|
Cosmocampus Maxweberi
''Cosmocampus maxweberi'' (Maxweber's pipefish) is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. It is found in the Red Sea from Sumatra to Tonga and Samoa, and from the Marshall Islands to the Great Barrier Reef. Adults live in reefs and reef-rubble to depths of 36 m, while planktonic juveniles have been found in the top 85m of 1500–2000 m water columns. Adults are expected to feed on small crustaceans, similar to other pipefish, and can grow to lengths of 10 cm. This species is ovoviviparous, with males carrying eggs until giving birth to live young. Etymology The specific name Specific name may refer to: * in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules: * Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ... honours the German-Dutch zoologist and biogeographer Max Carl Wilhelm Weber (1852-1937). Identifying Features This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Percy Whitley
Gilbert Percy Whitley (9 June 1903 – 18 July 1975) was a British-born Australian ichthyologist and malacologist who was Curator of Fishes at the Australian Museum in Sydney for about 40 years. He was born at Swaythling, Southampton, England, and was educated at King Edward VI School, Southampton and the Royal Naval College, Osborne. Whitley migrated with his family to Sydney in 1921 and he joined the staff of the Australian Museum in 1922 while studying zoology at Sydney Technical College and the University of Sydney. In 1925 he was formally appointed Ichthyologist (later Curator of Fishes) at the Museum, a position he held until retirement in 1964. During his term of office he doubled the size of the ichthyological collection to 37,000 specimens through many collecting expeditions. Whitley was also a major force in the Royal Zoological Society of New South Wales, of which he was made a Fellow in 1934 and where he served as president during 1940–41, 1959–60 and 1973� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
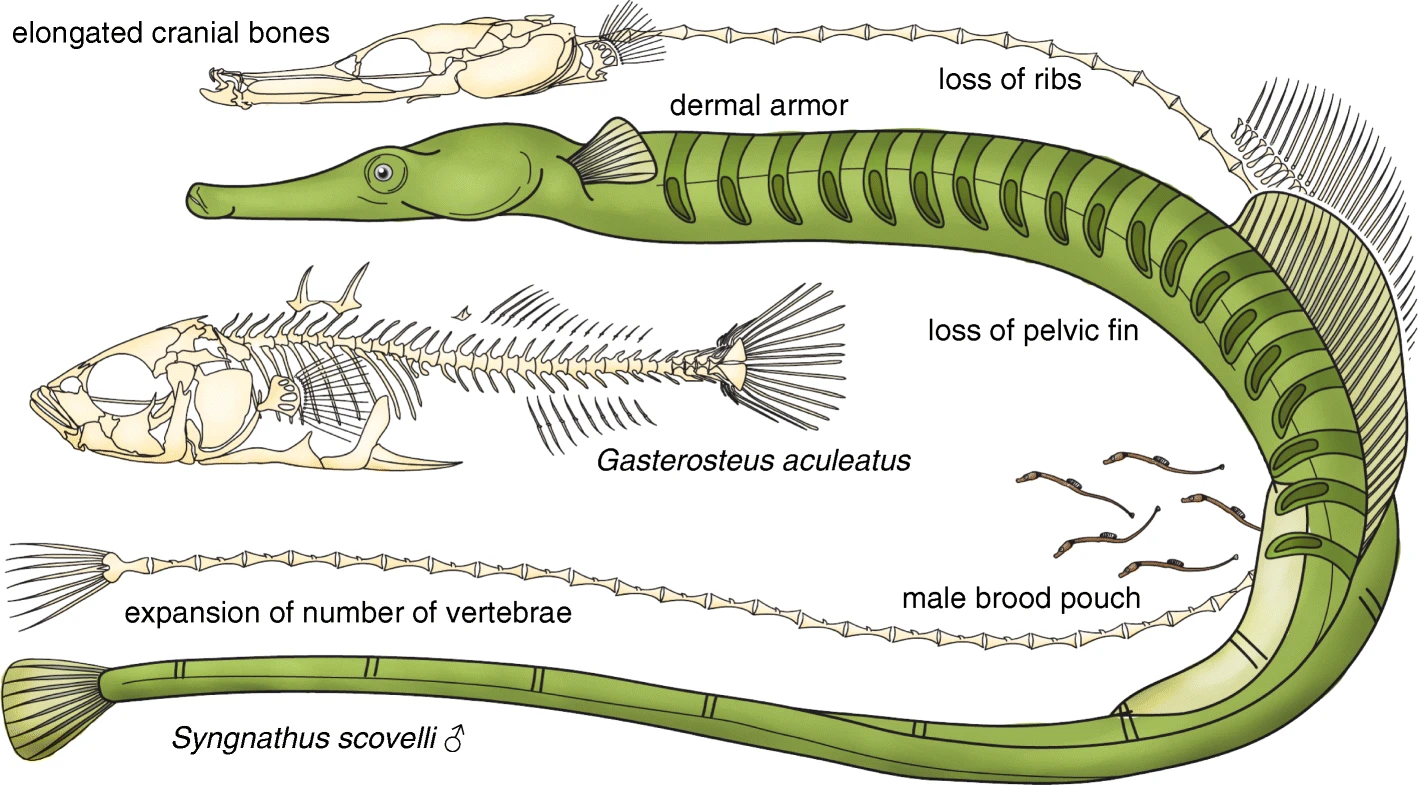
Pipefish
Pipefishes or pipe-fishes (Syngnathinae) are a subfamily of small fishes, which, together with the seahorses and seadragons ('' Phycodurus'' and '' Phyllopteryx''), form the family Syngnathidae. Description Pipefish look like straight-bodied seahorses with tiny mouths. The name is derived from the peculiar form of the snout, which is like a long tube, ending in a narrow and small mouth which opens upwards and is toothless. The body and tail are long, thin, and snake-like. They each have a highly modified skeleton formed into armored plating. This dermal skeleton has several longitudinal ridges, so a vertical section through the body looks angular, not round or oval as in the majority of other fishes. A dorsal fin is always present, and is the principal (in some species, the only) organ of locomotion. The ventral fins are consistently absent, and the other fins may or may not be developed. The gill openings are extremely small and placed near the upper posterior angle of the gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Fish
Saltwater fish, also called marine fish or sea fish, are fish that live in seawater. Saltwater fish can swim and live alone or in a large group called a school. Saltwater fish are very commonly kept in aquariums for entertainment. Many saltwater fish are also caught to be eaten, or grown in aquaculture. However, many fish species have been overfished and are otherwise threatened by marine pollution or ecological changes caused by climate change. Diet Fishes that live in the ocean can be carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores. Herbivores in the ocean eat things such as algae and flowering seagrasses. Many herbivores' diets consist of primarily algae. Most saltwater fish will eat both macroalgae and microalgae. Many fish eat red, green, brown, and blue algae, but some fish prefer certain types. Most saltwater fish that are carnivores will never eat algae under any circumstances. Carnivores' diets consist of shrimp, plankton, or tiny crustaceans. Captivity Saltwater aquariums a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmocampus
''Cosmocampus'' is a genus of pipefishes. Species There are currently 14 recognized species in this genus: * ''Cosmocampus albirostris'' ( Kaup, 1856) (Whitenose pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus arctus'' ( O. P. Jenkins & Evermann, 1889) (Snubnose pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus balli'' ( Fowler, 1925) (Ball's pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus banneri'' (Herald & J. E. Randall, 1972) (Roughridge pipefish) * '' Cosmocampus brachycephalus'' ( Poey, 1868) (Crested pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus coccineus'' (Herald, 1940) * ''Cosmocampus darrosanus'' ( C. E. Dawson & J. E. Randall, 1975) (D'Arros pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus elucens'' ( Poey, 1868) (Shortfin pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus heraldi'' ( Fritzsche, 1980) * '' Cosmocampus hildebrandi'' (Herald, 1965) (Dwarf pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus howensis'' ( Whitley, 1948) (Lord Howe pipefish) * '' Cosmocampus investigatoris'' ( Hora, 1926) * ''Cosmocampus maxweberi'' ( Whitley, 1933) (Max Weber's pipefish) * ''Cosmocampus profundus'' (Herald A herald, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber van Bosse or Max Wilhelm Carl Weber (5 December 1852, in Bonn – 7 February 1937, in Eerbeek) was a German- Dutch zoologist and biogeographer. Weber studied at the University of Bonn, then at the Humboldt University in Berlin with the zoologist Eduard Carl von Martens (1831–1904). He obtained his doctorate in 1877. Weber taught at the University of Utrecht then participated in an expedition to the Barents Sea. He became Professor of Zoology, Anatomy and Physiology at the University of Amsterdam in 1883. In the same year he received naturalised Dutch citizenship. His discoveries as leader of the Siboga Expedition led him to propose Weber's line, which encloses the region in which the mammalian fauna is exclusively Australasian, as an alternative to Wallace's Line. As is the case with plant species, faunal surveys revealed that for most vertebrate groups Wallace’s line was not the most significant biogeographic boundary. The Tanimbar Island g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovoviviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop inside eggs that remain in the mother's body until they are ready to hatch. The young of some ovoviviparous amphibians, such as '' Limnonectes larvaepartus'', are born as larvae, and undergo further metamorphosis outside the body of the mother. Members of genera '' Nectophrynoides'' and '' Eleutherodactylus'' bear froglets, not only the hatching, but all the most conspicuous metamorphosis, being completed inside the body of the mother before birth. Among insects that depend on opportunistic exploitation of transient food sources, such as many Sarcophagidae and other carrion flies, and species such as many Calliphoridae, that rely on fresh dung, and parasitoids such as tachinid flies that depend on entering the host as soon as possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |