|
Cornflower
''Centaurea cyanus'', commonly known as cornflower or bachelor's button (among other names), is an annual flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to Europe. In the past, it often grew as a weed in cornfields (in the broad sense of "corn", referring to Food grain, grains, such as wheat, barley, rye, or oats), hence its name. It is now endangered species, endangered in its native habitat by agriculture, agricultural intensification, particularly by over-use of herbicides. However, ''Centaurea cyanus'' is now also naturalisation (biology), naturalised in many other parts of the world, including North America and parts of Australia through introduction as an ornamental plant in gardens and as a seed contaminant in crop seeds. Description ''Centaurea cyanus'' is an annual plant growing to tall, with grey-green branched stems. The leaves are lanceolate and long. The flowers are most commonly an intense blue colour and arranged in inflorescence, flowerheads (capitula) of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaurea Cyanus 3
''Centaurea'' () is a genus of over 700 species of herbaceous thistle-like flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Members of the genus are found only north of the equator, mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere; the Middle East and surrounding regions are particularly species-rich. Common names Common names for this genus are centaury, centory, starthistles, knapweeds, centaureas and the more ambiguous "bluets"; a vernacular name used for these plants in parts of England is "loggerheads" ( common knapweed). The ''Plectocephalus'' group – possibly a distinct genus – is known as basketflowers. "Cornflower" is used for a few species, but that term more often specifically means either '' C. cyanus'' (the annual cornflower) or '' Centaurea montana'' (the perennial cornflower). The common name "centaury" is sometimes used, although this also refers to the unrelated plant genus '' Centaurium''.Keil (2006), Keil & Ochsmann (2006). The name is said to be in reference to Chiro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocyanin
Protocyanin is an anthocyanin pigment that is responsible for the red colouration of roses, but in cornflowers is blue. The pigment was first isolated in 1913 from the blue cornflower ('' Centaurea cyanus''), and the identical pigment was isolated from a red rose in 1915. The difference in colour had been explained as a difference in flower-petal pH, but the pigment in the blue cornflower has been shown to be a supermolecular pigment consisting of anthocyanin, flavone, one ferric ion, one magnesium and two calcium Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ... ions forming a copigmentation complex. The molecular formula of protocyanin complex is of the type of C366H384O228FeMg. References {{Anthocyanins Anthocyanins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeophyte
An archaeophyte is a plant species which is non-native to a geographical region, but which was an introduced species in "ancient" times, rather than being a modern introduction. Those arriving after are called neophytes. The cut-off date is usually the beginning of the early modern period (turn of the 15th or 16th century). In Britain, archaeophytes are considered to be those species first introduced prior to the year 1492, when Christopher Columbus arrived in the New World and the Columbian Exchange began. Background Archaeophytes include numerous weed species the seeds of which have been found in archaeological excavations – to which they had been brought by people ( anthropochory), animals ( zoochory) or the wind ( anemochory). In some cases, introduced species, whether archaeophytes or neophytes, may have been native species before the ice ages, which extirpated vast numbers of plant species. Central European archaeophytes almost all come from the Mediterranean region a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapeseed
Rapeseed (''Brassica napus'' subsp. ''napus''), also known as rape and oilseed rape and canola, is a bright-yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae (mustard or cabbage family), cultivated mainly for its oil-rich seed, which naturally contains appreciable amounts of mildly toxic erucic acid.Food Standards Australia New Zealand (June 2003Erucic acid in food: A Toxicological Review and Risk Assessment Technical report series No. 21; Page 4 paragraph 1; The term "canola" denotes a group of rapeseed cultivars that were bred to have very low levels of erucic acid and which are especially prized for use as human and animal food. Rapeseed is the third-largest source of vegetable oil and the second-largest source of protein meal in the world. Description ''Brassica napus'' grows to in height with hairless, fleshy, pinnatifid and glaucous lower leaves which are stalked whereas the upper leaves have no petioles. Rapeseed flowers are bright yellow and about acr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cereals
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize (Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, such as amaranth, buckwheat and quinoa, are pseudocereals. Most cereals are annuals, producing one crop from each planting, though rice is sometimes grown as a perennial. Winter varieties are hardy enough to be planted in the autumn, becoming dormant in the winter, and harvested in spring or early summer; spring varieties are planted in spring and harvested in late summer. The term cereal is derived from the name of the Roman goddess of grain crops and fertility, Ceres. Cereals were domesticated in the Neolithic around 8,000 years ago. Wheat and barley were domesticated in the Fertile Crescent; rice and some millets were domesticated in East Asia, while sorghum and other millets were domesticated in West Africa. Maize was domesticated by In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice-county
A vice-county (also spelled vice county) is a geographical division of the British Isles. It is also called biological vice-county as it is used for purposes of biological recording and other scientific data-gathering, or sometimes called a Watsonian vice-county as vice-counties were introduced by Hewett Cottrell Watson in the third volume of his ''Cybele Britannica'', published in 1852. Watson's vice-counties were based on the ancient counties of Britain, but often subdividing these boundaries to create smaller, more uniform units, and considering exclaves to be part of the surrounding vice-county. In 1901 Robert Lloyd Praeger introduced a similar system for Ireland and its off-shore islands. Vice-counties are the "standard geographical area for county based ..recording". They provide a stable basis for recording using similarly sized units, and, although National Grid-based reporting has grown in popularity, vice-counties remain a useful mapping boundary, employed in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
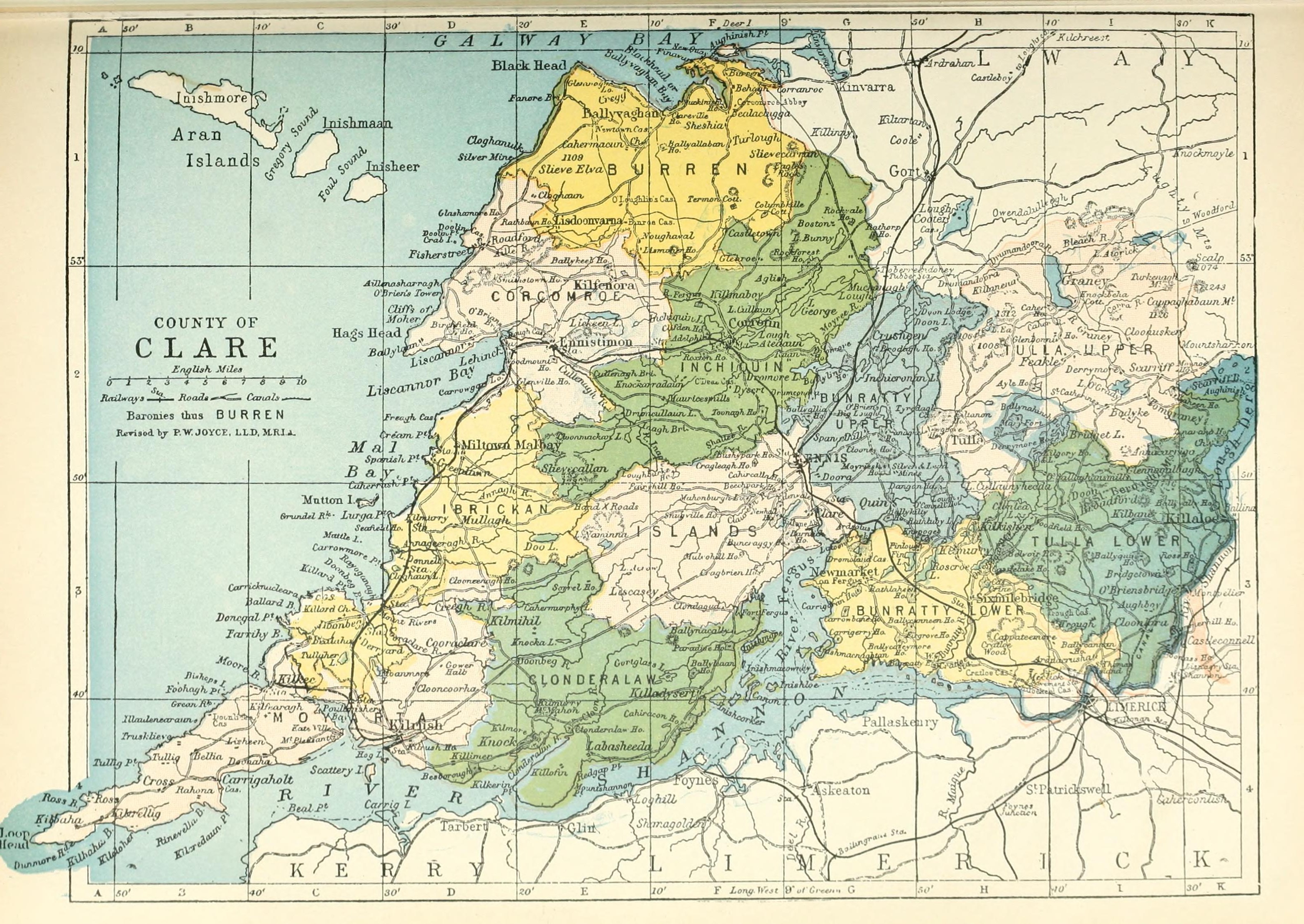
County Clare
County Clare () is a Counties of Ireland, county in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster in the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern part of Republic of Ireland, Ireland, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority. The county had a population of 127,938 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. The county seat and largest settlement is Ennis. Etymology There are two main hypotheses for the origins of the county name "Clare". One is that the name is derived from Thomas de Clare, Lord of Thomond, Thomas de Clare an Anglo-Norman peer and soldier from the de Clare family, who was deeply embroiled in local politics and fighting in the 1270s and 1280 and had had acquired land in Kilkenny and Thomond that included the Castle of Clare. In 1590 County Clare was named after the castle, which is in a strategic location. An alternative hypothesis is that the county name ''Clare'' comes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantlife
Plantlife is a wild plant conservation charity. , it manages 24 nature reserves around the United Kingdom. HM King Charles III is patron of the charity. History Plantlife was founded in 1989. Its first president was Professor David Bellamy. Peter James was also a founder member and early vice-president. Its president is Philip Mould OBE and its chairman is Professor David Hill CBE. English gardener and television presenter Rachel De Thame is their vice-president. The chief executive is Ian Dunn, who took over from Marian Spain in 2020. Function Plantlife's principal activities in Britain include the management of of rare and important plant habitats as nature reserves, lobbying and campaigning in support of wild plant conservation, and organising surveys aimed at generating public interest in wild plants. Plantlife helps run an annual National Plant Monitoring Survey, and a rare species conservation programme, "Back from the Brink". It was a lead partner of HRH the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout the year and more distinct seasonal changes compared to tropical climates, where such variations are often small; they usually differ only in the amount of precipitation. In temperate climates, not only do latitude, latitudinal positions influence temperature changes, but various sea currents, prevailing wind direction, continentality (how large a landmass is) and altitude also shape temperate climates. The Köppen climate classification defines a climate as "temperate" C, when the mean temperature is above but below in the coldest month to account for the persistence of frost. However, some adaptations of Köppen set the minimum at . Continental climate, Continental climates are classified as D and considered to be varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |