|
Curphey Peaks
Explorers Range () is a large mountain range in the Bowers Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica, extending from Mount Bruce in the north to Carryer Glacier and McLin Glacier in the south. Exploration and naming The Explorers Range was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) for the northern party of New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1963–64, whose members carried out a topographical and geological survey of the area. The names of several party members are assigned to features in and about this range. Location The Explorers Range is south of the Stuhlinger Ice Piedmont, Cape Cheetham and Gannutz Glacier. The Rennick Glacier flows north to the sea along its western side. Glaciers originating in the northern Explorer Range that flow into this glacier include, from north to south, Arruiz Glacier, Alvarez Glacier and Sheehan Glacier. Ob' Bay is to the east of the northern part of the range, which is fed by glaciers originat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barber Glacier
Ob' Bay () is a bay lying between Lunik Point and Cape Williams in Antarctica. Lillie Glacier Tongue occupies the east part of the bay. The bay was charted by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition (1958) and named after the expedition ship ''Ob''. Location Ob' Bay is on the Pacific Ocean to the east of the Explorers Range of the Bowers Mountains. It is northwest of the Anare Mountains The bay stretches between Lunik Point below Mount Dergach in the west and Cape Williams in the east. Astapenko Glacier enters the bay to the south of Mount Dergach, and is joined at its point of entry by Chugunov Glacier and Astakhov Glacier to the east. Further east, past Platypus Ridge, Lillie Glacier enters the bay, with Lillie Glacier Tongue extending into the bay. The Sputnik Islands are in the entrance to the bay. ''Sailing Directions for Antarctica'' (1943) says "Lillie Glacier Tongue extends northward from snow-covered rounded hills between Cape Cheetham and Williams Head for a distance of ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Loon Glacier
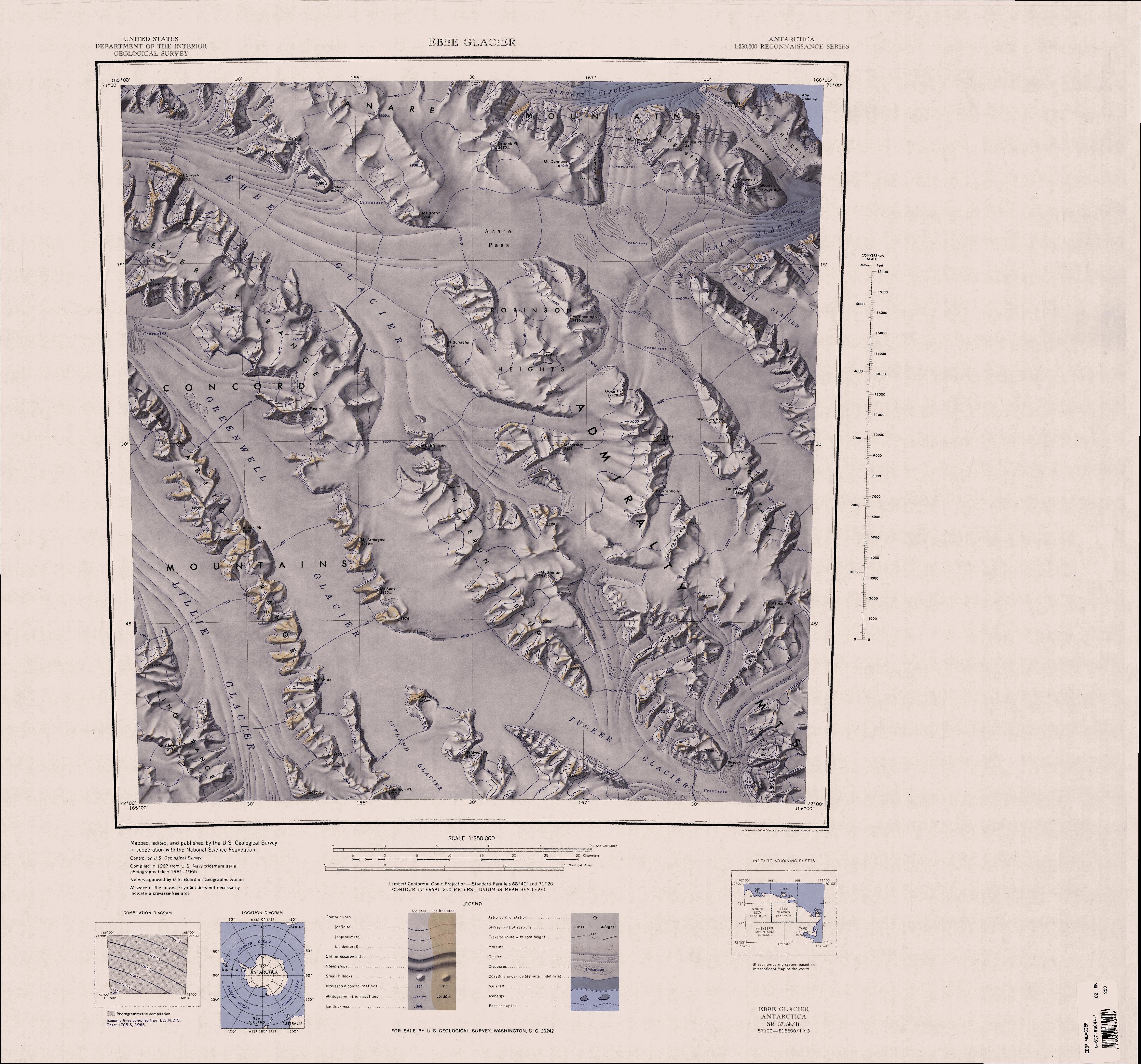
Lillie Glacier () is a large glacier in Antarctica, about long and wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue. Discovery and naming The glacier tongue was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, and was named by the expedition for Dennis G. Lillie, a biologist on the ''Terra Nova''. The name Lillie has since been extended to the entire glacier. The lower half of the glacier was plotted by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (ANARE) ('' Thala Dan'') in 1962, which explored the area and utilized air photos taken by United States Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The whole feature was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–62. On 22 October 1964 a United States Navy ski-equipped LC-47 airplane flew from Hallett Station to establish a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Névé
Névé is a young, granular type of snow which has been partially melted, refrozen and compacted, yet precedes the form of ice. This type of snow can contribute to glacier formation through the process of ''nivation''. Névé that survives a full season of ablation turns into firn, which is both older and slightly denser. Firn eventually becomes glacial ice – the long-lived, compacted ice that glaciers are composed of. Glacier formation can take years to hundreds of years, depending on freeze-thaw factors and snow-compaction rates. Névé is annually observed in skiing slopes, and is generally disliked as an icy falling zone. Névé has a minimum density of 500 kg/m3, which is Density#Water, roughly half of the density of liquid water at 1 Atmosphere (unit), atm. Névé can also refer to the Alpine climate, alpine region in which snowfall accumulates, becomes névé, and feeds a glacier. See also * Suncup (snow), Suncup Notes External links * Névés, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edlin Névé
Lillie Glacier () is a large glacier in Antarctica, about long and wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue. Discovery and naming The glacier tongue was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, and was named by the expedition for Dennis G. Lillie, a biologist on the ''Terra Nova''. The name Lillie has since been extended to the entire glacier. The lower half of the glacier was plotted by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (ANARE) ('' Thala Dan'') in 1962, which explored the area and utilized air photos taken by United States Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The whole feature was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–62. On 22 October 1964 a United States Navy ski-equipped LC-47 airplane flew from Hallett Station to establish a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanterman Range
The Lanterman Range () is a mountain range about long and wide, forming the southwest part of the Bowers Mountains in Antarctica. It is bounded by the Rennick Glacier, Sledgers Glacier, Black Glacier and Canham Glacier. Exploration and naming The range was mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–62. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander William Lanterman, an aerological officer for U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze, 1959–62. Location The Lanterman Range lies to the east of the Rennick Glacier and its tributary Canham Glacier. The Sledgers Glacier flows past its northeast end. The MacKinnon Glacier drains the range to the north into Sledgers Glacier. Glaciers draining to the west include Orr Glacier, Linder Glacier, Hunter Glacier, Hoshko Glacier, Zenith Glacier and Johnstone Glacier. The Molar Massif lies to the east. The Crown Hills form t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sledgers Glacier
Rennick Glacier () is a broad glacier, nearly long, which is one of the largest in Antarctica. It rises on the polar plateau westward of Mesa Range and is wide, narrowing to near the coast. It takes its name from Rennick Bay where the glacier reaches the sea. Early exploration The seaward part of the glacier was photographed by United States Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The upper reaches of the Rennick Glacier were discovered and explored by the U.S. Victoria Land Traverse (VLT) in February 1960, and the first ascent made of Welcome Mountain by John Weihaupt, Alfred Stuart, Claude Lorius and Arnold Heine of the VLT party. On February 10, 1960, Lieutenant Commander Robert L. Dale, pilot of U.S. Navy (USN) Squadron VX-6, evacuated the VLT from , on this glacier, and then conducted an aerial photographic reconnaissance to Rennick Bay on the coast before returning the VLT team to McMurdo Station. Course The Rennick Glacier rises to the east of the Tobin Mesa in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lillie Glacier
Lillie Glacier () is a large glacier in Antarctica, about long and wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue. Discovery and naming The glacier tongue was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, and was named by the expedition for Dennis G. Lillie, a biologist on the ''Terra Nova''. The name Lillie has since been extended to the entire glacier. The lower half of the glacier was plotted by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (ANARE) (''Thala Dan'') in 1962, which explored the area and utilized air photos taken by United States Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The whole feature was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–62. On 22 October 1964 a United States Navy ski-equipped LC-47 airplane flew from Hallett Station to establish a cac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |