|
CpG Island
The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG islands. Cytosines in CpG dinucleotides can be methylated to form 5-methylcytosines. Enzymes that add a methyl group are called DNA methyltransferases. In mammals, 70% to 80% of CpG cytosines are methylated. Methylating the cytosine within a gene can change its expression, a mechanism that is part of a larger field of science studying gene regulation that is called epigenetics. Methylated cytosines often mutate to thymines. In humans, about 70% of promoters located near the transcription start site of a gene (proximal promoters) contain a CpG island. CpG characteristics Definition ''CpG'' is shorthand for ''5'—C—phosphate—G—3' '', that is, cytosine and guanine separated by only one phosphate group; phosphate links any two nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CpG Vs C-G Bp
CpG may refer to: * CpG site The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG isl ... - methylated sequences of DNA significant in gene regulation * CpG island - regions of DNA that contain several CpG sites * CpG oligodeoxynucleotide - unmethylated sequences of DNA that have immunostimulatory properties {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrian Bird
Sir Adrian Peter Bird (born 3 July 1947) is a British geneticist and Buchanan Professor of Genetics at the University of Edinburgh. Bird has spent much of his academic career in Edinburgh, from receiving his PhD in 1970 to working at the Medical Research Council (United Kingdom), MRC Mammalian Genome Unit and later serving as director of the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Biology. His research focuses on understanding DNA methylation and CpG islands, and their role in diseases such as Rett syndrome. Education and early life Bird was born in Rowley Regis near Wolverhampton, England, but from age 4 lived in the town of Kidderminster, near Birmingham. He attended a grammar school in Hartlebury, achieving grades CCD for his GCE Advanced Level, A-level results. Whilst at school, Bird played cricket and hockey for a local team. Bird received his PhD from the University of Edinburgh in 1970 for research supervised by Max Birnstiel, following undergraduate study of Biochemistry at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Arnheim
Norman Arnheim is an American biologist specializing in aging and development biology, biochemistry, and molecular biology. He is currently a Distinguished Professor and the Ester Dornsife Chair at the University of Southern California, and an Elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is a United States–based international nonprofit with the stated mission of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific responsib .... References Year of birth missing (living people) Living people University of Southern California faculty 21st-century American biologists {{US-biologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Palmer Green
Philip Palmer Green is a theoretical and computational biologist noted for developing important algorithms and procedures used in gene mapping and DNA sequencing. He earned his doctorate from Berkeley in mathematics in 1976 with a dissertation on C*-algebra under the direction of Marc Rieffel, but transitioned from pure mathematics into applied work in biology and bioinformatics. Green has obtained numerous important results, including in developing Phred, a widely used DNA trace analyzer, in mapping techniques, and in genetic analysis. Green was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2001 and won the Gairdner Award in 2002.National Academy of Sciences (2004Biography of Phil Green PNAS ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of S ... 101(39), 13991–13993. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition (genetics)
Transition, in genetics and molecular biology, refers to a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (Adenine, A ↔ Guanine, G), or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (Cytosine, C ↔ Thymine, T). Approximately two out of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are transitions. Transitions can be caused by oxidative deamination and tautomerization. Although there are twice as many possible transversions, transitions appear more often in genomes, possibly due to the molecular mechanisms that generate them. Transitions are more likely to be Synonymous substitution, synonymous substitutions than transversions, as one observes in the DNA and RNA codon tables, codon table. 5-Methylcytosine is more prone to transition than unmethylated cytosine, due to spontaneous deamination. This mechanism is important because it dictates the rarity of CpG islands. See also * Transversion References External links Diagram at mun.ca Mutation {{Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Excision Repair
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky helix-distorting lesions. BER is important for removing damaged bases that could otherwise cause mutations by mispairing or lead to breaks in DNA during replication. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. These are then cleaved by an AP endonuclease. The resulting single-strand break can then be processed by either short-patch (where a single nucleotide is replaced) or long-patch BER (where 2–10 new nucleotides are synthesized). Lesions processed by BER Single bases in DNA can be chemically damaged by a variety of mechanisms, the most common ones being deamination, oxidation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uracil
Uracil () (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat Cereal germ, germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Uracil that was formed extraterrestrially has been detected in the Murchison meteorite, in near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, Ryugu, and possibly on the surface of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. In RNA, thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil. Thymine was first isolated in 1893 by Albrecht Kossel and Albert Neumann from calf thymus glands, hence its name. Derivation As its alternate name (5-methyluracil) suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. In RNA, thymine is replaced with uracil in most cases. In DNA, thymine (T) binds to adenine (A) via two hydrogen bonds, thereby stabilizing the nucleic acid structures. Thymine combined with deoxyribose creates the nucleoside deoxythymidine, which is synonymous with the term thymidine. Thymidine can be phosphorylated with up to three phosphoric acid groups, producing dTMP (deoxythymidine monophosphate), dTDP, or dTTP (for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deamination
Deamination is the removal of an amino group from a molecule. Enzymes that catalysis, catalyse this reaction are called deaminases. In the human body, deamination takes place primarily in the liver; however, it can also occur in the kidney. In situations of excess protein intake, deamination is used to break down amino acids for energy. The amino group is removed from the amino acid and converted to ammonia. The rest of the amino acid is made up of mostly carbon and hydrogen, and is recycled or oxidized for energy. Ammonia is toxic to the human system, and enzymes convert it to urea or uric acid by addition of carbon dioxide molecules (which is not considered a deamination process) in the urea cycle, which also takes place in the liver. Urea and uric acid can safely diffuse into the blood and then be excreted in urine. Deamination reactions in DNA Cytosine Spontaneous deamination is the hydrolysis reaction of cytosine into uracil, releasing ammonia in the process. This can occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
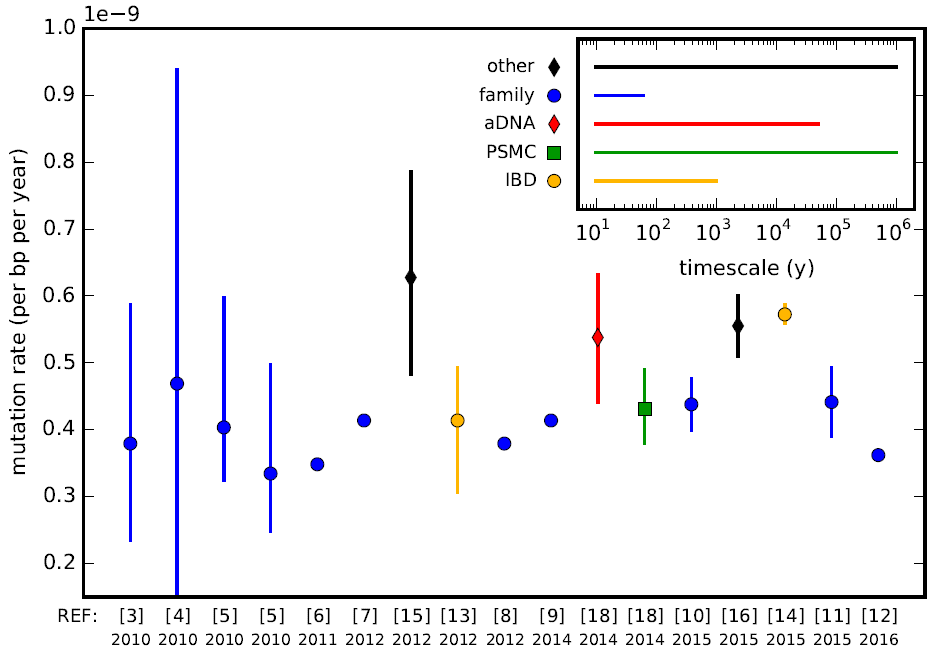
Mutation Rate
In genetics, the mutation rate is the frequency of new mutations in a single gene, nucleotide sequence, or organism over time. Mutation rates are not constant and are not limited to a single type of mutation; there are many different types of mutations. Mutation rates are given for specific classes of mutations. Point mutations are a class of mutations that are changes to a single base. Missense, nonsense, and synonymous mutations are three subtypes of point mutations. The rate of these types of substitutions can be further subdivided into a mutation spectrum, which describes the influence of the genetic context on the mutation rate. There are several natural units of time for each of these rates, with rates being characterized either as mutations per base pair per cell division, per gene per generation, or genome per generation. The mutation rate of an organism is an evolved characteristic and is strongly influenced by the genetics of each organism, in addition to a strong in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GC Content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of an implied four total bases, also including adenine and thymine in DNA and adenine and uracil in RNA. GC-content may be given for a certain fragment of DNA or RNA or for an entire genome. When it refers to a fragment, it may denote the GC-content of an individual gene or section of a gene (domain), a group of genes or gene clusters, a non-coding region, or a synthetic oligonucleotide such as a primer. Structure Qualitatively, guanine (G) and cytosine (C) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (A) bonds specifically with thymine (T) in DNA and with uracil (U) in RNA. Quantitatively, each GC base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while AT and AU base pairs are held together by two hydrogen bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |