|
Crab-plover
The crab-plover or crab plover (''Dromas ardeola)'' is a coastal wader (shorebird). It is the only member of the genus ''Dromas'' and the family Dromadidae. It is unique among waders in making use of ground warmth to aid the incubation of its eggs. The crab-plover is classified in the suborder Lari, making it more closely related to gulls and auks than to most other waders such as plovers (suborder Charadrii) and sandpipers (suborder Scolopaci). Description This bird resembles a plover, but has very long grey legs and a strong heavy black bill similar to a tern. Its black-and-white plumage and long-necked upright posture with heavy bill makes it distinctive and unmistakable. Its bill is unique among waders, and specialised for eating crabs. It has partially webbed toes. The plumage is white except for black on its back and in the primary feathers of the wings. They are noisy birds, calling frequently on their breeding sites and in their wintering grounds. The usual call is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Robert Gray
George Robert Gray (8 July 1808 – 6 May 1872) was an English zoology, zoologist and author, and head of the Ornithology, ornithological section of the British Museum, now the Natural History Museum, London, Natural History Museum, London for forty-one years. He was the younger brother of the zoologist John Edward Gray and the son of the botanist Samuel Frederick Gray. George Gray's most important publication was his ''Genera of Birds'' (1844–49), illustrated by David William Mitchell and Joseph Wolf, which included 46,000 references. Biography He was bornon 8 July 1808 in Little Chelsea, London, to Samuel Frederick Gray, naturalist and pharmacologist, and Elizabeth (née Forfeit), his wife. He was educated at Merchant Taylor's School. Gray started at the British Museum as Assistant Keeper of the Zoology Branch in 1831. He began by cataloguing insects, and published an ''Entomology of Australia'' (1833) and contributed the entomogical section to an English edition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing (sense), hearing, olfaction, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbaby, bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsier, tarsiers and some owl, owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as ''Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
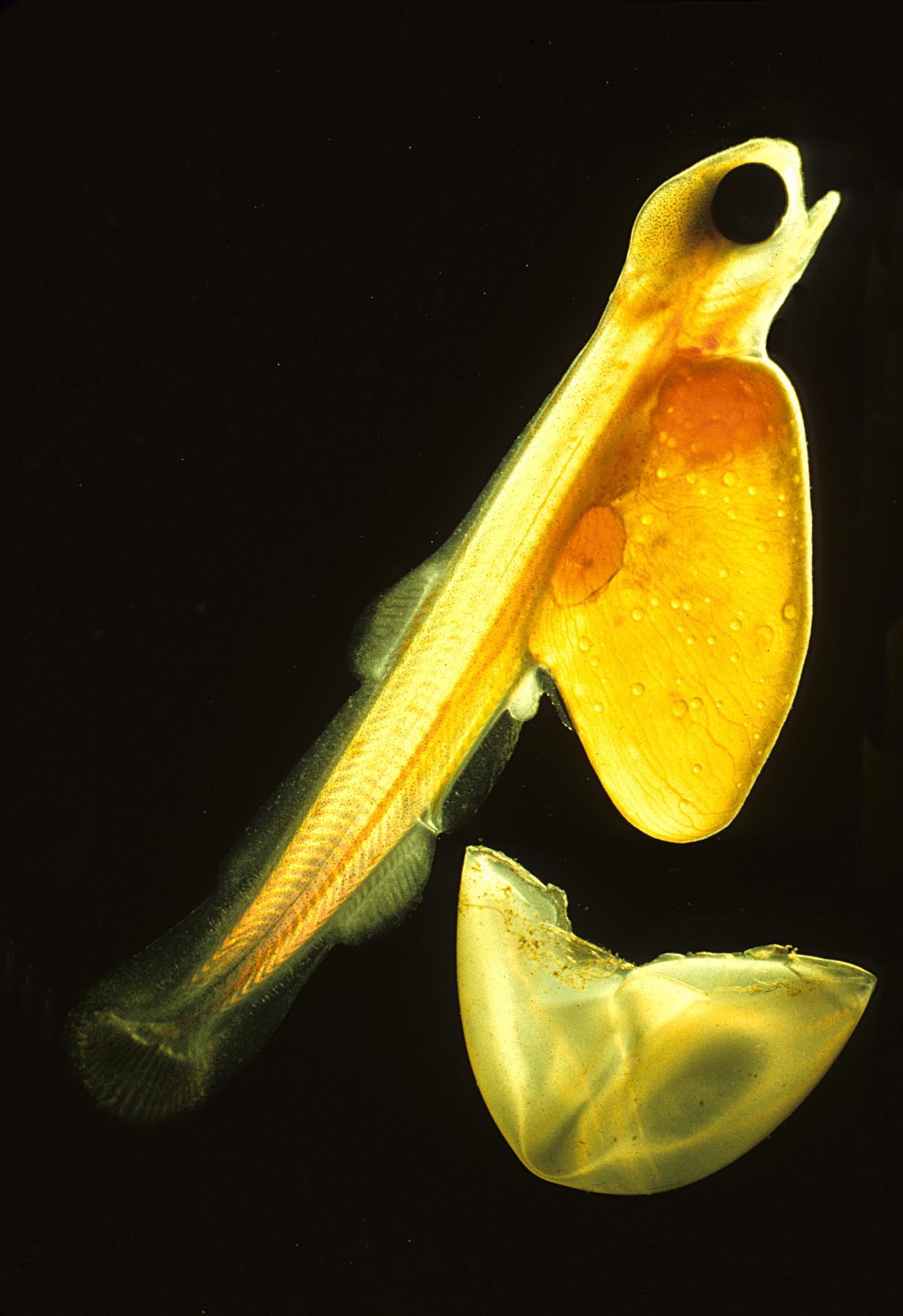
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilization, fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to egg incubation, incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and Mollusca, mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective eggshell, shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Colony
A bird colony is a large congregation of individuals of one or more species of bird that nest or roost in proximity at a particular location. Many kinds of birds are known to congregate in groups of varying size; a congregation of nesting birds is called a breeding colony. Colonial nesting birds include seabirds such as auks and albatrosses; wetland species such as herons; and a few passerines such as weaverbirds, certain blackbirds, and some swallows. A group of birds congregating for rest is called a communal roost. Evidence of colonial nesting has been found in non- neornithine birds (Enantiornithes), in sediments from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Romania. Variations on colonial nesting in birds Approximately 13% of all bird species nest colonially. Nesting colonies are very common among seabirds on cliffs and islands. Nearly 95% of seabirds are colonial, leading to the usage, seabird colony, sometimes called a rookery. Many species of terns nest in colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burrow
file:Chipmunk-burrow (exits).jpg, An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of Animal locomotion, locomotion. Burrows provide a form of shelter against predation and exposure to the elements, and can be found in nearly every biome and among various biological interactions. Many animal species are known to form burrows. These species range from small amphipods, to very large vertebrate species such as the polar bear. Burrows can be constructed into a wide variety of substrates and can range in complexity from a simple tube a few centimeters long to a complex network of interconnecting tunnels and chambers hundreds or thousands of meters in total length; an example of the latter level of complexity, a well-developed burrow, would be a rabbit Warren (burrow), warren. Vertebrate burrows A large variety of vertebrates constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, fourth largest island, the List of island countries, second-largest island country, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 46th largest country overall. Its capital and List of cities in Madagascar, largest city is Antananarivo. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from Africa during the Early Jurassic period, around 180 million years ago, and separated from the Indian subcontinent approximately 90 million years ago. This isolation allowed native plants and animals to evolve in relative seclusion; as a result, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot and one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries, with over 90% of its wildlife of Madagascar, wildlife being endemic. The island has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. According to a 2024 estimate, Tanzania has a population of around 67.5 million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania. In the Stone and Bronze Age, prehistoric migrations into Tanzania included South Cushitic languages, Southern Cushitic speakers similar to modern day Iraqw people who moved south from present-day Ethiopia; Eastern Cushitic people who moved into Tanzania from north of Lake Turkana about 2,000 and 4,000 years ago; and the Southern Nilotic languages, Southern Nilotes, including the Datooga people, Datoog, who originated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, Indian peninsula by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. It shares a maritime border with the Maldives in the southwest and India in the northwest. Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is the legislative capital of Sri Lanka, while the largest city, Colombo, is the administrative and judicial capital which is the nation's political, financial and cultural centre. Kandy is the second-largest urban area and also the capital of the last native kingdom of Sri Lanka. The most spoken language Sinhala language, Sinhala, is spoken by the majority of the population (approximately 17 million). Tamil language, Tamil is also spoken by approximately five million people, making it the second most-spoken language in Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka has a population of appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andaman Islands
The Andaman Islands () are an archipelago, made up of 200 islands, in the northeastern Indian Ocean about southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a maritime boundary between the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Andaman Sea to the east. Most of the islands are part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India, while the Coco Islands and Preparis Island are part of the Yangon Region of Myanmar. The Andaman Islands are home to the Andamanese peoples, Andamanese, a group of indigenous people made up of a number of tribes, including the Jarawas (Andaman Islands), Jarawa and Sentinelese. While some of the islands can be visited with permits, entry to others, including North Sentinel Island, is banned by law. The Sentinelese are generally hostile to visitors and have had Uncontacted peoples, little contact with any other people. The Indian government and coast guard protect th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, the Gulf of Aden to the north, and the Indian Ocean to the east. Somalia has the longest coastline on Africa's mainland. Somalia has an estimated population of 18.1 million, of which 2.7 million live in the capital and largest city, Mogadishu. Around 85% of Somalia's residents are ethnic Somali people, Somalis. The official languages of the country are Somali language, Somali and Arabic, though Somali is the Languages of Somalia, primary language. Somalia has historic and religious ties to the Arab world. The people in Somalia are mainly Muslims, following the Sunni Islam, Sunni branch.. In antiquity, Somalia was an important commercial center. During the Middle Ages, several powerful Somali empires dominated the regional trade, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly , is about long, and wide at its widest point. It has an average depth of , and in the central Suakin Trough, it reaches its maximum depth of . Approximately 40% of the Red Sea is quite shallow at less than deep and about 25% is less than deep. The extensive shallow shelves are noted for their marine life and corals. More than 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral live in the sea. The Red Sea is the world's northernmost tropical sea and has been designated a Global 200 ecoregion. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |