|
Criodrilidae
The family Criodrilidae is represented by genus ''Criodrilus'' comprising limicolous (mud-dwelling) and/or aquatic earthworms endemic to the Palaearctic currently known only from Europe and Japan, respectively. Only three or four species are described, and the type, ''Criodrilus lacuum'', has been introduced into North and South Americas, and is found rarely in plant pots or paddy fields. The Criodrilidae are characterised by holoic nephridia absent from anterior segments (cf. ''Pontodrilus''), a simple gut with no gizzard and no typhlosole. They are true earthworms, having a complex vascular system with capillaries, the male pores (on 15 or 13) behind the female pores (on 14) and a multicelled clitellum. They were at one time placed in the earthworm families Glossoscolecidae or Almidae, but at present are considered to constitute their own family. Criodrilidae species (criodrilids) are found in mud next to lakes and waterways (cf. North American ''Sparganophilus''). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almidae
The animal family Almidae includes about six genera of Oligochaeta, segmented worms. A notable peculiarity of some species in this family is a tendency to extensions of the body wall in the vicinity of or including the male pores. These extensions may be mere protuberances, as in some species of ''Drilocrius''; or involve a greater extent of the body wall, as in genus ''Glyphidrilocrius''. They take the form of wing or keel-like structures called alae in ''Glyphidrilus'' species and paddle-shaped claspers in ''Drilocrius alfari''. All species of genus ''Alma'' have claspers. The male pores are near the tips of these claspers, and they are furnished with genital chaetae and sucker-like structures. Most members of this family have one pair of male pores on segment 15 through 30. Female pores are located on segment 14. ''Glyphidrilus kukenthali'' is one of only three ‘earthworm’ species known to have two pairs of female pores, in 13 and 14. A possibly related family, Criodr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthworm
An earthworm is a soil-dwelling terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. The term is the common name for the largest members of the class (or subclass, depending on the author) Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they were in the order of Opisthopora since the male pores opened posterior to the female pores, although the internal male segments are anterior to the female. Theoretical cladistic studies have placed them in the suborder Lumbricina of the order Haplotaxida, but this may change. Other slang names for earthworms include "dew-worm", "rainworm", "nightcrawler", and "angleworm" (from its use as angling hookbaits). Larger terrestrial earthworms are also called megadriles (which translates to "big worms") as opposed to the microdriles ("small worms") in the semiaquatic families Tubificidae, Lumbricidae and Enchytraeidae. The megadriles are characterized by a distinct clitellum (more extensive than that of microdriles) and a vascular system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Biwa
is the largest freshwater lake in Japan. It is located entirely within Shiga Prefecture (west-central Honshu), northeast of the former capital city of Kyoto. Lake Biwa is an ancient lake, over 4 million years old. It is estimated to be the 13th oldest lake in the world. Because of its proximity to the country's historical capital Kyoto, references to Lake Biwa appear frequently in Japanese literature, particularly in poetry and in historical accounts of battles. Name The name ''Biwako'' was established in the Edo period. There are various theories about the origin of the name ''Biwako'', but it is generally believed to be so named because of the resemblance of its shape to that of a stringed instrument called the ''biwa''. Kōsō, a learned monk of Enryaku-ji in the 14th century, gave a clue to the origin of the name ''Biwako'' in his writing: "The lake is the Pure land of the goddess Benzaiten because she lives on Chikubu Island and the shape of the lake is similar to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criodrilus
''Criodrilus'' is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Criodrilidae. The species of this genus are found in Europe and America. Species: *''Criodrilus aidae'' *''Criodrilus lacuum'' *''Criodrilus miyashitai'' *''Criodrilus venezuelanus ''Criodrilus'' is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Criodrilidae. The species of this genus are found in Europe and America. Species: *''Criodrilus aidae'' *''Criodrilus lacuum'' *''Criodrilus miyashitai ''Criodrilus'' is a genu ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q18519465 Annelids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criodrilus Lacuum
''Criodrilus'' is a genus of annelids belonging to the family Criodrilidae The family Criodrilidae is represented by genus ''Criodrilus'' comprising limicolous (mud-dwelling) and/or aquatic earthworms endemic to the Palaearctic currently known only from Europe and Japan, respectively. Only three or four species are de .... The species of this genus are found in Europe and America. Species: *'' Criodrilus aidae'' *'' Criodrilus lacuum'' *'' Criodrilus miyashitai'' *'' Criodrilus venezuelanus'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q18519465 Annelids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is a biogeographic realm of the Earth, the largest of eight. Confined almost entirely to the Eastern Hemisphere, it stretches across Europe and Asia, north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa. The realm consists of several bioregions: the Mediterranean Basin; North Africa; North Arabia; Western, Central and East Asia. The Palaearctic realm also has numerous rivers and lakes, forming several freshwater ecoregions. Both the eastern and westernmost extremes of the Paleartic span into the Western Hemisphere, including Cape Dezhnyov in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the east and Iceland to the west. The term was first used in the 19th century, and is still in use as the basis for zoogeographic classification. History In an 1858 paper for the ''Proceedings of the Linnean Society'', British zoologist Philip Sclater first identified six terrestrial zoogeographic realms of the world: Palaearctic, Aethiopian/ Afrotropic, Indian/ Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephridia
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia come in two basic categories: metanephridia and protonephridia. All nephridia- and kidney- having animals belong to the clade Nephrozoa. Metanephridia A metanephridium (''meta'' = "after") is a type of excretory gland found in many types of invertebrates such as annelids, arthropods and mollusca. (In mollusca, it is known as the Bojanus organ.) A metanephridium typically consists of the nephrostome (a ciliated funnel) opening into the body cavity, connected to a duct which may be variously glandularized, folded or expanded (vesiculate) and which typically opens to the organism's exterior. These ciliated tubules pump water carrying surplus ions, metabolic waste, toxins from food, and useless hormones out of the organism by directing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gizzard
The gizzard, also referred to as the ventriculus, gastric mill, and gigerium, is an organ found in the digestive tract of some animals, including archosaurs (birds and other dinosaurs, crocodiles, alligators, pterosaurs), earthworms, some gastropods, some fish, and some crustaceans. This specialized stomach constructed of thick muscular walls is used for grinding up food, often aided by particles of stone or grit. In certain insects and molluscs, the gizzard features chitinous plates or teeth. Etymology The word ''gizzard'' comes from the Middle English ''giser'', which derives from a similar word in Old French ''gésier'', which itself evolved from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''gésier'', which itself evolved from the Latin ''gigeria'', meaning giblets. Structure In birds Birds swallow food and store it in their crop if necessary. Then the food passes into thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhlosole
In Morphology (biology), biological morphology, a typhlosole is an internal fold of the Gut (anatomy), intestine or intestine inner wall. Typhlosoles occur in bivalve mollusks, lampreys and some annelids and echinoderms. In earthworms, it is a dorsal flap of the intestine that runs along most of its length, effectively forming a tube within a tube, and increasing the absorption area by that of its inner surface. Its function is to increase intestine surface area for more efficient absorption of digested nutrients. In different earthworm families, the typhlosole appears to have multiple origins. The Lumbricidae, for example, have a typhlosole which is an infolding of all layers of the intestine wall, whereas in some other families (e.g. Megascolecidae), it is an infolding of only the inner layer, and in many earthworms it is absent. In shipworms, the typhlosole is the organ where the lignin in wood are digested by Symbiosis, symbiont bacteria of the "Alteromonas, Alteromonas-like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
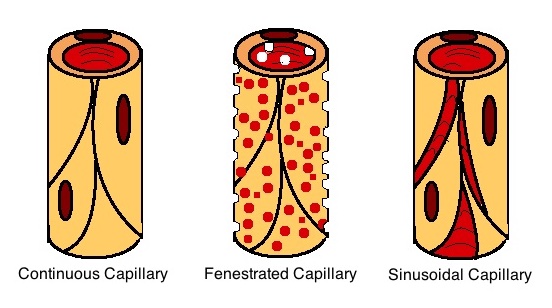
Capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Pore
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender, in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineages, an example of convergent evolution. The repeated pattern is sexual reproduction in isogamous species with two or more mating types with gametes of identical form and behavior (but different at the molecular level) to anisogamous species with gametes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Pore
An organism's sex is female (symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes (unlike isogamy where they are the same size). The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Characteristics of organisms with a female sex vary between different species, having different female reproductive systems, with some species showing characteristics secondary to the reproductive system, as with mammary glands in mammals. In humans, the word ''female'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |