by a bombing raid in 1942 and in 1944, the family narrowly escaped death as a bomb partially destroyed the cellar in which they were sheltering. Only after the war ended and schools resumed, could Brunnée finish his high school education and enter university. He entered the Universität Rostock in 1946, but fled in 1948 due to the increasingly repressive climate in eastern Germany, crossing the boundary between the Soviet occupation zone and the west illegally. He then enrolled a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostock
Rostock (; Polabian language, Polabian: ''Roztoc''), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (), is the largest city in the German States of Germany, state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, close to the border with Pomerania. With around 210,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast after Kiel and Lübeck, the eighth-largest city in the area of former East Germany, as well as the List of cities in Germany by population, 39th-largest city of Germany. Rostock was the largest coastal and most important port city in East Germany. Rostock stands on the estuary of the Warnow, River Warnow into the Bay of Mecklenburg of the Baltic Sea. The city stretches for about along the river. The river flows into the sea in the very north of the city, between the boroughs of Warnemünde and Hohe Düne. The city center lies further upstream, in the very south of the city. Most of Rostock's inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (, ), is the capital of the States of Germany, German state of the Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 577,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city is the List of cities in Germany by population, 11th-largest city of Germany and the second-largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its River mouth, mouth into the North Sea at Bremerhaven, and is completely surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. Bremen is the centre of the Northwest Metropolitan Region, which also includes the cities of Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, and has a population of around 2.8 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhorst, Stuhr, Achim, Wey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson Medal Recipients
Thomson may refer to: Names * Thomson (surname), a list of people with this name and a description of its origin * Thomson baronets, four baronetcies created for persons with the surname Thomson Businesses and organizations * SGS-Thomson Microelectronics, an electronics manufacturer * Various travel subsidiaries of TUI Group: ** Thomson Airways (now TUI Airways), a UK-based airline ** Thomson Cruises (now Marella Cruises), a UK-based cruise line ** Thomson Travel (now TUI UK), a UK-based travel company ** Thomsonfly, a former UK airline, formerly Britannia Airways * Thomson Directories, local business search company and publisher of: ** Thomson Local, the UK business directory * Thomson Multimedia, former name of Technicolor SA, a French multinational corporation * Thomson Reuters, Canadian media and information services company ** Thomson Corporation, former name of the company prior to its 2008 merger with Reuters ** Thomson Financial, former business division of Thomso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2023 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1928 Births
Events January * January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly demonstrating that DNA is the genetic material. * January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris Bazhanov, Joseph Stalin's personal secretary, crosses the border to Iran to defect from the Soviet Union. * January 17 – The OGPU arrests Leon Trotsky in Moscow; he assumes a status of passive resistance and is exiled with his family. * January 26 – The volcanic island Anak Krakatau appears. February * February – The Ford River Rouge Complex at Dearborn, Michigan, an automobile plant begun in 1917, is completed as the world's largest integrated factory. * February 8 – Scottish-born inventor John Logie Baird broadcasts a transatlantic television signal from London to Hartsdale, New York. * February 11 – February 19, 19 – The 1928 Winter Olympics are held in St. Moritz, Switzerland, the first as a separate event. Sonja Henie of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curt Brunnée Award
The International Mass Spectrometry Foundation (IMSF) is a non-profit scientific organization in the field of mass spectrometry. It operates the International Mass Spectrometry Society, which consists of 37 member societies and sponsors the International Mass Spectrometry Conference that is held once every two years. Aims The foundation has four aims: # organizing international conferences and workshops in mass spectrometry # improving mass spectrometry education # standardizing terminology in the field # aiding in the dissemination of mass spectrometry through publications Conferences Before the formation of the IMSF, the first International Mass Spectrometry Conference was held in London in 1958 and 41 papers were presented. Since then, conferences were held every three years until 2012, and every two years since. Conference proceedings are published in a book series, ''Advances in Mass Spectrometry'', which is the oldest continuous series of publications in mass spectrometry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnigan Instrument Corporation
Robert Emmet Finnigan (May 27, 1927August 14, 2022) was an American pioneer in the development of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry equipment (GC/MS). Finnigan founded the Scientific Instruments Division of Electronic Associates, Inc., producing the first commercial quadrupole mass spectrometer in 1964. He then formed Finnigan Instruments Corporation to combine a computer system with a quadrupole mass spectrometer and gas chromatograph. Finnigan's GC/MS/computer systems are used to detect and identify trace organic compounds, making them important instruments for the monitoring and protection of the environment. They were adopted by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as a standard instrument for monitoring water quality and were fundamental to the work of the EPA. Early life and education Robert Finnigan was born on May 27, 1927, in Buffalo, New York, to Charles M. and Marie F. Finnigan. He was one of seven children, who were raised primarily by their fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Engineering Corporation
Consolidated Engineering Corporation was a chemical instrument manufacturer from 1937 to 1960 when it became a subsidiary of Bell and Howell Corp. History CEC was founded in 1937 by Herbert Hoover Jr., eldest son of former United States president Herbert Hoover, as sole proprietor. Harold Washburn was hired in 1938 as VP for Research, with a mandate to develop instruments applicable to petroleum prospecting. Like his father, Hoover had trained as a mining engineer at Stanford University, studying under Washburn. He earned a PhD in Electrical Engineering from California Institute of Technology in 1932. His thesis Professor was Ernest Lawrence, a physicist at the University of California, Berkeley. Four physicists from California Institute of Technology were hired into the Research Department in a project to develop a mass spectrometer. The initial product was the 21-101 Mass Spectrometer delivered in December 1942, installed in early 1943, initial price $12,000, with no opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
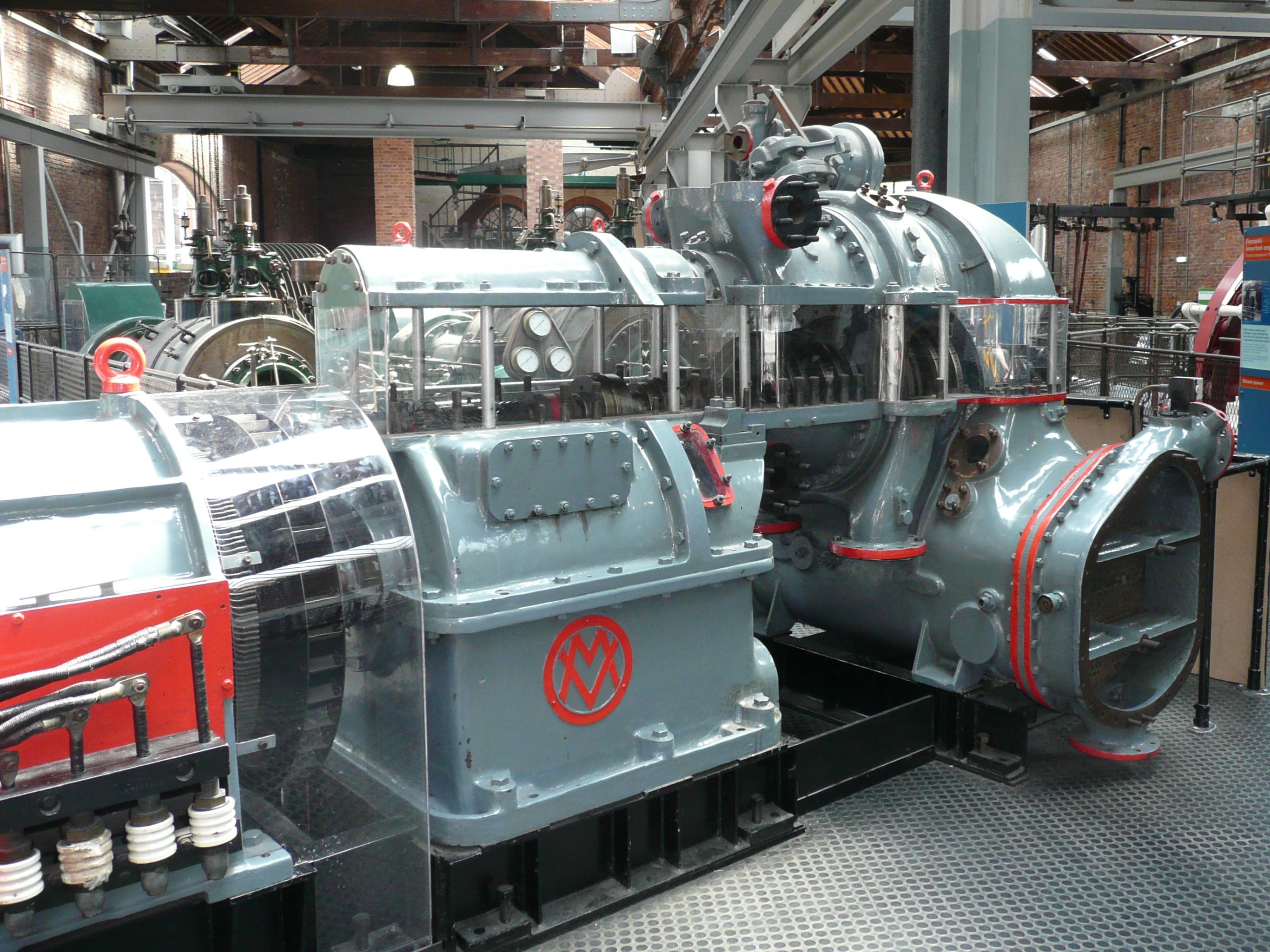
Metrovick
Metropolitan-Vickers, Metrovick, or Metrovicks, was a British heavy electrical engineering company of the early-to-mid 20th century formerly known as British Westinghouse. Highly diversified, it was particularly well known for its industrial electrical equipment such as generators, steam turbines, switchgear, transformers, electronics and railway traction equipment. Metrovick holds a place in history as the builders of the first commercial transistor computer, the Metrovick 950, and the first British axial-flow jet engine, the Metropolitan-Vickers F.2. Its factory in Trafford Park, Manchester, was for most of the 20th century one of the biggest and most important heavy engineering facilities in Britain and the world. History Metrovick started as a way to separate the existing British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company factories from United States control, which had proven to be a hindrance to gaining government contracts during the First World War. In 1917 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |