|
Ctenochaetus Marginatus
''Ctenochaetus marginatus'', the blue-spotted bristletooth, blue-spotted surgeonfish or striped-fin surgeonfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the biology Acanthuridae which includes the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. The blue-spotted bristletooth is found in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. Taxonomy ''Ctenochaetus marginatus'' was first formally described as ''Acanthurus marginatus'' in 1835 by the French zoologist Achille Valenciennes with its type locality given as Lukonor Island (part of the Federated States of Micronesia) in the Caroline Islands. The genera ''Ctenochaetus'' and ''Acanthurus'' make up the tribe Acanthurini which is one of three tribes in the subfamily Acanthurinae which is one of two subfamilies in the family Acanthuridae. Etymology ''Ctenochaetus marginatus'' has the specific name ''marginatus'', meaning "bordered" or "edged", which is a reference to the band on the bases of the dorsal and anal fins. Description ''Cten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achille Valenciennes
Achille Valenciennes (9 August 1794 – 13 April 1865) was a French zoology, zoologist. Valenciennes was born in Paris, and studied under Georges Cuvier. His study of parasitic worms in humans made an important contribution to the study of parasitology. He also carried out diverse systematic classifications, linking fossil and current species. He worked with Cuvier on the 22-volume "''Histoire Naturelle des Poissons''" (Natural History of Fish) (1828–1848), carrying on alone after Cuvier died in 1832. In 1832, he succeeded Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (1777–1850) as chair of ''Histoire naturelle des mollusques, des vers et des zoophytes'' at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. Early in his career, he was given the task of classifying animals described by Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) during his travels in the American tropics (1799 to 1803), and a lasting friendship was established between the two men. He is the binomial authority for many species of fish, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish ( Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish ( Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenochaetus
''Ctenochaetus'', or bristletooth tangs, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, which includes the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. These fishes are found in the Indo-Pacific region. They have many, small flexible teeth and some species have the common name bristletooth. Taxonomy ''Ctenochaetus'' was first proposed as a genus in 1884 by the American biologist Theodore Gill with ''Acanthurus strigosus'' as its type species. ''A. strigosus'' had originally been described in 1828 by Edward Turner Bennett from the Sandwich Islands. Paraphyly It has been proposed that this genus and ''Acanthurus'' should be merged as otherwise ''Acanthurus'' is paraphyletic. ''Ctenochaetus'' species all nest within ''Acanthurus'', while '' A. nubilis'' and '' A. pyroferus'' are furthermore nested within ''Ctenochaetus''. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' recognises these two genera as valid and classifies them as the two genera in the tribe Acan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgona Island (Colombia)
Gorgona is a Colombian island in the Pacific Ocean situated about off the Colombian Pacific coast. The island is long and across at its widest, with a maximum height of and a total area of . Gorgona is separated from the continent by a deep underwater depression. Administratively, the island is part of the Municipality of Guapí in the Department of Cauca. Gorgona functioned as a prison from 1959 until 1984 when it was turned into a National Natural Park. The island, noted for its many endemic species and unique ecosystems, was established as Gorgona Island National Park in 1985, in order to preserve its richly varied wildlife of the sub-tropical forest and the coral reefs offshore. History Early settlements Gorgona was first inhabited by people possibly associated with the Tumaco-Tolita culture. The indigenous Kuna or Cuna of Urabá (Colombia) and San Blas (Panama), have the tradition of being the first settlers of the island. They left archeological remains dating back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocos Island
Cocos Island () is a volcanic island in the Pacific Ocean administered by Costa Rica, approximately southwest of the Costa Rican mainland. It constitutes the 11th of the 15 districts of Puntarenas Canton of the Puntarenas Province, Province of Puntarenas. With an area of approximately , the island is roughly rectangular in shape. It is the Extreme points of North America, southernmost point of geopolitical North America if Island#Continental islands, non-continental islands are included, and the only landmass above water on the Cocos Plate, Cocos tectonic plate. The entirety of Cocos Island has been designated a Costa Rican National Parks of Costa Rica, National Park since 1978, and has no permanent inhabitants other than Costa Rican park rangers. As a result, it has been labelled as the world's largest uninhabited tropical island. Surrounded by deep waters with Equatorial Counter Current, counter-currents, Cocos Island is admired by Scuba set, scuba divers for its populations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clipperton Atoll
Clipperton Island ( ; ), also known as Clipperton Atoll and previously as Clipperton's Rock, is an uninhabited France, French coral atoll in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The only French territory in the North Pacific, Clipperton is from Paris, France; from Papeete, French Polynesia; and from Acapulco, Mexico. Clipperton was documented by French merchant-explorers in 1711 and formally claimed as part of the French protectorate of Kingdom of Tahiti, Tahiti in 1858. Despite this, American guano miners began working the island in the early 1890s. As interest in the island grew, Mexico asserted a claim to the island based upon Spanish records from the 1520s that may have identified the island. Mexico established a small military colony on the island in 1905, but during the Mexican Revolution contact with the mainland became infrequent, most of the colonists died, and lighthouse keeper Victoriano Álvarez instituted a short, brutal reign as "king" of the island. Eleven survivors we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
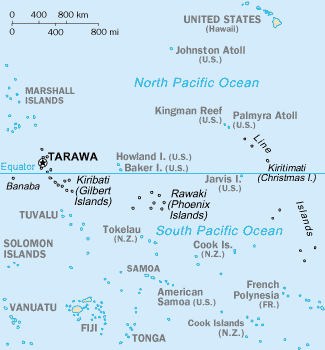
Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands () are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons, except Vostok and Jarvis) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. Eight of the atolls are parts of Kiribati. The remaining three— Jarvis Island, Kingman Reef, and Palmyra Atoll—are territories of the United States grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands. The Line Islands, all of which were formed by volcanic activity, are one of the longest island chains in the world, stretching from northwest to southeast. One of them, Starbuck Island, is near the geographic center of the Pacific Ocean (). Another, Kiritimati, has the largest land area of any atoll in the world. Only Kiritimati, Tabuaeran, and Teraina have a permanent population. Besides the 11 confirmed atolls and islands, Filippo Reef is shown on some maps, but its existence is doubted. The International Date L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Islands
The Society Islands ( , officially ; ) are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Mo'orea, Moorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of France, overseas country of the France, French Republic. Geographically, they form part of Polynesia. Name The term ''Society Islands'' was first used by Captain James Cook when he visited the Leeward Islands (Society Islands), Leeward Islands, a subgroup of six of the modern-day Society Islands, during his First voyage of James Cook, expedition to the south Pacific Ocean in 1769. It has been asserted that the name honors the Royal Society, the sponsor of his voyage, but this is disputed. Cook wrote in his journal: History Settlement The first Polynesians are understood to have arrived on these islands around 1000AD. Oral history origin The islanders explain their origins in terms of an oral tradition, orally transmitted sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquesas Islands
The Marquesas Islands ( ; or ' or ' ; Marquesan language, Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan language, North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan language, South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcano, volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific Ocean. Their highest point is the peak of Mont Oave, Mount Oave () on Ua Pou island, at 1,230 m (4,035 ft) above sea level. Archaeological research suggests the islands were colonized in the 10th century AD by voyagers from West Polynesia. Over the centuries that followed, the islands have maintained a "remarkably uniform culture, biology and language". The Marquesas were named after the 16th-century Spanish Viceroy of Peru, the García Hurtado de Mendoza, 5th Marquis of Cañete, Marquis of Cañete (), by navigator , who visited them in 1595. The Marquesas Islands constitute one of the administrative divisions of French Polynesia, five administrative di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
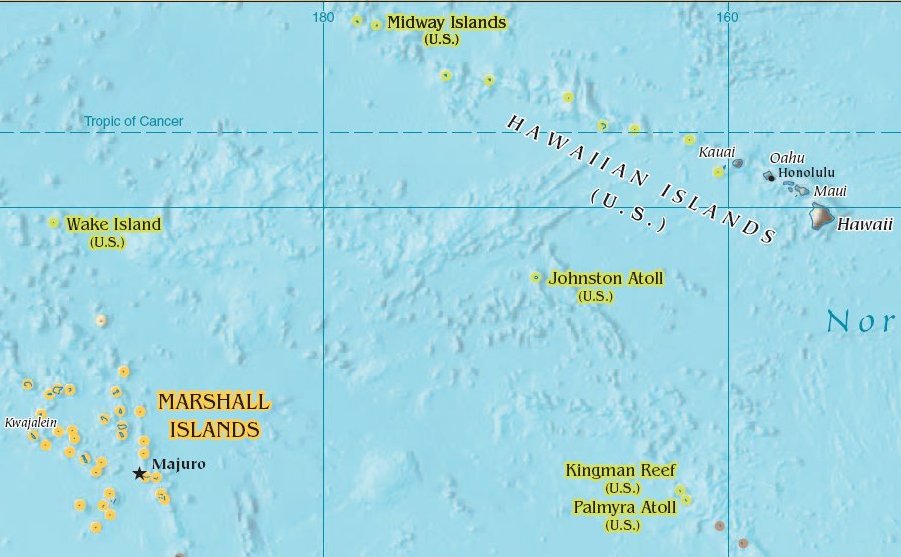
Johnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll is an Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States, under the jurisdiction of the United States Air Force (USAF). The island is closed to public entry, and limited access for management needs is only granted by a letter of authorization from the USAF. A special use permit is also required from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) to access the island by boat or enter the waters surrounding the island, which are designated as a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Islands Heritage Marine National Monument. The Johnston Atoll National Wildlife Refuge extends from the shore out to 12 nautical miles, continuing as part of the National Wildlife Refuge System out to 200 nautical miles. The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument extends from the shore out to 200 nautical miles. The isolated atoll has been under the control of the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military since 1934. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. The territory consists of 29 coral atolls and five main islands as well as 1,220 other very small ones, divided across two Archipelago, island chains: Ratak in the east and Ralik in the west. 97.87% of its territory is water, the largest proportion of water to land of any sovereign state. The country shares Maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and the Federated States of Micronesia to the west. The capital city, capital and largest city is Majuro, home to approximately half of the country's population. The Marshall Islands are one of only four atoll based nations in the entire world. Austronesian settlers reached the Marshall Islands as early as the 2nd millennium BC and introduced Southeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
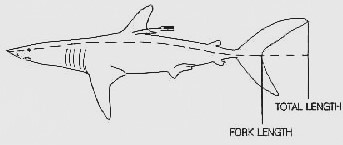
Total Length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |