|
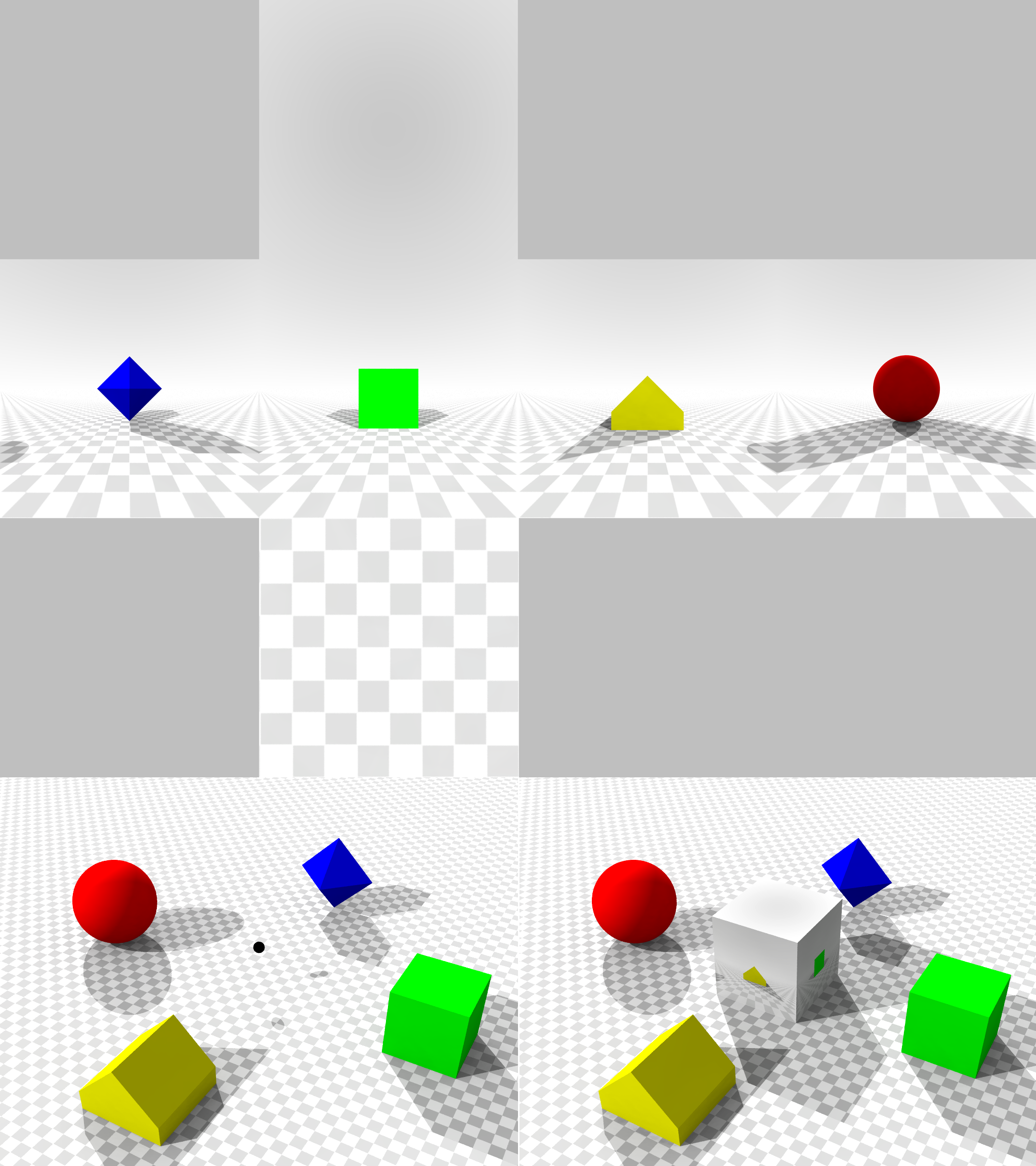
Cube Mapping
In computer graphics, cube mapping is a method of environment mapping that uses the six faces of a cube as the map shape. The environment is projected onto the sides of a cube and stored as six square textures, or unfolded into six regions of a single texture. The cube map is generated by first rendering the scene six times from a viewpoint, with the views defined by a 90 degree view frustum representing each cube face. Or if the environment is first considered to be projected onto a sphere, then each face of the cube is its Gnomonic projection. In the majority of cases, cube mapping is preferred over the older method of sphere mapping because it eliminates many of the problems that are inherent in sphere mapping such as image distortion, viewpoint dependency, and computational inefficiency. Also, cube mapping provides a much larger capacity to support real-time rendering of reflection (computer graphics), reflections relative to sphere mapping because the combination of ineffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panorama Cube Map
A panorama (formed from Greek language, Greek πᾶν "all" + ὅραμα "view") is any Obtuse angle, wide-angle view or representation of a physical space, whether in painting, drawing, photography (panoramic photography), film, seismic images, or 3D modeling. The word was coined in the 18th century by the English (Irish people, Irish descent) painter Robert Barker (painter), Robert Barker to describe his panoramic paintings of Edinburgh and London. The motion-picture term Panning (camera), ''panning'' is derived from ''panorama''. A panoramic view is also purposed for multimedia, cross-scale applications to an outline overview (from a distance) along and across repositories. This so-called "cognitive panorama" is a panoramic view over, and a combination of, cognitive spaces used to capture the larger scale. History The device of the panorama existed in painting, particularly in murals, as early as 20 A.D., in those found in Pompeii, as a means of generating an immersive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specular Highlight
A specular highlight is the bright spot of light that appears on shiny objects when illuminated (for example, see image on right). Specular highlights are important in 3D computer graphics, as they provide a strong visual cue for the shape of an object and its location with respect to light sources in the scene. Microfacets The term ''specular'' means that light is specular reflection, perfectly reflected in a mirror-like way from the light source to the viewer. Specular reflection is visible only where the surface normal is oriented precisely halfway between the direction of incoming light and the direction of the viewer; this is called the half-angle direction because it bisects (divides into halves) the angle between the incoming light and the viewer. Thus, a specularly reflecting surface would show a specular highlight as the perfectly sharp reflected image of a light source. However, many shiny objects show blurred specular highlights. This can be explained by the existe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube Map
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It is a type of parallelepiped, with pairs of parallel opposite faces, and more specifically a rhombohedron, with congruent edges, and a rectangular cuboid, with right angles between pairs of intersecting faces and pairs of intersecting edges. It is an example of many classes of polyhedra: Platonic solid, regular polyhedron, parallelohedron, zonohedron, and plesiohedron. The dual polyhedron of a cube is the regular octahedron. The cube can be represented in many ways, one of which is the graph known as the cubical graph. It can be constructed by using the Cartesian product of graphs. The cube is the three-dimensional hypercube, a family of polytopes also including the two-dimensional square and four-dimensional tesseract. A cube with unit side length is the canonical unit of volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadow Volume
Shadow volume is a technique used in 3D computer graphics to add shadows to a rendered scene. It was first proposed by Frank Crow in 1977 as the geometry describing the 3D shape of the region occluded from a light source. A shadow volume divides the virtual world in two: areas that are in shadow and areas that are not. The stencil buffer implementation of shadow volumes is generally considered among the most practical general purpose real-time shadowing techniques for use on modern 3D graphics hardware. It has been popularized by the video game '' Doom 3'', and a particular variation of the technique used in this game has become known as Carmack's Reverse. Shadow volumes have become a popular tool for real-time shadowing, alongside the more venerable shadow mapping. The main advantage of shadow volumes is that they are accurate to the pixel (though many implementations have a minor self-shadowing problem along the silhouette edge, see ''construction'' below), whereas the accura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Texture Mapping
Projective texture mapping is a method of texture mapping that allows a textured image to be projected onto a scene as if by a slide projector. Projective texture mapping is useful in a variety of lighting techniques and it is the starting point for shadow mapping. Projective texture mapping is essentially a special matrix Matrix (: matrices or matrixes) or MATRIX may refer to: Science and mathematics * Matrix (mathematics), a rectangular array of numbers, symbols or expressions * Matrix (logic), part of a formula in prenex normal form * Matrix (biology), the m ... transformation which is performed per-vertex and then linearly interpolated as standard texture mapping. Fixed function pipeline approach Historically, using projective texture mapping involved considering a special form of eye linear texture coordinate generation transform (''tcGen'' for short). This transform was then multiplied by another matrix representing the projector's properties which were stored in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Conference On Computer Vision
The International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) is a research conference sponsored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) held every other year. It is considered to be one of the top conferences in computer vision, alongside CVPR and ECCV, and it is held on years in which ECCV is not. The conference is usually spread over four to five days. Typically, experts in the focus areas give tutorial talks on the first day, then the technical sessions (and poster sessions in parallel) follow. Recent conferences have also had an increasing number of focused workshops and a commercial exhibition. Awards Azriel Rosenfeld Lifetime Achievement Award The Azriel Rosenfeld Award, or Azriel Rosenfeld Lifetime Achievement Award, recognizes researchers who have made significant contributions to the field of computer vision over their careers. It is named in memory of computer scientist and mathematician Azriel Rosenfeld. The following people have received this award ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Illumination
Global illumination (GI), or indirect illumination, is a group of algorithms used in 3D computer graphics that are meant to add more realistic lighting Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. ... to 3D scenes. Such algorithms take into account not only the light that comes directly from a light source (''direct illumination''), but also subsequent cases in which light rays from the same source are reflected by other surfaces in the scene, whether reflective or not (''indirect illumination''). Theoretically, reflections, refractions, and shadows are all examples of global illumination, because when simulating them, one object affects the rendering of another (as opposed to an object being affected only by a direct source of light). In practice, however, only the simulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Mapping
In computer graphics, reflection mapping or environment mapping is an efficient image-based lighting technique for approximating the appearance of a reflective surface by means of a precomputed texture. The texture is used to store the image of the distant environment surrounding the rendered object. Several ways of storing the surrounding environment have been employed. The first technique was sphere mapping, in which a single texture contains the image of the surroundings as reflected on a spherical mirror. It has been almost entirely surpassed by cube mapping, in which the environment is projected onto the six faces of a cube and stored as six square textures or unfolded into six square regions of a single texture. Other projections that have some superior mathematical or computational properties include the paraboloid mapping, the pyramid mapping, the octahedron mapping, and the HEALPix mapping. Reflection mapping is one of several approaches to reflection rendering, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual feedback from a display device, most commonly shown in a video format on a television set, computer monitor, flat-panel display or touchscreen on handheld devices, or a virtual reality headset. Most modern video games are audiovisual, with Sound, audio complement delivered through loudspeaker, speakers or headphones, and sometimes also with other types of sensory feedback (e.g., haptic technology that provides Touch, tactile sensations). Some video games also allow microphone and webcam inputs for voice chat in online gaming, in-game chatting and video game livestreaming, livestreaming. Video games are typically categorized according to their hardware platform, which traditionally includes arcade video games, console games, and PC game, comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective Projection
Linear or point-projection perspective () is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. It is based on the optical fact that for a person an object looks N times (linearly) smaller if it has been moved N times further from the eye than the original distance was. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to , meaning that an object's dimensions parallel to the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions perpendicular to the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skybox (video Games)
A skybox is a method of creating backgrounds to make a video game level appear larger than it really is. When a skybox is used, the level is enclosed in a cuboid. The sky, distant mountains, distant buildings, and other unreachable objects are projected onto the cube's faces (using a technique called cube mapping), thus creating the illusion of distant three-dimensional surroundings. A skydome employs the same concept but uses either a sphere or a hemisphere instead of a cube. Processing of 3D graphics is computationally expensive, especially in real-time games, and poses multiple limits. Levels have to be processed at tremendous speeds, making it difficult to render vast skyscapes in real-time. Additionally, real-time graphics generally have depth buffers with limited bit-depth, which puts a limit on the amount of details that can be rendered at a distance. To avoid these problems, games often employ skyboxes. Traditionally, these are simple cubes with up to six different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |