|
Covox Voice Master
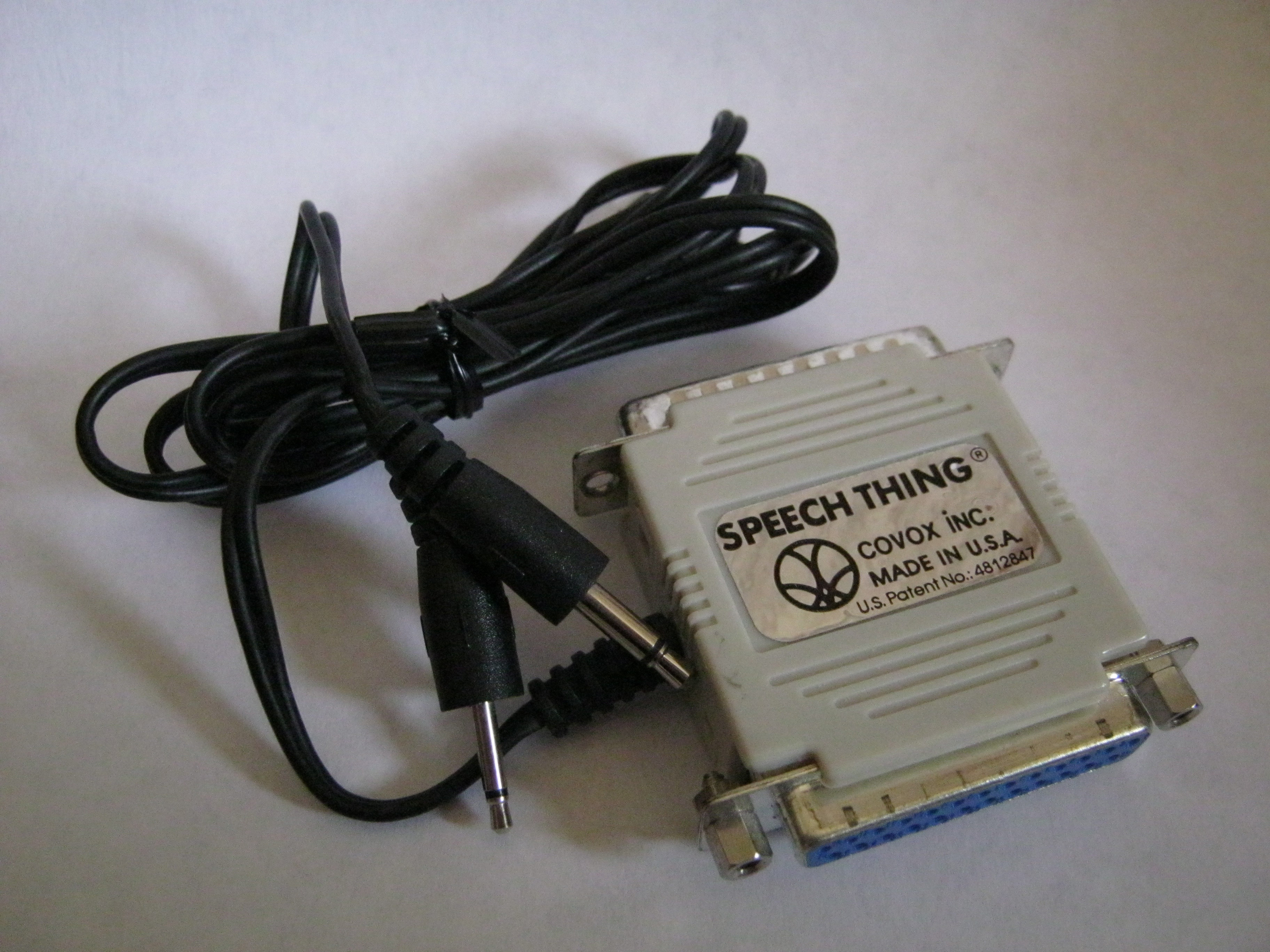
The Covox Speech Thing is an external digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that plugs into the parallel printer port of a PC. It converts 8-bit digital sound using a simple R-2R resistor ladder into an analog signal output. The Speech Thing was introduced on December 18, 1987 by Covox, Inc. of Eugene, Oregon, for about US$70 () and priced US$79.95 as of 1989. People soon started to build their own (DIY) variants, since its communication protocol and DAC is simple and only requires soldering a few cheap parts. The novelty of its patent "Parallel port pass-through digital to analog converter" (filed in 1987, granted in 1989) wasn't specifically the use of a resistor ladder as a DAC, but rather the patent's discussion is around its ease of plugging into the parallel port and how its resistor ladder design didn't block other devices from using the parallel port. , as sound cards were still very expensive at that time. The plug was also quite popular in the demoscene. An inherent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covox
SRT, Inc., doing business as Covox, Inc., was a small, privately owned American technology company active from 1975 to 1994. The company released a number of sound-generating devices for microcomputers and personal computers from the 1980s to the 1990s. They are perhaps best known for the Speech Thing, a digital-to-analog converter that plugs into a parallel port of the IBM Personal Computer. Covox was originally based in Southern California but moved their headquarters to Eugene, Oregon, in the early 1980s. History SRT, Inc., was founded by Larry Stewart in Southern California in 1975. Stewart had previously worked in the aerospace industry into the 1960s, where he got the idea for Av-Alarm, a sound-generating device intended to scare off birds from outside locations such as vegetable crops and vineyards. SRT relocated to Eugene, Oregon, in 1982, Stewart finding Oregon to be a cheaper state in which to conduct his business. Around this time, he hired his sons Mike Stewart and Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal representing sound or a video signal representing images, in an electronic device or communication channel. Distortion is usually unwanted, and so engineers strive to eliminate or minimize it. In some situations, however, distortion may be desirable. For example, in noise reduction systems like the Dolby noise-reduction system, Dolby system, an audio signal is deliberately distorted in ways that emphasize aspects of the signal that are subject to electrical noise, then it is symmetrically "undistorted" after passing through a noisy communication channel, reducing the noise in the received signal. Distortion is also used as a Distortion (music), musical effect, particularly with electric guitars. The addition of Electronic noise, noise o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanofarad
The farad (symbol: F) is the unit of electrical capacitance, the ability of a body to store an electrical charge, in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to 1 coulomb per volt (C/V). It is named after the English physicist Michael Faraday (1791–1867). In SI base units 1 F = 1 kg−1⋅ m−2⋅ s4⋅ A2. Definition The capacitance of a capacitor is one farad when one coulomb of charge changes the potential between the plates by one volt. Equally, one farad can be described as the capacitance which stores a one-coulomb charge across a potential difference of one volt. The relationship between capacitance, charge, and potential difference is linear. For example, if the potential difference across a capacitor is halved, the quantity of charge stored by that capacitor will also be halved. For most applications, the farad is an impractically large unit of capacitance. Most electrical and electronic applications are covered by the following SI prefixes: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I486SX
The i486SX was a microprocessor originally released by Intel in 1991. It was a modified Intel i486, i486DX microprocessor with its Floating-point unit, floating-point unit (FPU) disabled. It was intended as a lower-cost CPU for use in low-end systems—selling for United States dollar, US$258—adapting the ''SX'' suffix of the earlier i386SX in order to connote a lower-cost option. However, unlike the i386SX, which had a 16-bit external data bus and a 24-bit external address bus (compared to the fully 32-bit i386DX, its higher-cost counterpoint), the i486SX was entirely 32-bit. The Intel486 SX-20 CPU can perform up 20 MIPS at 25 MHertz, Hz while this can also perform 70% faster than the 33 MHz Intel386 DX with external cache. Overview In the early 1990s, common applications, such as word processors and database applications, did not need or benefit from a floating-point unit, such as that included in the i486, introduced in 1989. Among the rare exceptions were Computer-aided desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non- multiplexed address and data buses and also the first with memory management and wide protection abilities. It had a data size of 16 bits, and had an address width of 24 bits, which could address up to 16M of memory with a suitable operating system such as Windows compared to 1M for the 8086. The 80286 used approximately 134,000 transistors in its original nMOS ( HMOS) incarnation and, just like the contemporary 80186, it can correctly execute most software written for the earlier Intel 8086 and 8088 processors. The 80286 was employed for the IBM PC/AT, introduced in 1984, and then widely used in most PC/AT compatible computers until the early 1990s. In 1987, Intel shipped its five-millionth 80286 microprocessor. History and performance Intel's first 80286 chips were specified for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
44,100 Hz
In digital audio, 44,100 Hz (alternately represented as 44.1 kHz) is a common sampling frequency. Analog audio is often recorded by sampling it 44,100 times per second, and then these samples are used to reconstruct the audio signal when playing it back. The audio sampling rate is widely used due to the compact disc (CD) format, dating back to its use by Sony from 1979. History The 44.1 kHz sampling rate originated in the late 1970s with PCM adaptors, which recorded digital audio on video cassettes,Specifically U-matic cassettes notably the Sony PCM-1600 introduced in 1979 and carried forward in subsequent models in this series. This then became the basis for Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD-DA), defined in the Red Book standard in 1980. Its use has continued as an option in 1990s standards such as the DVD, and in 2000s, standards such as HDMI. This sampling frequency is commonly used for MP3 and other consumer audio file formats which were originally create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling Rate
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous-time signal to a discrete-time signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of "samples". A sample is a value of the signal at a point in time and/or space; this definition differs from the term's usage in statistics, which refers to a set of such values. A sampler is a subsystem or operation that extracts samples from a continuous signal. A theoretical ideal sampler produces samples equivalent to the instantaneous value of the continuous signal at the desired points. The original signal can be reconstructed from a sequence of samples, up to the Nyquist limit, by passing the sequence of samples through a reconstruction filter. Theory Functions of space, time, or any other dimension can be sampled, and similarly in two or more dimensions. For functions that vary with time, let s(t) be a continuous function (or "signal") to be sampled, and let sampling be performed by measuring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
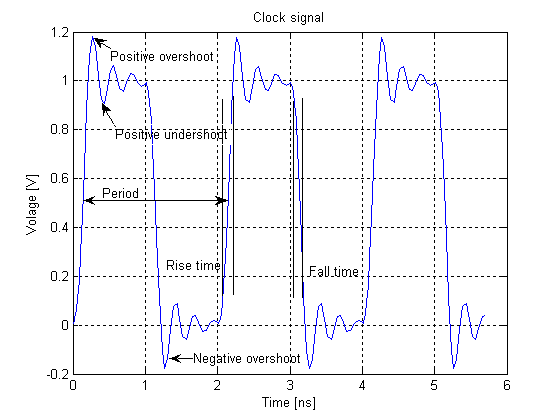
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Logic
In automata theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends on the present value of its input signals and on the sequence of past inputs, the input history. This is in contrast to '' combinational logic'', whose output is a function of only the present input. That is, sequential logic has ''state'' (''memory'') while combinational logic does not. Sequential logic is used to construct finite-state machines, a basic building block in all digital circuitry. Virtually all circuits in practical digital devices are a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. A familiar example of a device with sequential logic is a television set with "channel up" and "channel down" buttons. Pressing the "up" button gives the television an input telling it to switch to the next channel above the one it is currently receiving. If the television is on channel 5, pressing "up" switches it to receive channel 6. However, if the television is on channel 8, pressing "up" switch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Load
An electrical load is an electrical component or portion of a Electric Circuit, circuit that consumes (active) electric power, such as electrical appliances and Electric light, lights inside the home. The term may also refer to the power Power consumption, consumed by a circuit. This is opposed to a power supply source, such as a Electric battery, battery or Electric generator, generator, which ''provides'' power. The term is used more broadly in electronics for a device connected to a electrical signal, signal source, whether or not it consumes power. If an electric circuit has an output port (circuit theory), port, a pair of terminals that produces an electrical signal, the circuit connected to this terminal (or its input Electrical impedance, impedance) is the ''load''. For example, if a CD player is connected to an amplifier, the CD player is the source, and the amplifier is the load, and to continue the concept, if loudspeakers are connected to that amplifier, then that ampli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. The driver is a linear motor connected to a diaphragm, which transmits the motor's movement to produce sound by moving air. An audio signal, typically originating from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is electronically amplified to a power level sufficient to drive the motor, reproducing the sound corresponding to the original unamplified signal. This process functions as the inverse of a microphone. In fact, the ''dynamic speaker'' driver—the most common type—shares the same basic configuration as a dynamic microphone, which operates in reverse as a generator. The dynamic speaker was invented in 1925 by Edward W. Kellogg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phone Connector (audio)
A phone connector is a family of Cylinder, cylindrically-shaped electrical connectors primarily for Analog signal, analog audio signals. Invented in the late 19th century for Telephone switchboard, tele''phone'' switchboards, the phone connector remains in use for interfacing wired audio equipment, such as Headphone, head''phones'', Loudspeaker, speakers, Microphone, micro''phones'', mixing consoles, and electronic musical instruments (e.g. electric guitars, Electronic keyboard, keyboards, and effects units). A Gender of connectors and fasteners, ''male'' connector (a plug), is mated into a ''female'' connector (a socket), though #Other terms, other terminology is used. Plugs have 2 to 5 electrical contacts. The tip contact is indented with a groove. The sleeve contact is nearest the (conductive or Insulator (electricity), insulated) handle. Contacts are insulated from each other by a band of non-conductive material. Between the tip and sleeve are 0 to 3 ring contacts. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |