|
Crimson (color)
Crimson is a rich, deep red color, inclining to purple. It originally meant the color of the kermes dye produced from a scale insect, ''Kermes vermilio'', but the name is now sometimes also used as a generic term for slightly bluish-red colors that are between red and rose. It is the national color of Nepal. History Crimson (NR4) is produced using the dried bodies of a scale insect, ''Kermes'', which were gathered commercially in Mediterranean countries, where they live on the kermes oak, and sold throughout Europe. Kermes dyes have been found in burial wrappings in Anglo-Scandinavian York. They fell out of use with the introduction of cochineal, also made from scale insects, because although the dyes were comparable in quality and color intensity, ten to twelve times as much kermes is needed to produce the same effect as cochineal. Carmine is a slightly different shade of red, extracted from a different insect (female cochineal), although these denominations are sometimes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Colors
Web colors are colors used in Web design, displaying web pages on the World Wide Web; they can be described by way of three methods: a color may be specified as an RGB color model, RGB triplet, in hexadecimal format (a ''hex triplet'') or according to its common English name in some cases. A color tool or other graphics software is often used to generate color values. In some uses, hexadecimal color codes are specified with notation using a leading number sign (#). A color is specified according to the intensity of its red, green and blue components, each represented by eight bits. Thus, there are 24 bits used to specify a web color within the sRGB gamut, and 16,777,216 colors that may be so specified. Colors outside the sRGB gamut can be specified in CSS, Cascading Style Sheets by making one or more of the red, green and blue components negative or greater than 100%, so the color space is theoretically an unbounded extrapolation of sRGB similar to scRGB. Specifying a non-sRGB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietro Andrea Mattioli
Pietro Andrea Gregorio Mattioli (; 12 March 1501– ) was a doctor and naturalist born in Siena. His most important work was a commentary on the medicinal plants of Pedanius Dioscorides first published in 1544 which was translated into several languages and went into thirteen editions in his lifetime. Biography Mattioli was born in Siena to physician Francesco and his wife Lucrezia Buoninsegna. Although belonging to the city elite, the family was economically stressed, with thirteen children. His early studies are unknown but he may have studied in Venice, Siena, and Padua before he received his MD at the University of Padua in 1523, and subsequently practiced the profession in Siena, Rome, Trento and Gorizia, becoming personal physician of Ferdinand II, Archduke of Further Austria in Prague and Ambras Castle, and of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor in Vienna. In 1527 he moved to Trent in the Val di Non. In 1528 he was a court physician for Bernardo Cles and he then married a wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Kluge
Friedrich Kluge (21 June 1856 – 21 May 1926) was a German philologist and educator. He is known for the ''Etymological Dictionary of the German Language'' (), which was first published in 1883. Biography Kluge was born in Cologne. He studied comparative linguistics and classical and modern philologies at the universities of Leipzig, Strasbourg and Freiburg. As a student, his instructors were August Leskien, Georg Curtius, Friedrich Zarncke and Rudolf Hildebrand at Leipzig and Heinrich Hübschmann, Bernhard ten Brink and Erich Schmidt at the University of Strasbourg.Kluge, Friedrich In: Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB). Band 12, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin 1980, , S. 140 f. He became a teacher of English and German philology at Strassburg (1880), an assistant professor of German at the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidia (Roman province), Numidia and Africa (Roman province), Africa Proconsularis under the Vandals, the Exarchate of Africa, Byzantines and the Kingdom of Altava, Romano-Berber Kingdoms, until it declined after the Arab conquest of North Africa, Arab Conquest. Medieval Latin in Southern and Central Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Hispania, conquered by the Arabs immediately after North Africa, experienced a similar fate, only recovering its importance after the Reconquista by the Northern Christian Kingdoms. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned as the main medium of scholarly exchange, as the liturgical language of the Roman Catholic Church, Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Spanish
Old Spanish (, , ; ), also known as Old Castilian or Medieval Spanish, refers to the varieties of Ibero-Romance spoken predominantly in Castile and environs during the Middle Ages. The earliest, longest, and most famous literary composition in Old Spanish is the (c. 1140–1207). Phonology Vowels Monophthongs Diphthongs Consonants ( and were apico-alveolar.) and These were still distinct phonemes in Old Spanish, judging by the consistency with which the graphemes and were distinguished. Nevertheless, the two could be confused in consonant clusters (as in ~ “dawn”) or in word-initial position, perhaps after or a pause. and appear to have merged in word-initial position by about 1400 and in all other environments by the mid–late 16th century at the latest. At an archaic stage, the realizations of (from Latin ) would have been approximately as follows: * before or * before or * or before By early Old Spanish, had been replaced with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umber
Umber is a natural earth pigment consisting of iron oxide and manganese oxide; it has a brownish color that can vary among shades of yellow, red, and green. Umber is considered one of the oldest pigments known to humans, first used in the Ajanta Caves from 200 BC to 600 AD. Umber's advantages are its highly versatile color, warm tone, and quick drying abilities. While some sources indicate that umber's name comes from its geographic origin in Umbria, other scholars suggest that it derives from the Latin word ''umbra'', which means "shadow". The belief that its name derives from the word for shadow is fitting, as the color helps create shadows. The color is primarily produced in Cyprus. Umber is typically mined from Open-pit mining, open pits or Mining, underground mines and ground into a fine powder that is washed to remove impurities. In the 20th century, the rise of synthetic dyes decreased the demand for natural pigments such as umber. History The earliest documente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
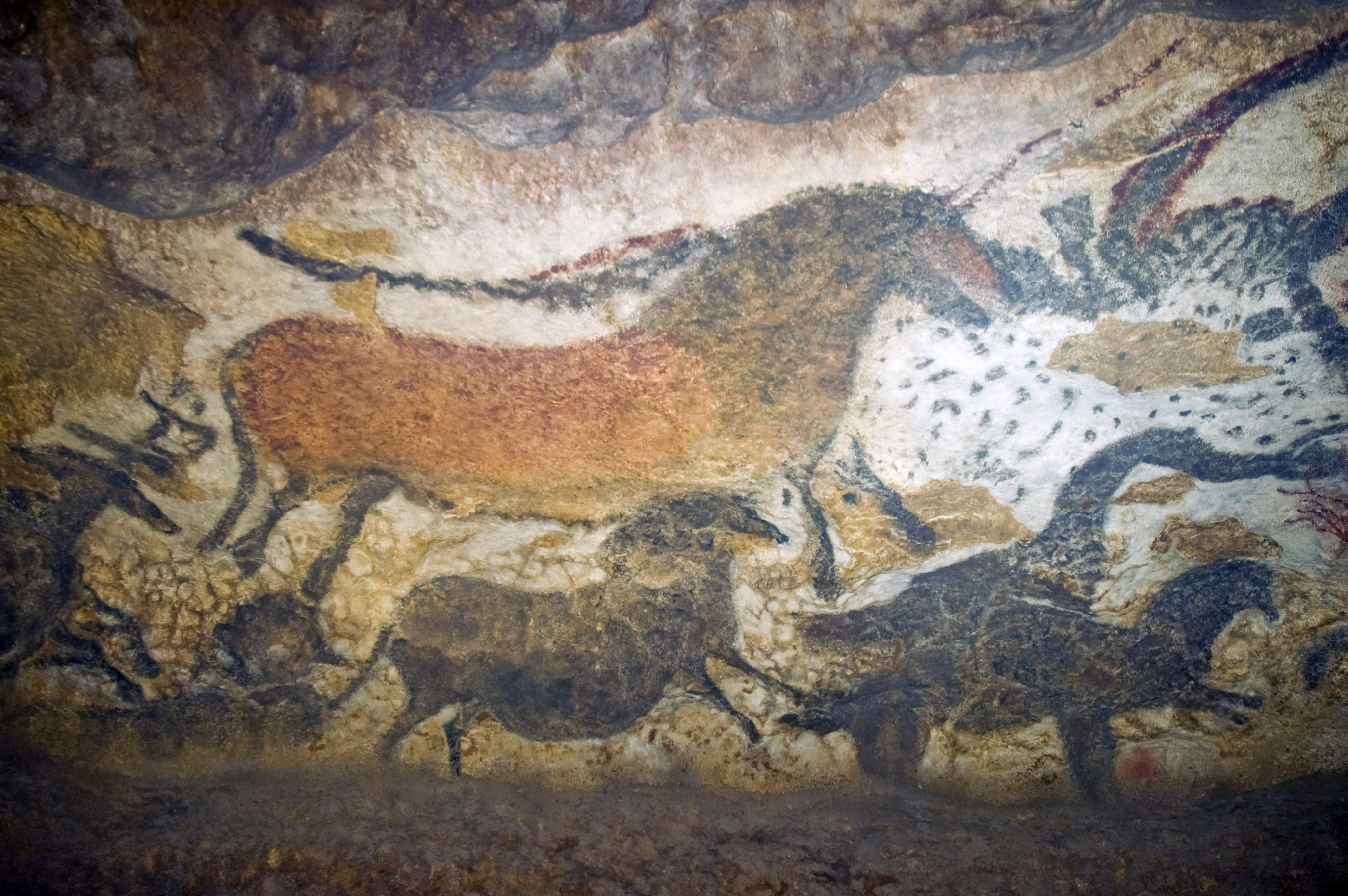
Sienna
Sienna () is an earth pigment containing iron oxide and manganese oxide. In its natural state, it is yellowish brown, and it is called raw sienna. When heated, it becomes a reddish brown, and it is called burnt sienna.''Shorter Oxford English Dictionary'', 5th Edition (2002) It takes its name from the city-state of Siena, where it was produced during the Renaissance. Along with ochre and umber, it was one of the first pigments to be used by humans, and is found in many cave paintings. Since the Renaissance, it has been one of the brown pigments most widely used by artists. The first recorded use of ''sienna'' as a color name in English was in 1760. The normalized color coordinates for sienna are identical to kobe, first recorded as a color name in English in 1924. Earth colors Like the other earth colors, such as yellow ochre and umber, sienna is a clay which is partially composed of iron oxides. In the case of sienna, the most prevalent iron oxides are limonite (which in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), iron ochre, or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colours produced by this pigment, especially a light brownish-yellow. A variant of ochre containing a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide, has a reddish tint known as red ochre (or, in some dialects, ruddle). The word ochre also describes clays coloured with iron oxide derived during the extraction of tin and copper. Earth pigments Ochre is a family of earth pigments, which includes yellow ochre, red ochre, purple ochre, sienna, and umber. The major ingredient of all the ochres is iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, known as limonite, which gives them a yellow colour. A range of other minerals may also be included in the mixture:Krivovichev V. G. Mineralogical glossary. Scientific editor :uk:Булах Андрій Глібович, A. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula . Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum. The name "alum" is also used, more generally, for salts with the same formula and structure, except that aluminium is replaced by another Valence (chemistry), trivalent metal ion like chromium#Chromium(III), chromium, or sulfur is replaced by another chalcogen like selenium. The most common of these analogs is chrome alum . In most industries, the name "alum" (or "papermaker's alum") is used to refer to aluminium sulfate, , which is used for most industrial flocculation (the variable is an integer whose size depends on the amount of water absorbed into the alum). For medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
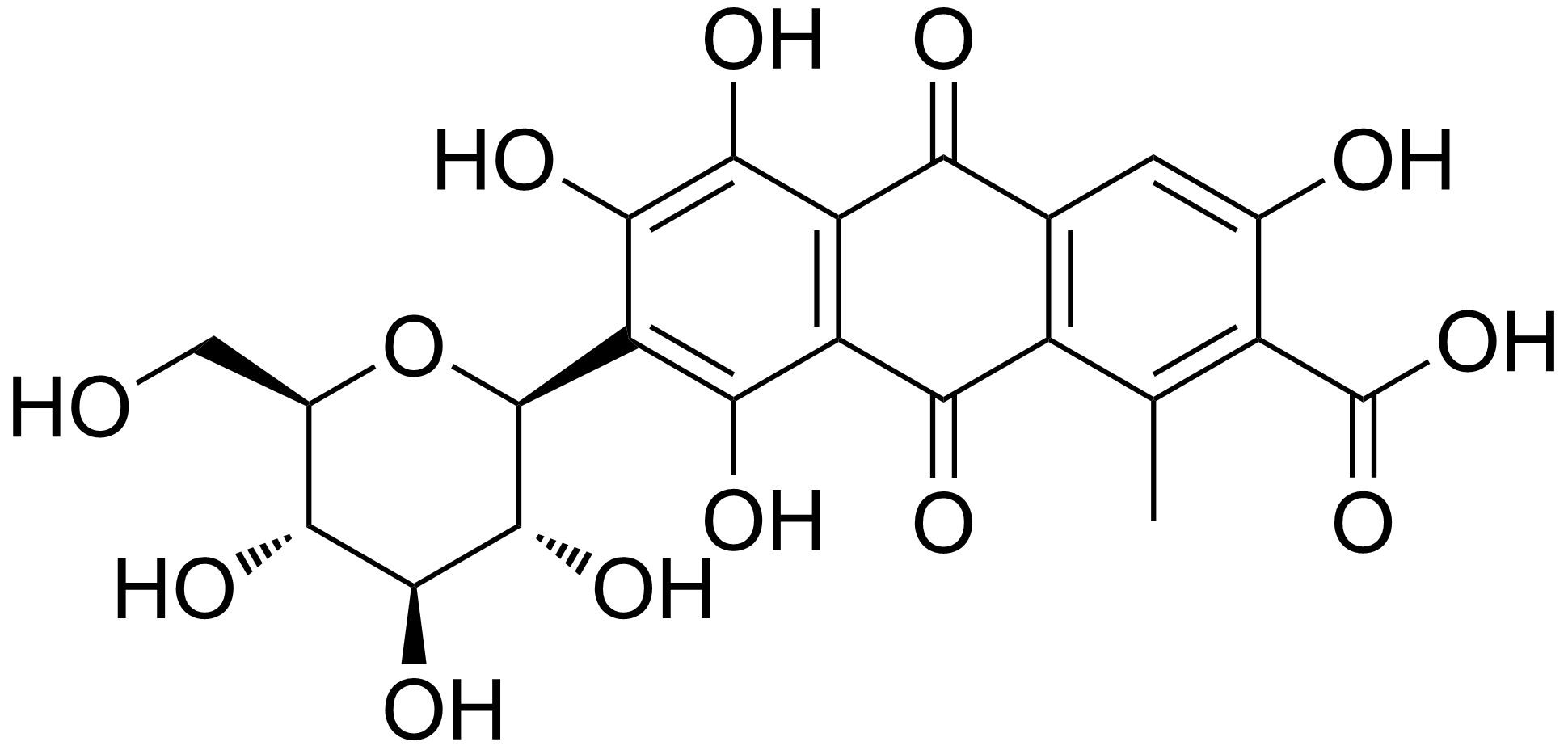
Madder Lake
Alizarin (also known as 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone, Mordant Red 11, C.I. 58000, and Turkey Red) is an organic compound with formula that has been used throughout history as a red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus.The primary madder species from which alizarin historically has been obtained is '' Rubia tinctorum''. See also In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically. Alizarin is the main ingredient for the manufacture of the madder lake pigments known to painters as rose madder and alizarin crimson. Alizarin in the most common usage of the term has a deep red color, but the term is also part of the name for several related non-red dyes, such as Alizarine Cyanine Green and Alizarine Brilliant Blue. A use of alizarin in modern times is as a staining agent in biological research because it stains free calcium and certain calcium compounds a red or light purple color. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Liebermann
Carl Theodor Liebermann (23 February 1842 – 28 December 1914) was a German chemist and student of Adolf von Baeyer. Life Liebermann first studied at the University of Heidelberg where Robert Wilhelm Bunsen was teaching. He then joined the group of Adolf von Baeyer at the University of Berlin where he received his PhD in 1865. Together with Carl Gräbe, Liebermann synthesised the orange-red dye alizarin in 1868. After his habilitation in 1870 he became professor at the University of Berlin after Adolf von Baeyer left for the University of Strasbourg. Shortly after Liebermann retired, in 1914, he died. Work In 1826, the French chemist Pierre Jean Robiquet had isolated from the root of a plant, madder, and defined the structure of, alizarin, a remarkable red dye. Liebermann's 1868 discovery that alizarin can be reduced to form anthracene, which is an abundant component in coal tar, opened the road for synthetic alizarin. The patent of Liebermann and Carl Gräbe for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |