|
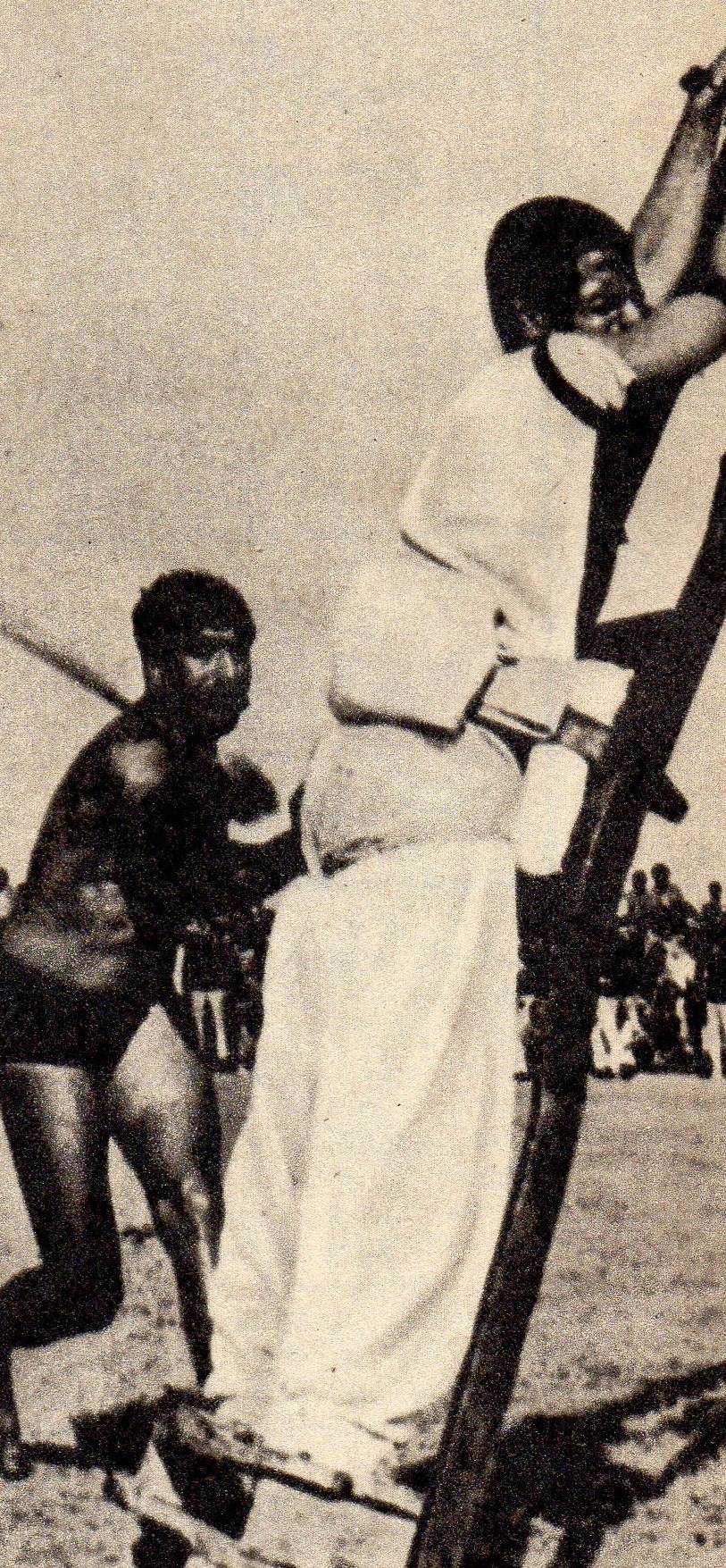
Cross-amputation
Cross-amputation () is one of the Hudud punishments prescribed under Islamic jurisprudence (Sharia law) and involves cutting off the right hand and left foot of the alleged transgressor. The scriptural authority for the double amputation procedure is in the Quran ( ''surah'' 5: 33-34) which stipulates: The right hand is always amputated during administration of the punishment regardless of whether the victim is right- or left-handed. This is because the Muslim faith decrees that the right hand should be used for clean purposes such as writing or eating, while the left is reserved for unclean tasks, such as cleaning following defecation. By removing the right hand as part of the punishment, the victim is subsequently forced to use his or her 'unclean' left hand for tasks such as eating, and this added humiliation or indignity is regarded as part of the punishment. Practice The punishment, typically used for highway robbery ('' hirabah'', ''qat' al-tariq'') and civil disturban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
September 1983 Laws
In September 1983, president Gaafar Nimeiry introduced Islamic sharia laws in Sudan, known as September Laws (), disposing of alcohol and implementing hudud punishments, ''hudud'' punishments such as public flogging for alcohol consumption and Cross-amputation, amputations for theft. Nimeiry declared himself the "imam of the Sudanese Ummah, umma", leading to concerns about the undemocratic implementation of these laws. Hasan Al-Turabi, Hassan al-Turabi (then the Attorney General of Sudan, attorney general) assisted with drafting the laws and later supported the laws, unlike the leader of the opposition Sadiq al-Mahdi. Nimeiry's alliance with the Islamism in Sudan, Sudanese Muslim Brotherhood aimed to end Al-Mirghani and al-Mahdi rivalry, sectarian divisions and consolidate Islamic governance. Despite Nimeiry's assertion that the sharia laws reduced crime rates, his economic policies, including Islamic banking and finance, Islamic banking, led to severe economic issues in Sudan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudud
''Hudud'' is an Arabic word meaning "borders, boundaries, limits". The word is applied in classical Islamic literature to punishments (ranging from public lashing, public stoning to death, amputation of hands, crucifixion, depending on the crime), for a limited number of crimes (murder, adultery, slander, theft, etc.), for which punishments have been determined (or traditionally thought to have been determined) in the verses of Quran. In classical Islamic literature, punishments are mainly of three types; Qisas-diya, Hudud, and Ta'zeer. Hudud covers the punishments given to people who exceed the limits associated with the Quran and deemed to be set by Allah (Hududullah is a phrase repeated several times in the Quran without labeling any type of crime), and in this respect it differs from Ta'zeer (). These punishments were applied in pre-modern Islam, Wael Hallaq (2009), ''An introduction to Islamic law'', p.173. Cambridge University Press. . and their use in some modern st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amputation
Amputation is the removal of a Limb (anatomy), limb or other body part by Physical trauma, trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as cancer, malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on individuals as a Preventive healthcare, preventive surgery for such problems. A special case is that of congenital amputation, a congenital disorder, where fetus, fetal limbs have been cut off by constrictive bands. In some countries, judicial amputation is currently used punishment, to punish people who commit crimes. Amputation has also been used as a tactic in war and acts of terrorism; it may also occur as a war injury. In some cultures and religions, minor amputations or mutilations are considered a ritual accomplishment. When done by a person, the person executing the amputation is an amputator. The oldest evidence of this practice comes from a skeleton found buried in Liang Tebo c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic, Arabic language. It is the object of a modern field of academic research known as Quranic studies. Muslims believe the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final Islamic Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad through the Angel#Islam, angel Gabriel#Islam, Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning on the Night of Power, Laylat al-Qadr, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important Islamic view of miracles, miracle, a proof of his prophet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia Legal Terminology
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intangible divine law; contrary to ''fiqh'', which refers to its interpretations by Ulama, Islamic scholars. Sharia, or fiqh as traditionally known, has always been used alongside urf, customary law from the very beginning in Islamic history; has been elaborated and developed over the centuries by fatwa, legal opinions issued by mufti, qualified jurists – reflecting the tendencies of Schools of Fiqh, different schools – and integrated and with various economic, penal and administrative laws issued by Muslims, Muslim rulers; and implemented for centuries by Qadi, judges in the courts until recent times, when secularism was widely adopted in Islamic societies. Traditional Principles of Islamic jurisprudence, theory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is often described as the style of human understanding, research and practices of the sharia; that is, human understanding of the divine Islamic law as revealed in the Quran and the sunnah (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions). Fiqh expands and develops Shariah through interpretation (''ijtihad'') of the Quran and ''Sunnah'' by Islamic jurists (''ulama'') and is implemented by the rulings (''fatwa'') of jurists on questions presented to them. Thus, whereas ''sharia'' is considered immutable and infallible by Muslims, ''fiqh'' is considered fallible and changeable. ''Fiqh'' deals with the observance of rituals, morals and social legislation in Islam as well as econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ma'idah
Al-Ma'idah (; 'The Table pread with Food is the fifth chapter of the Quran, containing 120 verses. Al-Mā'idah means "Meal" or "Banquet" . This name is taken from verses 112 to 115, which tell the request of the followers of Prophet 'Isa (Jesus) that Allah send down a meal from the sky as a sign of the truth of his message. Regarding the timing and contextual background of the revelation, it is a Medinan chapter, which means it is believed to have been revealed in Medina rather than Mecca. The chapter's topics include animals which are forbidden, and Jesus's and Moses's missions. Verse 90 prohibits "the intoxicant" (alcohol). Verse 8 contains the passage: "Do not let the hatred of a people lead you to injustice". Al-Tabligh Verse 67 is relevant to the Farewell Pilgrimage and Ghadir Khumm. Verses have been quoted to denounce killing, by using an abbreviated form such as, "If anyone kills a person, it would be as if he killed the whole people: and if anyone saved a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirabah
In Islamic law, ''Ḥirābah'' () is a legal category that comprises highway robbery (traditionally understood as aggravated robbery or grand larceny, unlike theft, which has a different punishment), rape, and terrorism. Ḥirābah means piracy or unlawful warfare. It comes from the triliteral root ''ḥrb'', which means “to become angry and enraged”. The noun ''ḥarb'' (, pl. ''ḥurūb'' ) means 'war' or 'wars'. Crane, Robert D., �Hirabah versus Jihad��, ''IFRI.org'' (Islamic Research Foundation International, Inc., 2006) ''Moharebeh'' (also spelled ''muharebeh'') is a Persian language term that is treated as interchangeable with ''ḥirabah'' in Arabic lexicons. The related term ''muḥārib'' () has been translated by English-language Iranian media as "enemy of God". In English-language media sources, moḥarebeh in Iran has been translated variously as "waging war against God," "war against God and the state," [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In Saudi Arabia
Capital punishment in Saudi Arabia is a legal punishment. Most executions in the country are carried out by decapitation (beheading). Saudi Arabia is the only country that still uses this method. Capital punishment is used both for offenders of lethal crimes and non-lethal crimes, as well as juvenile offenders. Among those executed are individuals charged with non-lethal terrorism, a charge that has been used against individuals who participated in protests against the authoritarian regime in Saudi Arabia. Death sentences are almost exclusively based on the system of judicial sentencing discretion (''tazir''), following the classical principle of avoiding ''Sharia-prescribed ( hudud)'' penalties when possible. In response to a 1970s rise in violent crime, these sentences increased. This paralleled similar developments in the U.S. and mainland China in the late 20th century. A central square in the Kingdom's capital, Riyadh, became known in the West as " Chop-Chop Square" due to pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In Sudan
Capital punishment in Sudan is legal under Article 27 of the Sudanese Criminal Act 1991. The Act is based on Sharia law which prescribes both the death penalty and corporal punishment, such as amputation. Sudan has moderate execution rates, ranking 8th overall in 2014 when compared to other countries that still continue the practice, after at least 29 executions were reported (although it is expected that over 100 occurred). History Even though Sudan's legal systems have been drawn from various other jurisdictions, capital punishment has always existed in the country. During the twentieth century, there were several changes to Sudanese law. In the early 1900s until 1974 the death penalty was active in a legal system based on Indian criminal law, which itself was influenced by British law. In 1974, during President Gaafar Nimeiry's time in office, largescale amendments to the penal code were carried out which included some elements of civil law. However, the civil law amendments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In Somalia
__NOTOC__ Capital punishment is a legal criminal penalty in Somalia, a nation in East Africa. Legally sanctioned executions of the death penalty in Somalia are carried out by shooting, in accordance with the 1962 Somali Penal Code and the Military Penal Code. Sharia and Islamic tribunals are recognised in Somalia in parallel with the civil law: these would have the authority to order execution by other means, such as beheading and stoning. Since at least the start of the 21st century, all executions by such methods have been applied ad-hoc, without official sanction, by non-state insurgent militias, in the context of an unstable government, and the ongoing civil war in the country. A number of these extrajudicial executions have violated sharia legal principles and appear to have a conflict-related tactical aim of inciting fear amongst civilians. Both officially sanctioned and extrajudicial executions by firing squad often occur in public. Occurrences In 2011 three soldiers wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment In Mauritania
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Mauritania. However, the country is considered " Abolitionist in Practice" due to having a moratorium on executions since 1987. Mauritania last executed in 1987. Mauritania has an unenforced death penalty for homosexuality; there have been no reported death sentences for homosexual acts. Mauritania also has the death penalty for blasphemy. A law was passed in 2018 making capital punishment the mandatory sentence for blasphemy. References Mauritania Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Maghreb, Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to Mauritania–Western Sahara border, the north and northwest, ... Law of Mauritania {{capital-punishment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |