|
Cryspovirus
''Cryspovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family ''Partitiviridae''. Protists serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: ''Cryptosporidium parvum virus 1''. Cryptosporidium, a genus of Apicomplexan parasites, is known to cause human diarrheal illness. A bi-segmented dsRNA virus linked with Cryptosporidium was discovered and found to have similarities with picobirnaviruses and partitiviruses. This discovery led to the identification of a distinct virus called Cryptosporidium parvum virus 1 (CSpV1). It was suggested to be the sole partitivirus found in a protozoan host. Based on this, a new genus named Cryspovirus was proposed within the Partitiviridae family, which was subsequently approved by the ICTV Executive Committee in 2009. CSpV1, also known as Cryspovirus, is believed to be transmitted intracellularly through Cryptosporidium oocysts and is linked with persistent, mostly non-virulent infections. The virus features isometric virions and has a genome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitiviridae
''Partitiviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Plants, fungi, and protozoa serve as natural hosts. It has been suggested that they can also infect bacteria. The name comes from the Latin ''partitius,'' which means divided, and refers to the segmented genome of partitiviruses. There are five genera and 60 species in the family, 15 of which are unassigned to a genus. Structure Viruses in the family ''Partitiviridae'' are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries and T=1 symmetry. The diameter of partitiviruses is around 25–43 nm. Genome Partitiviruses have double-stranded RNA genomes divided into two genomic segments, and there may be additional subgenomic segments. The two genome segments are packaged in separate virus particles. They code for two separate proteins. The first segment codes for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and the second segment codes for the coat protein. The segments are around 1.4–3.0 kbp in length, while the tota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ... of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathway Of How Double Stranded RNA Viruses Replicate
Pathway or pathways may refer to: Entertainment *The Pathway (novel), ''The Pathway'' (novel), a 1914 work by Gertrude Page *''The Pathway'', a 2001 album by Officium Triste * Pathway (album), ''Pathway'' (album), by the Flaming Stars * Pathways (album), ''Pathways'' (album) (2010), by the Dave Holland Octet * Pathway (comics), a superhero featured in Marvel comics * Pathways (band), an American progressive metalcore band Organizations * Pathways Foundation, an Australian non-profit organisation * Pathways out of Poverty, a workforce programme in the U.S. Schools * Pathway Academy, a charter school in Jacksonville, Florida * Pathways Academy, Detroit school serving students who are pregnant or new mothers, closed Others * NHS Pathways, triage software used by the National Health Service of the United Kingdom * Pathway Intermediates Limited, company producing biosurfactants * Pathway Studios, a North London recording studio * Pathway commons, a database of biological pathways and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Genera
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents ( pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. '' Mycobacterium tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virology
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy. The identification of the causative agent of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV) as a novel pathogen by Martinus Beijerinck (1898) is now acknowledged as being the official beginning of the field of virology as a discipline distinct from bacteriology. He realized the source was neither a bacterial nor a fungal infection, but something completely different. Beijerinck used the word "virus" to describe the mysterious agent in his 'contagium vivum fluidum' ('contagious living fluid'). Rosalind Franklin proposed the full structure of the tobacco mosaic virus in 1955. Virology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protista
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and '' protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-stranded RNA Viruses
Double-stranded RNA viruses (dsRNA viruses) are a polyphyletic group of viruses that have double-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The double-stranded genome is used to transcribe a positive-strand RNA by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The positive-strand RNA may be used as messenger RNA (mRNA) which can be translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. The positive-strand RNA can also be replicated by the RdRp to create a new double-stranded viral genome. Double-stranded RNA viruses are classified in two separate phyla '' Duplornaviricota'' and '' Pisuviricota'' (specifically class '' Duplopiviricetes''), which are in the kingdom '' Orthornavirae'' and realm ''Riboviria''. The two groups do not share a common dsRNA virus ancestor. Double-stranded RNA viruses evolved two separate times from positive-strand RNA viruses. In the Baltimore classification system, dsRNA viruses belong to Group III. Virus group members vary widely in host ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
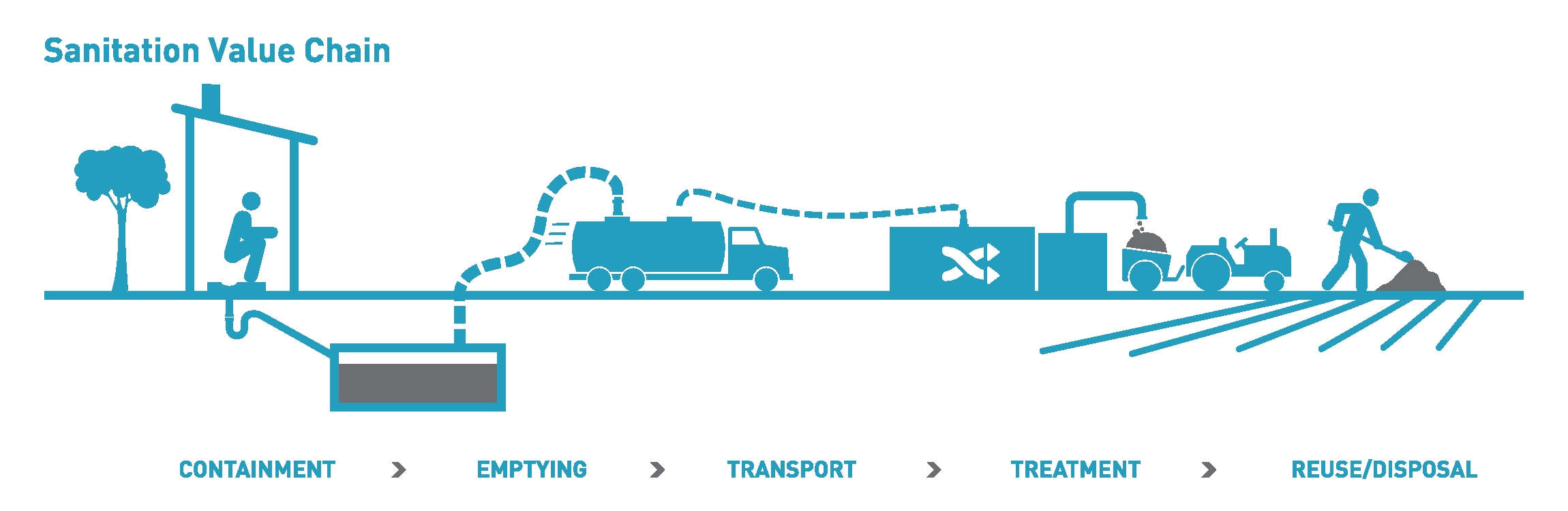
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |