|
Cornwall Bridge Railroad Station
Cornwall Bridge station is a former train station in Cornwall Bridge, Connecticut. The station building was built in the 1880s to serve passengers on the Housatonic Railroad. Passenger service on the line ended in 1971, at which time Penn Central auctioned off the station. The following year, the station received a National Register of Historic Places designation. History The station, a Stick style wood-frame structure, was built by the Housatonic Railroad in the 1880s to replace an earlier station. The Housatonic was acquired by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in 1892. The New Haven Railroad was acquired by the Penn Central Railroad in 1969, which went bankrupt by 1970. The station was added to the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall Bridge, Connecticut
Cornwall Bridge is a census-designated place (CDP) comprising the hamlets of Cornwall Bridge and Calhoun Corners in the towns of Cornwall and Sharon, Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. It is primarily in the southwest corner of the town of Cornwall but extends west across the Housatonic River The Housatonic River ( ) is a river, approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 in western Massachusetts and western Connecticut in the United S ... into the town of Sharon in the northern part of the CDP. U.S. Route 7 runs the length of the CDP, following the east side of the Housatonic River and crossing it on the Cornwall Bridge in the northern part of the CDP. Cornwall Bridge was first listed as a CDP prior to the 2020 census. References {{authority control Census-designated places in Litchfield County, Connecticut Census-designated places in Connecticut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Housatonic Railroad
The Housatonic Railroad ( ) is a Class III railroad operating in southwestern New England and eastern New York. It was chartered in 1983 to operate a short section of ex-New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in northwestern Connecticut, and has since expanded north and south, as well as west into New York State. The Housatonic Railroad was also a company chartered in 1836 and leased by the New Haven in 1892. It followed much the same route as the current company, but did not run west into New York. History Regional railroad: 1836–1898 The Housatonic Railroad, originally (mis)spelled as 'Ousatonic Railroad', was chartered in May 1836 to build a line from Bridgeport, Connecticut, north to the Massachusetts state line, along the Housatonic River valley. On February 19, 1840, regular service began from Bridgeport to New Milford, and on December 1, 1842, it opened to the state line. On the other side of the line, the Berkshire Railroad was incorporated April 13, 183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
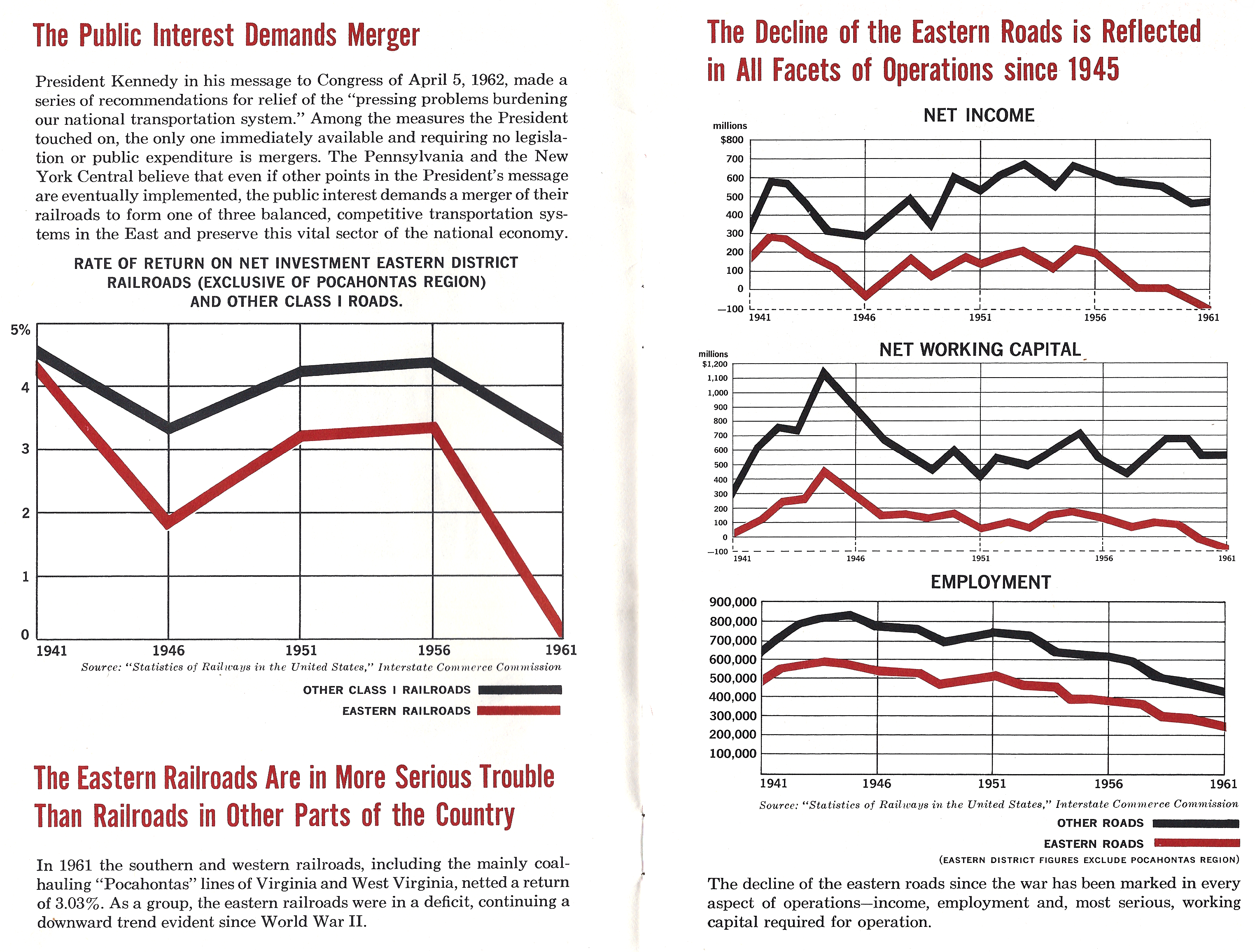
Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford railroads), all united by heavy service into the New York metropolitan area and (to a lesser extent) New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. The Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with the other bankrupt northeastern roads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing northeastern American railroads during the late 1960s. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew revenues from long-distance shipments of commodities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall Bridge Station 1960s Postcard
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, with the River Tamar forming the border between them. Cornwall forms the westernmost part of the South West Peninsula of the island of Great Britain. The southwesternmost point is Land's End and the southernmost Lizard Point. Cornwall has a population of and an area of . The county has been administered since 2009 by the unitary authority, Cornwall Council. The ceremonial county of Cornwall also includes the Isles of Scilly, which are administered separately. The administrative centre of Cornwall is Truro, its only city. Cornwall was formerly a Brythonic kingdom and subsequently a royal duchy. It is the cultural and ethnic origin of the Cornish d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York, New Haven And Hartford Railroad
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad , commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of the New York and New Haven Railroad, New York and New Haven and Hartford and New Haven Railroad, Hartford and New Haven railroads, the company had near-total dominance of railroad traffic in Southern New England for the first half of the 20th century. Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penn Central Railroad
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford railroads), all united by heavy service into the New York metropolitan area and (to a lesser extent) New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. The Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with the other bankrupt northeastern roads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing northeastern American railroads during the late 1960s. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew revenues from long-distance shipments of commodities such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places Listings In Litchfield County, Connecticut
__NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Litchfield County, Connecticut. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map. There are 174 properties and districts listed on the National Register in the county, including 4 National Historic Landmarks. Current listings :*Addresses of listed places in Winchester are "Winsted, CT" See also *List of National Historic Landmarks in Connecticut This article describes National Historic Landmarks in the United States state of Connecticut. These inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall, Connecticut
Cornwall is a New England town, town in Litchfield County, Connecticut, Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 1,567 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. History The town of Cornwall, Connecticut, is named after the county of Cornwall, England. The town was incorporated in 1740, nearly four decades before the United States declared its independence. The town encompasses three distinct townships: Cornwall Bridge and West Cornwall, each bordered by the Housatonic River to the west, and Cornwall Village, located three miles east of the river. One significant natural feature is the vast amount of forested land, including hundreds of acres of Mohawk State Forest, resulting in Cornwall often being called “the “Greenest Town in Connecticut”. The proximity of its settlements to the Housatonic River offered an efficient means of transporting materials and goods, which helped stimulate Cornwall's early farming economy as well as assisting in the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations On The National Register Of Historic Places In Connecticut
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transportation Buildings And Structures In Litchfield County, Connecticut
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack animals. Vehicles may i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |