|
Cryptomitrium Tenerum
''Cryptomitrium tenerum'' is a species of liverwort native to North America. It is the only representative of its genus on the continent. Description Like most other Marchantiales, it has a flat, dichotomously branched thallus, which in this species is pale green, flattened, dichotomously branched, thin, and somewhat shiny, measuring 0.6 to 1.5 cm long, less than 1 cm wide. The thallus margins are brownish purple in patches and somewhat undulate, curling upward when dry. The dorsal surface has a faint pattern of irregular polygons, and around inconspicuous pores to the air chambers below. The ventral surface is dark purple, shiny towards the margins, and green medially. The ventral scales are small, dark, and purple, poorly developed at maturity. The peculiar oil bodies found in so many liverworts are found scattered throughout the thallus, ventral scales, and sporogonial receptacle. Cryptomitrium does not reproduce asexually via Gemma (botany), gemmae. It usually rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverwort
The Marchantiophyta () are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information. It is estimated that there are about 9000 species of liverworts. Some of the more familiar species grow as a flattened leafless thallus, but most species are leafy with a form very much like a flattened moss. Leafy species can be distinguished from the apparently similar mosses on the basis of a number of features, including their single-celled rhizoids. Leafy liverworts also differ from most (but not all) mosses in that their leaves never have a costa (present in many mosses) and may bear marginal cilia (very rare in mosses). Other differences are not universal for all mosses and liverworts, but the occurrence of leaves arranged in three ranks, the presence of deep lobes or segmented leaves, or a lack of clearly di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizoid
Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the root hairs of vascular land plants. Similar structures are formed by some fungi. Rhizoids may be unicellular or multicellular. Evolutionary development Plants originated in aquatic environments and gradually migrated to land during their long course of evolution. In water or near it, plants could absorb water from their surroundings, with no need for any special absorbing organ or tissue. Additionally, in the primitive states of plant development, tissue differentiation and division of labor was minimal, thus specialized water absorbing tissue was not required. The development of specialized tissues to absorb water efficiently and anchor themselves to the ground enabled the spread of plants to the land. Description Rhizoids absorb water mainly by capillary action, in which water moves up between threads of rhizoids and not through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of California
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms '' gut flora'' or ''skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elater
An elater is a cell (or structure attached to a cell) that is hygroscopic, and therefore will change shape in response to changes in moisture in the environment. Elaters come in a variety of forms, but are always associated with plant spores. In many plants that do not have seeds, they function in dispersing the spores to a new location. Mosses do not have elaters, but peristomes which change shape with changes in humidity or moisture to allow for a gradual release of spores. Horsetail elaters In the horsetails, elaters are four ribbon-like appendages attached to the spores. These appendages develop from an outer spiral layer of the spore wall. At maturity, the four strips peel away from the inner wall, except at a single point on the spore where all four strips are attached. Under moist conditions, the elaters curl tightly around the spore. The wet spores tend to stick to each other and to nearby surfaces because of surface tension. When conditions are dry, the spores no lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellucid
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamella (cell Biology)
A lamella (plural: "lamellae") in biology refers to a thin layer, membrane or plate of tissue. This is a very broad definition, and can refer to many different structures. Any thin layer of organic tissue can be called a lamella and there is a wide array of functions an individual layer can serve. For example, an intercellular lipid lamella is formed when lamellar disks fuse to form a lamellar sheet. It is believed that these disks are formed from vesicles, giving the lamellar sheet a lipid bilayer that plays a role in water diffusion. Another instance of cellular lamellae can be seen in chloroplasts. Thylakoid membranes are actually a system of lamellar membranes working together, and are differentiated into different lamellar domains. This lamellar system allows plants to convert light energy into chemical energy. Chloroplasts are characterized by a system of membranes embedded in a hydrophobic proteinaceous matrix, or stroma. The basic unit of the membrane system is a flat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areolate
Lichens are composite organisms made up of multiple species: a fungal partner, one or more photosynthetic partners, and sometimes a basidiomycete yeast. They are regularly grouped by their external appearance – a characteristic known as their growth form. Lichenologists have described a dozen of these forms: areolate, byssoid, calicioid, cladoniform, crustose, filamentous, foliose, fruticose, gelatinous, leprose, placoidioid and squamulose. Of these, crustose, foliose and fruticose are the most commonly encountered. With the exception of calicioid lichens, growth forms are based on the appearance of the thallus, which is the vegetative (non-reproductive) part of the lichen. In most species, this form is determined by the lichen's fungal partner, though in a small number, it is instead the photobiont that determines the lichen's morphology. In some growth forms, the outermost layer of the thallus consists of tightly woven fungal . This layer, known as the cortex, may be foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
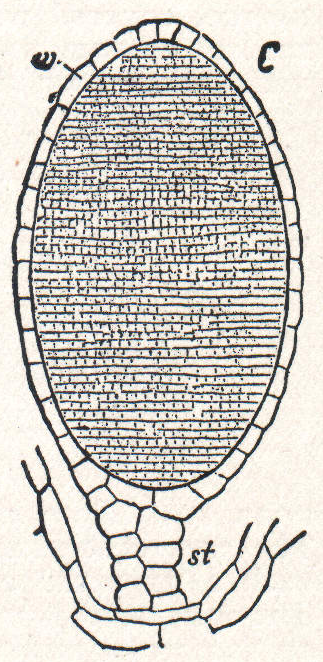
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomitrium Tenerum Sporophyte 25x
''Cryptomitrium'' is a genus of complex thalloid liverworts in the family Aytoniaceae. The genus name means “hidden turban” in reference to the inconspicuous sheath around the immature sporangium. Description Sporophyte bearing receptacles are unlobed on elongate, somewhat grooved stalks, which appear pale throughout or brownish purple near the base. The receptacle is a convex-expanded disc, thinning towards the margins. Mature sporangia are brown, nearly spherical with very short seta, three to seven per receptacle, each opening by a lid-like operculum. The sporangia mature in early spring. Species *''Cryptomitrium himalayense'' Kashyap *''Cryptomitrium oreades Perold *''Cryptomitrium tenerum ''Cryptomitrium tenerum'' is a species of liverwort native to North America. It is the only representative of its genus on the continent. Description Like most other Marchantiales, it has a flat, dichotomously branched thallus, which in this s ...'' (Hook.) Austin ex Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheridium
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cells and spermatogenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchantiales
Marchantiales is an order of thallose liverworts (also known as "complex thalloid liverworts") that includes species like '' Marchantia polymorpha'', a widespread plant often found beside rivers, and ''Lunularia cruciata'', a common and often troublesome weed in moist, temperate gardens and greenhouses. As in other bryophytes, the gametophyte generation is dominant, with the sporophyte existing as a short-lived part of the life cycle, dependent upon the gametophyte. The genus '' Marchantia'' is often used to typify the order, although there are also many species of '' Asterella'' and species of the genus '' Riccia'' are more numerous. The majority of genera are characterized by the presence of (a) special stalked vertical branches called archegoniophores or carpocephala, and (b) sterile cells celled elaters inside the sporangium. Phylogeny (extant Marchantiales) Based on the work by Villarreal et al. 2015 Phylogeny (extant and extinct Marchantiales) Extinct complex thal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |