|
Cryphonectria Longirostris
''Cryphonectria'' is a fungal genus in the order Diaporthales. The most well-known and well-studied species in the genus is ''Cryphonectria parasitica'', the species which causes chestnut blight. The genus was, for a time, considered synonymous with '' Endothia'', but the two are now recognised as distinct. Taxonomic studies in 2006 limited the genus to four species, but a fifth, '' Cryphonectria naterciae'', was described in 2011 from Portugal. Species *'' Cryphonectria abscondita'' *'' Cryphonectria acaciarum'' *''Cryphonectria cubensis'' *'' Cryphonectria decipiens'' *'' Cryphonectria japonica'' *'' Cryphonectria macrospora'' *'' Cryphonectria moriformis'' *'' Cryphonectria naterciae'' *'' Cryphonectria nitschkei'' *''Cryphonectria parasitica'' *'' Cryphonectria variicolor'' According to Murr) (And.et And.)Chestnut blight was first discovered in North America in 1904 on ''Castanea dentata''. By the 1940s it had killed most wild American chestnut trees, which were formerly one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryphonectria Decipiens
''Cryphonectria'' is a fungal genus in the order Diaporthales. The most well-known and well-studied species in the genus is ''Cryphonectria parasitica'', the species which causes chestnut blight. The genus was, for a time, considered synonymous with '' Endothia'', but the two are now recognised as distinct. Taxonomic studies in 2006 limited the genus to four species, but a fifth, '' Cryphonectria naterciae'', was described in 2011 from Portugal. Species *'' Cryphonectria abscondita'' *'' Cryphonectria acaciarum'' *''Cryphonectria cubensis'' *'' Cryphonectria decipiens'' *'' Cryphonectria japonica'' *'' Cryphonectria macrospora'' *'' Cryphonectria moriformis'' *'' Cryphonectria naterciae'' *'' Cryphonectria nitschkei'' *''Cryphonectria parasitica'' *'' Cryphonectria variicolor'' According to Murr) (And.et And.)Chestnut blight was first discovered in North America in 1904 on ''Castanea dentata''. By the 1940s it had killed most wild American chestnut trees, which were formerly one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
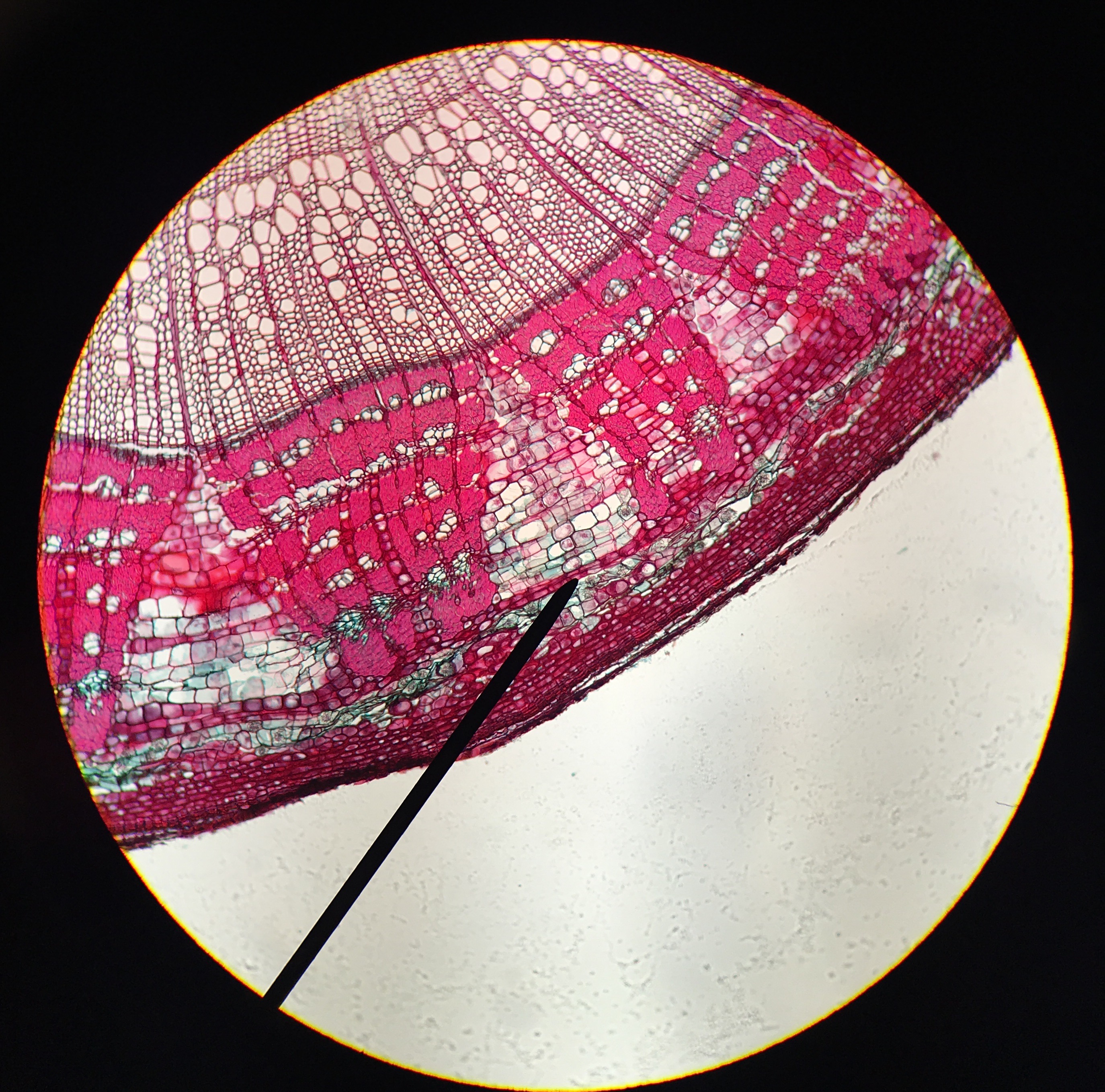
Cambium
A cambium (: cambiums or cambia), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castanea Dentata
The American chestnut (''Castanea dentata'') is a large, fast-growing deciduous tree of the beech family native to eastern North America. As is true of all species in the genus '' Castanea'', the American chestnut produces burred fruit with edible nuts. The American chestnut was once common in its Appalachian Mountain range and was a dominant species in the oak-chestnut forest region of its central and southern range. During the early to mid-20th century, American chestnut trees were devastated by chestnut blight, a fungal disease that came from Japanese chestnut trees that were introduced into North America from Japan. It is estimated that the blight killed between three and four billion American chestnut trees in the first half of the 20th century, beginning in 1904.Griffin, Gary"Recent advances in research and management of chestnut blight on American chestnut" Phytopathology 98:S7. ''www.apsnet.org'', 2008. Retrieved January 12, 2016.Hebard, F.V"The American Chestnut Fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryphonectria Variicolor
''Cryphonectria'' is a fungal genus in the order Diaporthales. The most well-known and well-studied species in the genus is ''Cryphonectria parasitica'', the species which causes chestnut blight. The genus was, for a time, considered synonymous with '' Endothia'', but the two are now recognised as distinct. Taxonomic studies in 2006 limited the genus to four species, but a fifth, '' Cryphonectria naterciae'', was described in 2011 from Portugal. Species *'' Cryphonectria abscondita'' *'' Cryphonectria acaciarum'' *''Cryphonectria cubensis'' *''Cryphonectria decipiens'' *'' Cryphonectria japonica'' *'' Cryphonectria macrospora'' *'' Cryphonectria moriformis'' *'' Cryphonectria naterciae'' *'' Cryphonectria nitschkei'' *''Cryphonectria parasitica'' *'' Cryphonectria variicolor'' According to Murr) (And.et And.)Chestnut blight was first discovered in North America in 1904 on ''Castanea dentata''. By the 1940s it had killed most wild American chestnut trees, which were formerly one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryphonectria Cubensis
''Cryphonectria'' is a fungus, fungal genus in the order Diaporthales. The most well-known and well-studied species in the genus is ''Cryphonectria parasitica'', the species which causes chestnut blight. The genus was, for a time, considered synonymous with ''Endothia'', but the two are now recognised as distinct. Taxonomic studies in 2006 limited the genus to four species, but a fifth, ''Cryphonectria naterciae'', was described in 2011 from Portugal. Species *''Cryphonectria abscondita'' *''Cryphonectria acaciarum'' *''Cryphonectria cubensis'' *''Cryphonectria decipiens'' *''Cryphonectria japonica'' *''Cryphonectria macrospora'' *''Cryphonectria moriformis'' *''Cryphonectria naterciae'' *''Cryphonectria nitschkei'' *''Cryphonectria parasitica'' *''Cryphonectria variicolor'' According to [(Murr) (And.et And.)] Chestnut blight was first discovered in North America in 1904 on ''Castanea dentata''. By the 1940s it had killed most wild American chestnut trees, which were formerly one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaporthales
Diaporthales is an order (biology), order of sac fungi. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added a number of name families to the order. Diaporthales includes a number of plant pathogenic fungi, the most notorious of which is ''Cryphonectria parasitica'' (Murrill) Barr, the chestnut blight fungus that altered the landscape of eastern North America. Other diseases caused by members of this order include stem canker of soybeans (''Diaporthe phaseolorum'' (Cooke & Ellis) Sacc. and its varieties), stem-end rot of citrus fruits (''Diaporthe citri'' F.A. Wolf), and peach canker disease (''Phomopsis amygdali'' Del.). Some species produce secondary metabolites that result in Poisoning, toxicosis of animals such as lupinosis of sheep (''Diaporthe toxica'' P.M. Williamson et al.). A number of asexually reproducing plant pathogenic fungi also belong in the Diaporthales, such ''Greeneria uvicola'' (Berk. & Curt.) Punith., cause of bitter rot of grape, and ''Discula destructiva'' Redlin, cause of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryphonectria Acaciarum
''Cryphonectria'' is a fungal genus in the order Diaporthales. The most well-known and well-studied species in the genus is ''Cryphonectria parasitica'', the species which causes chestnut blight. The genus was, for a time, considered synonymous with '' Endothia'', but the two are now recognised as distinct. Taxonomic studies in 2006 limited the genus to four species, but a fifth, '' Cryphonectria naterciae'', was described in 2011 from Portugal. Species *'' Cryphonectria abscondita'' *'' Cryphonectria acaciarum'' *''Cryphonectria cubensis'' *''Cryphonectria decipiens'' *''Cryphonectria japonica'' *''Cryphonectria macrospora'' *''Cryphonectria moriformis'' *'' Cryphonectria naterciae'' *''Cryphonectria nitschkei'' *''Cryphonectria parasitica'' *''Cryphonectria variicolor'' According to Murr) (And.et And.)Chestnut blight was first discovered in North America in 1904 on ''Castanea dentata''. By the 1940s it had killed most wild American chestnut trees, which were formerly one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |