|
Ctenochirichthys
''Ctenochirichthys'' is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. The only species in the genus is ''Ctenochirichthys longimanus'' is known only from two locations, on in the Atlantic Ocean and the other in the Western Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy ''Ctenochirichthys'' was first proposed as genus in 1932 by the British ichthyologists Charles Tate Regan and Ethelwynn Trewavas when they described ''C. longimanus''. The type locality of ''C. longimanus'' was given as the Gulf of Panama at 7°06'N, 79°55'W, Dana station 3548, from a depth of . The 5th edition of Fishes of the World classifies this taxon in the family Oneirodidae in the suborder Ceratioidei of the anglerfish order Lophiiformes. Etymology ''Ctenochirichthys'' is a combination of ', which means "comb" with ', meaning "hand", a reference to the long pectoral fins, which have between 24 and 27 (in fact 28 to 30) comb-like rays alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneirodidae
Oneirodidae, the dreamers are a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Lophiiformes, the anglerfishes. These fishes are deepwater fishes found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans, and it is the most diverse family of fishes in the bathypelagic zone. Taxonomy Oneirodidae was first proposed as a family in 1879 by the American biologist Theodore Gill with ''Oneirodes'' as its only genus. ''Oneirodes ''had been proposed as a monospecific genus in 1871 by the Danish zoologist Christian Frederik Lütken when he described '' O. eschrichtii'', giving its type locality as off the western coast of Greenland. The 5th edition of Fishes of the World classifies this family in the suborder Ceratioidei of the anglerfish order Lophiiformes. Genera Oneirodidae has the following genera classified within it: With over 60 species classified within this family, it is the most species diverse family of fishes in the bathypelagic zone. Etymology Oneirodidae is derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Tate Regan
Charles Tate Regan (1 February 1878 – 12 January 1943) was a British ichthyology, ichthyologist, working mainly around the beginning of the 20th century. He did extensive work on fish classification schemes. Born in Sherborne, Dorset, he was educated at Derby School and Queens' College, Cambridge and in 1901 joined the staff of the Natural History Museum, London, Natural History Museum, where he became Keeper of Zoology, and later director of the entire museum, in which role he served from 1927 to 1938. Regan was elected Fellow of the Royal Society in 1917. Regan mentored a number of scientists, among them Ethelwynn Trewavas, who continued his work at the British Natural History Museum. Taxon described by him *See :Taxa named by Charles Tate Regan Among the species he described is the Siamese fighting fish (''Betta splendens''). In turn, a number of fish species have been named ''regani'' in his honour: Taxon named in his honor *A Thorny Catfish ''Anadoras regani'' (Stein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Publishing, publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, Academic journal, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, Technology, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of the Canary Islands, Spain, west of the Morocco and southwest of mainland Portugal. Madeira sits on the African Plate, African Tectonic Plate, but is culturally, politically and ethnically associated with Europe, with its population predominantly descended from Portuguese settlers. Its population was 251,060 in 2021. The capital of Madeira is Funchal, on the main island's south coast. The archipelago includes the islands of Madeira Island, Madeira, Porto Santo Island, Porto Santo, and the Desertas Islands, Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands. Roughly half of the population lives in Funchal. The region has political and administrative autonomy through the Autonomous Regions of Portugal#Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
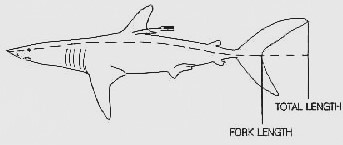
Standard Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of fish anatomy, their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the Glossary of ichthyology#H, hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal fin, caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most Actinopterygii, bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes (lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different things which can interfere with a normal sense of smell, including damage to the nose or smell receptors, anosmia, upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of Eleanor Gamble, published in 1898, which compared olfactory to othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Peduncle
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish (Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are predominantl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illicium (fisjh Anatomy)
''Illicium'' is a genus of flowering plants treated as part of the family Schisandraceae,''Illicium''. Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). or alternately as the sole genus of the .Watson, L. and M. J. Dallwitz. 1992 onwards Illiciaceae Van Tiegh. The Families of Flowering Plants. Version: 19 August 2013. It has a , with most species native to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish (Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are predominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
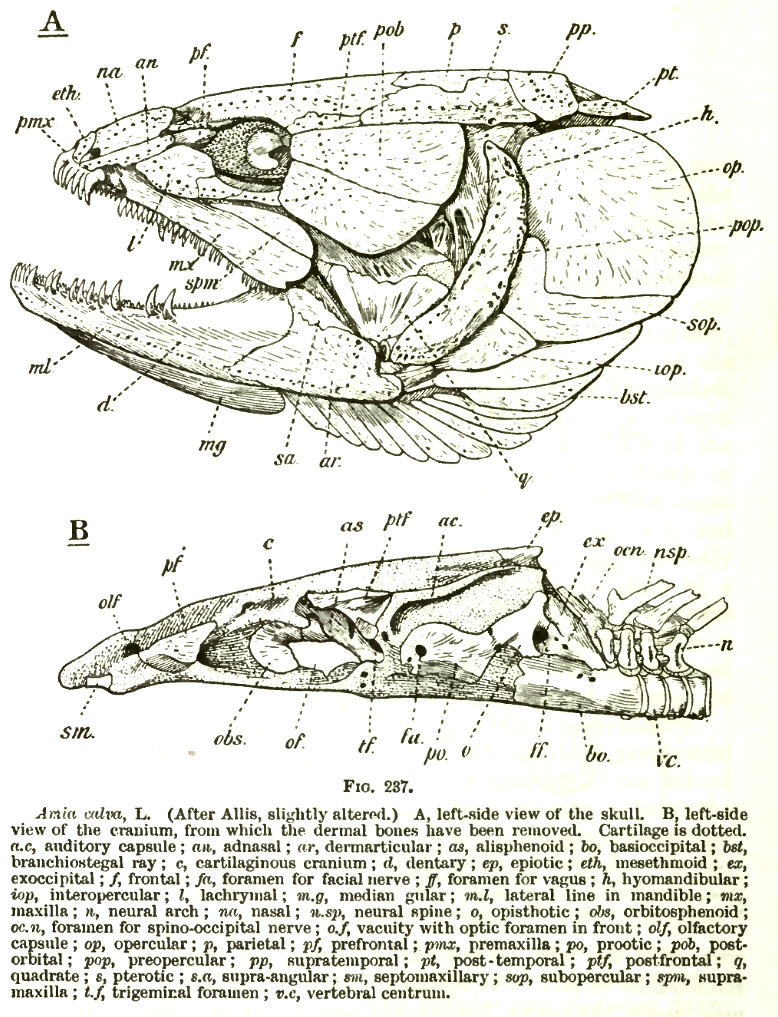
Operculum (fish)
The operculum is a series of bones found in bony fish and chimaeras that serves as a facial support structure and a protective covering for the gills; it is also used for respiration and feeding. Anatomy The opercular series contains four bone segments known as the preoperculum, suboperculum, interoperculum and operculum. The preoperculum is a crescent-shaped structure that has a series of ridges directed posterodorsally to the organism’s canal pores. The preoperculum can be located through an exposed condyle that is present immediately under its ventral margin; it also borders the operculum, suboperculum, and interoperculum posteriorly. The suboperculum is rectangular in shape in most bony fish and is located ventral to the preoperculum and operculum components. It is the thinnest bone segment out of the opercular series and is located directly above the gills. The interoperculum is triangular shaped and borders the suboperculum posterodorsally and the preoperculum anterodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyomandibula
The hyomandibula, commonly referred to as hyomandibular one(, from , "upsilon-shaped" (υ), and Latin: mandibula, "jawbone"), is a set of bones that is found in the hyoid region in most fishes. It usually plays a role in suspending the jaws and/or operculum ( teleostomi only). It is commonly suggested that in tetrapods (land animals), the hyomandibula evolved into the columella ( stapes). Evolutionary context In jawless fishes, a series of gills opened behind the mouth, and these gills became supported by cartilaginous elements. The first set of these elements surrounded the mouth to form the jaw. There is ample evidence For example: (1) both sets of bones are made from neural crest cells (rather than mesodermal tissue like most other bones); (2) both structures form the upper and lower bars that bend forward and are hinged in the middle; and (3) the musculature of the jaw seem homologous to the gill arches of jawless fishes. (Gilbert 2000) that vertebrate jaws are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |