|
Coutada Publica Do Luiana
Six-week-old a bush Luengue-Luiana National Park () is a national park in Angola. Geography The park covers an area of 42,000 km². It is located in Cuando Province in the southeastern corner of Angola. The park is bounded on the west and southwest by the Kavango River, on the south by the border with Namibia, on the east by the Cuando River , which forms the border with Zambia, and on the north by Longa-Mavinga National Park.Tarr, Peter (2020). ''Management Plan for the Luengue- Luiana National Park, Kuando Kubango, Angola 2016-2020''. Southern Africa Regional Environment Programme/ref> Ecology The majority of the park is open woodland. The predominant trees are species of '' Burkea (plant), Burkea, Baikiaea, Pterocarpus'', and ''Erythrophleum'' in the southern portion of the park, and ''Erythrophleum, Burkea, Julbernardia'', and ''Guibourtia'' in the northern areas of the park. The spacing of the trees varies considerably from place to place. The ground is covered with sparse g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuando Province
Cuando is a province of Angola. It was created on 5 September 2024 from the eastern part of Cuando Cubango Province. Its capital is Mavinga. Geography and climate Cuando borders the Angolan provinces of Cubango to the west and Moxico to the north. It also borders Zambia's Western Province to the east, and the Namibian regions of Zambezi and Kavango East to the southeast and south respectively. The province is drained by the Cubango and Cuando rivers. The Cubango forms part of the province's border with Namibia, and its tributary the Cuito River forms much of the province's border with Cubango Province. The Cuando River runs along or close to much of the province's borders with Moxico Province and Zambia. Luengue-Luiana National Park and Mavinga National Park are located in the province. Both parks are components of the Kavango–Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area, the world's largest land-based transboundary protected area. The northern part of the province belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Bush Elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), also known as the African savanna elephant, is a species of elephant native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of three extant elephant species and, along with the African forest elephant, one of two extant species of African elephant. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with fully grown bulls reaching an average shoulder height of and a body mass of ; the largest recorded specimen had a shoulder height of and an estimated body mass of . The African bush elephant is characterised by its long prehensile trunk with two finger-like processes; a convex back; large ears which help reduce body heat; and sturdy tusks that are noticeably curved. The skin is grey with scanty hairs, and bending cracks which support thermoregulation by retaining water. The African bush elephant inhabits a variety of habitats such as forests, grasslands, woodlands, wetlands and agricultural land. It is a mixed herbivore feeding mostly on grasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Mines
A land mine, or landmine, is an explosive weapon often concealed under or camouflaged on the ground, and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets as they pass over or near it. Land mines are divided into two types: anti-tank mines, which are designed to disable tanks or other vehicles; and anti-personnel mines, designed to injure or kill people. Land mines are typically pressure activated, exploding automatically when stepped on by a person or driven over by a vehicle, though alternative detonation mechanisms are sometimes used. A land mine may cause damage by direct blast effect, by fragments that are thrown by the blast, or by both. Land mines are typically laid throughout an area, creating a ''minefield'' which is dangerous to cross. The use of land mines is controversial because of their indiscriminate nature and their potential to remain dangerous many years after a conflict has ended, harming civilians and the economy. With pressure from a number of campaign grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angolan Civil War
The Angolan Civil War () was a civil war in Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with interludes, until 2002. The war began immediately after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. It was a power struggle between two former anti-colonial guerrilla movements, the communist MPLA, People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and the anti-communist UNITA, National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA). The MPLA and UNITA had different roots in Angolan society and mutually incompatible leaderships, despite their shared aim of ending colonial rule. A third movement, the National Front for the Liberation of Angola (FNLA), having fought the MPLA with UNITA during the Angolan War of Independence, played almost no role in the Civil War. Additionally, the Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda (FLEC), an association of separatist militant groups, fought for the independence of the province of Cabinda (province), Cabinda from Angola. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impala
The impala or rooibok (''Aepyceros melampus'', lit. 'black-footed high-horn' in Ancient Greek) is a medium-sized antelope found in eastern and southern Africa. The only extant member of the genus '' Aepyceros'', and tribe Aepycerotini, it was first described to Europeans by German zoologist Hinrich Lichtenstein in 1812. Two subspecies are recognised—the grassland-dwelling common impala (sometimes referred to as the Kenyan impala), and the larger and darker black-faced impala, which lives in slightly more arid, scrubland environments. The impala reaches at the shoulder and weighs . It features a glossy, reddish brown coat. The male's slender, lyre-shaped horns are long. Active mainly during the day, the impala may be gregarious or territorial depending upon the climate and geography. Three distinct social groups can be observed: the territorial males, bachelor herds and female herds. The impala is known for two characteristic leaps that constitute an anti-predator str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbuck
The waterbuck (''Kobus ellipsiprymnus'') is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus ''Kobus (antelope), Kobus'' of the family Bovidae. It was first Scientific description, described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies are grouped under two varieties: the common or ellipsiprymnus waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck. Their coat colour varies from brown to grey. The long, spiral horn (anatomy), horns, present only on males, curve backward, then forward, and are long. Waterbucks are rather sedentary in nature. As gregarious animals, they may form herds consisting of six to thirty individuals. These groups are either nursery herds with females and their offspring or bachelor herds. Males start showing territorial behaviour from the age of five years, but are most dominant from six to nine. The waterbuck cannot tolerate dehydration in hot weather, and thus inhabits areas close to sources of water. Predominantly a grazer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
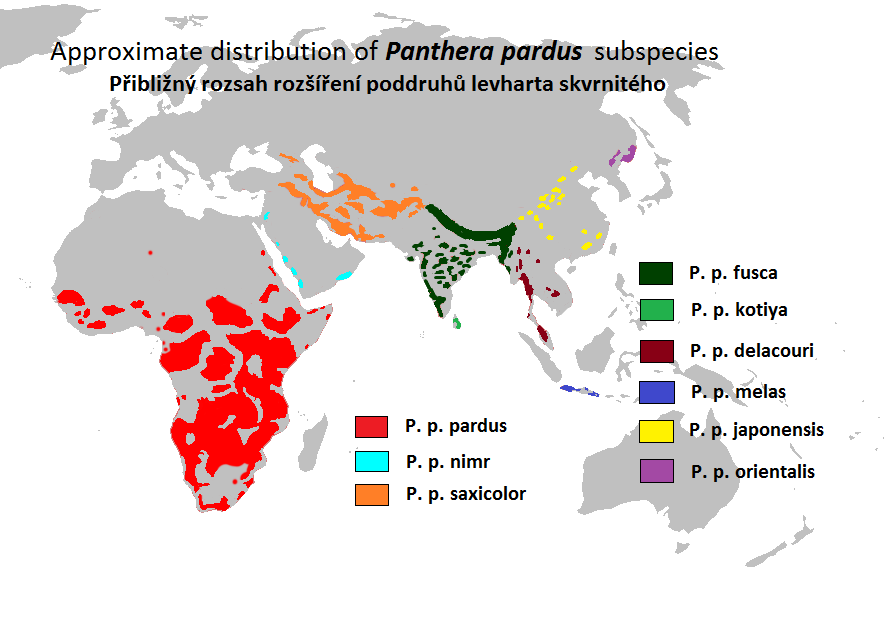
Leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a long tail and a shoulder height of . Males typically weigh , and females . The leopard was first described in 1758, and several subspecies were proposed in the 19th and 20th centuries. Today, eight subspecies are recognised in its wide range in Africa and Asia. It initially evolved in Africa during the Early Pleistocene, before migrating into Eurasia around the Early–Middle Pleistocene transition. Leopards were formerly present across Europe, but became extinct in the region at around the end of the Late Pleistocene-early Holocene. The leopard is adapted to a variety of habitats ranging from rainforest to steppe, including arid and montane areas. It is an opportunistic predator, hunting mostly ungulates and primates. It relies on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sable Antelope
The sable antelope (''Hippotragus niger'') is a large antelope which inhabits wooded savanna in East and Southern Africa, from the south of Kenya to South Africa, with a separated population in Angola. Taxonomy The sable antelope shares the genus '' Hippotragus'' with the extinct bluebuck (''H. leucophaeus'') and the roan antelope (''H. equinus''), and is a member of the family Bovidae. In 1996, an analysis of mitochondrial DNA extracted from a mounted specimen of the bluebuck showed that it is outside the clade containing the roan and sable antelopes. The cladogram below shows the position of the sable antelope among its relatives, following the 1996 analysis: Subspecies ''Hipotragus niger'' has four subspecies: * The southern sable antelope (''H. n. niger''; also known as the common sable antelope, black sable antelope, Matsetsi sable antelope or South Zambian sable antelope) is regarded as the Subspecies#Nominotypical subspecies and subspecies autonyms, nominate subspec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
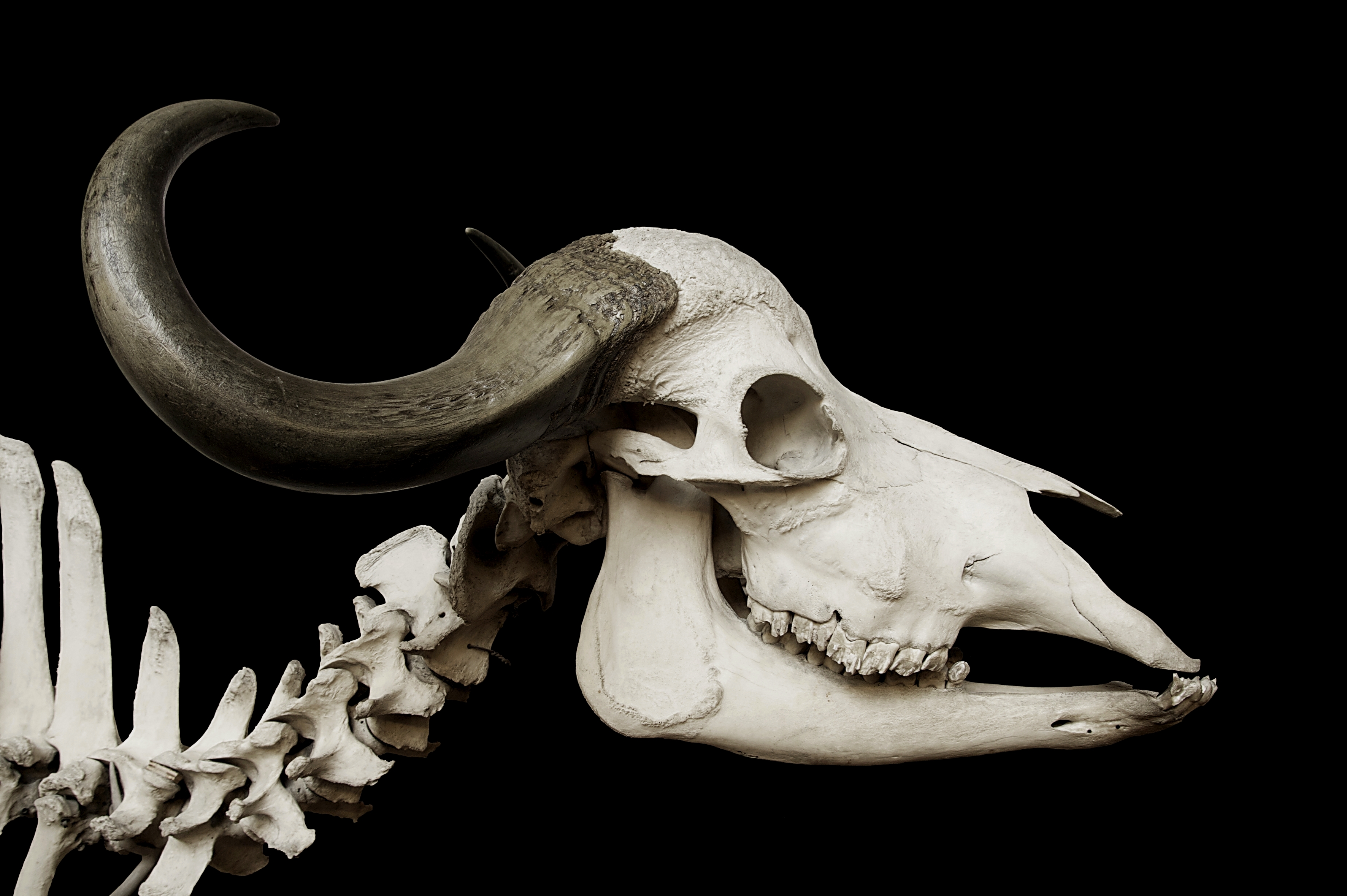
African Buffalo
The African buffalo (''Syncerus caffer)'' is a large sub-Saharan African bovine. The adult African buffalo's horns are its characteristic feature: they have fused bases, forming a continuous bone shield across the top of the head, referred to as a "boss". The African buffalo is more closely related to other buffalo species than it is to other bovids such as American bison or domestic cattle, with its closest living relative being the Asian water buffalo. Its unpredictable temperament may be part of the reason that the African buffalo has never been domesticated, which would also explain why the African buffalo has no domesticated descendants, unlike the wild yak and wild water buffalo which are the ancestors of the Yak, domestic yak and water buffalo. Natural predators of adult African buffaloes include lions, African wild dogs, spotted hyenas, and Nile crocodiles. As one of the Big Five game animals, the Cape buffalo is a sought-after trophy in hunting. Description The Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
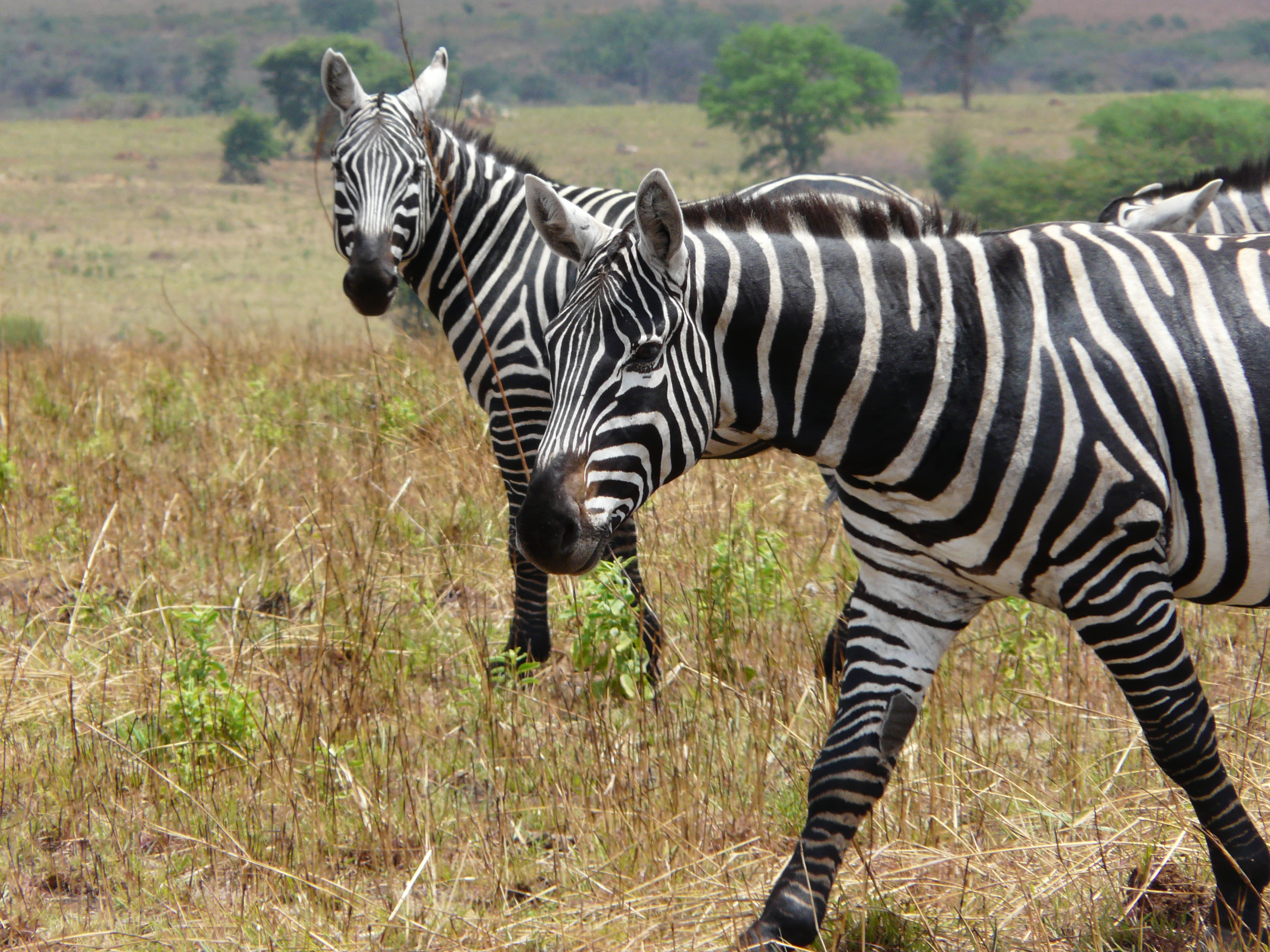
Plains Zebra
The plains zebra (''Equus quagga'', formerly ''Equus burchellii'') is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra. Its range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south of the Sahara. Six or seven subspecies have been recognised, including the quagga which was thought to be a separate species. More recent research supports variations in zebra populations being Cline (biology), clines rather than subspecies. Plains zebras are intermediate in size between the larger Grévy's zebra and the smaller mountain zebra and tend to have broader stripes than both. Great variation in coat patterns exists between clines and individuals. The plains zebra's habitat is generally, but not exclusively, treeless grasslands and savanna woodlands, both tropical and temperate. They generally avoid desert, dense rainforest and permanent wetlands. Zebras are preyed upon by lions and spotted hyenas, Nile crocodiles and, to a lesser extent, African leopard, leopards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
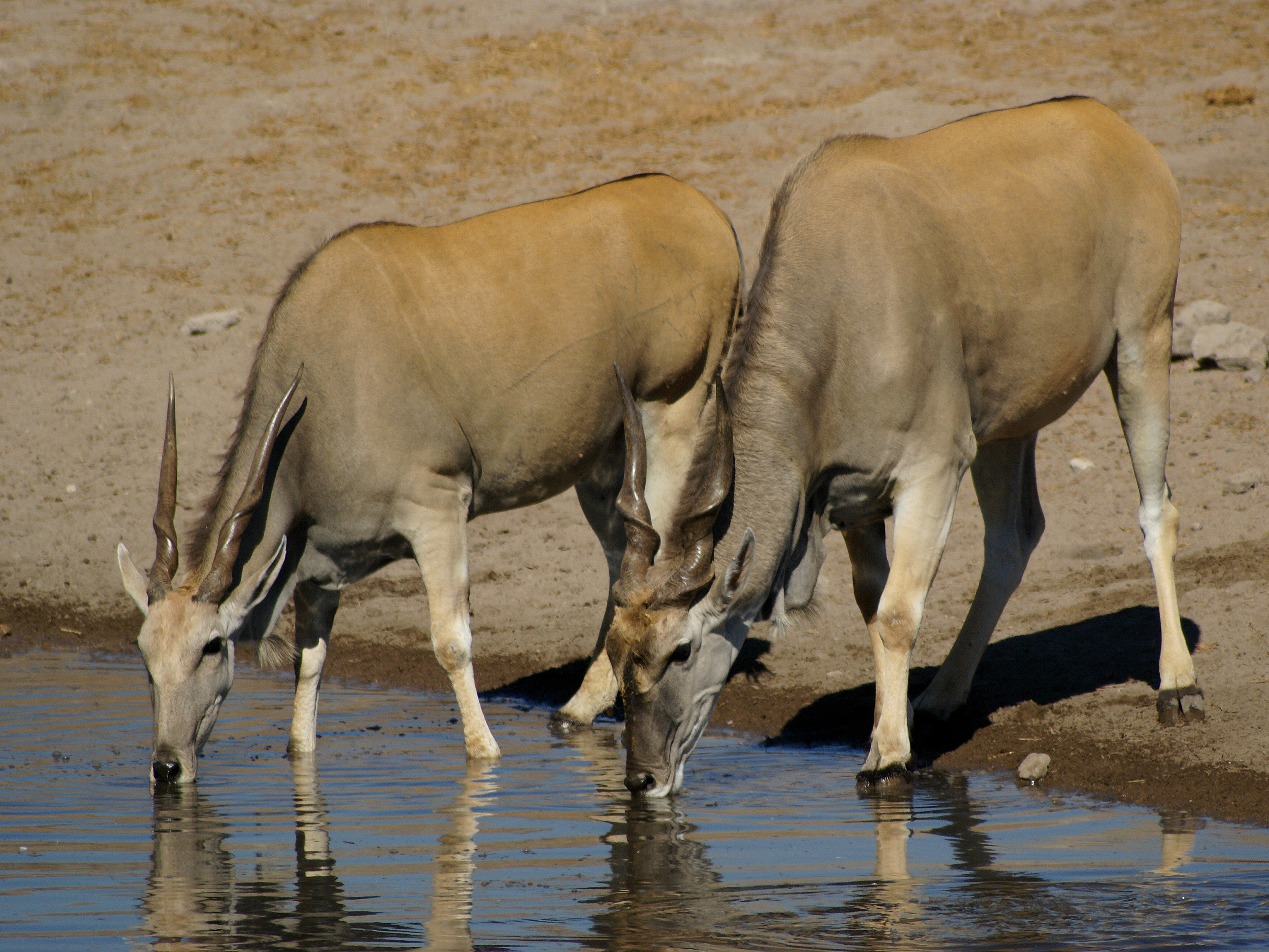
Common Eland
The common eland (''Taurotragus oryx''), also known as the southern eland or eland antelope, is a large savannah and plains antelope found in East Africa, East and Southern Africa. An adult male is around tall at the shoulder and can weigh up to with a typical range of . Females are around tall and weigh . It is the second-largest antelope in the world, being slightly smaller on average than the giant eland. It was scientifically described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Mainly a herbivore, its diet is primarily grasses and leaves. Common elands form herds of up to 500 animals, but are not Territory (animal), territorial. The common eland prefers habitats with a wide variety of flowering plants such as savannah, woodlands, and open and Montane ecology, montane grasslands; it avoids dense forests. It uses loud barks, visual and postural movements, and the flehmen response to Animal communication, communicate and warn others of danger. The common eland is used by humans for leat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |