|
Corinthian War
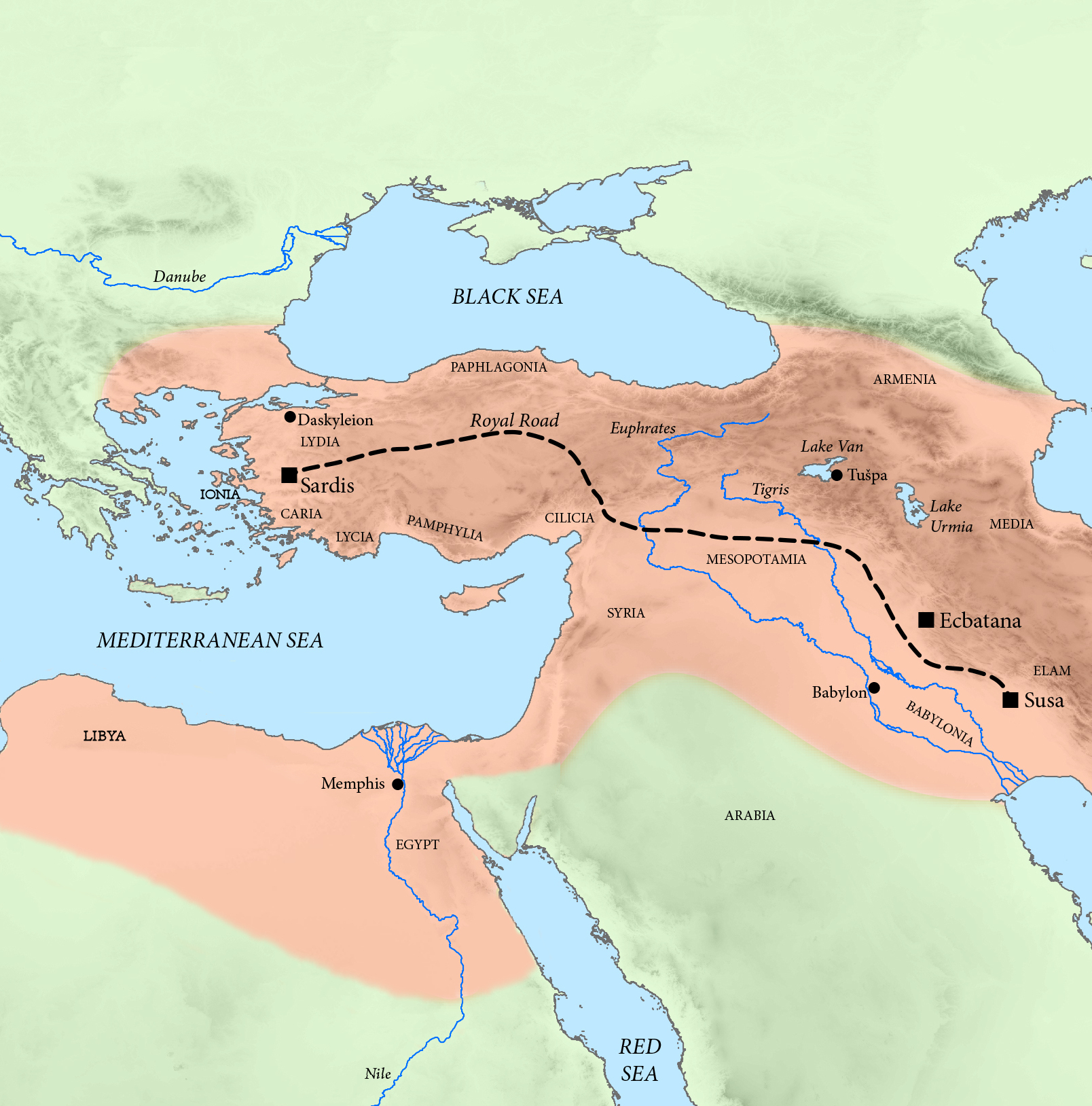
The Corinthian War (395–387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Greece, Thebes, Classical Athens, Athens, Ancient Corinth, Corinth and Argos, Peloponnese, Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with Spartan imperialism in the aftermath of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), both from Athens, the defeated side in that conflict, and from Sparta's former allies, Corinth and Thebes, who had not been properly rewarded. Taking advantage of the fact that the Spartan king Agesilaus II was away campaigning in Asia against the Achaemenid Empire, Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos forged an alliance in 395 BC with the goal of ending Spartan hegemony over Greece; the allies' war council was located in Corinth, which gave its name to the war. By the end of the conflict, the allies had failed to end Spartan hegemony over Greece, although Sparta was weakened by the war. At first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agesilaus II
Agesilaus II (; ; 445/4 – 360/59 BC) was king of Sparta from 400 to 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC). Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC. Despite the traditional secrecy fostered by the Spartiates, the reign of Agesilaus is particularly well-known thanks to the works of his friend Xenophon, who wrote a large history of Greece (the '' Hellenica'') covering the years 411 to 362 BC, therefore extensively dealing with Agesilaus' rule. Xenophon furthermore composed a panegyric biography of his friend, perhaps to clean his memory from the criticisms voiced against him. Another historical tradition—much more hostile to Agesilaus t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antalcidas
Antalcidas (; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta. __NOTOC__ Life Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spartan king Agesilaus II. Antalcidas is first recorded at the outset of the Corinthian War. Following the end of the Peloponnesian War after the destruction of the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, Sparta had launched a series of raids against the Persian satrapies of Asia Minor. Pharnabazus, satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia, finally responded by sending the Rhodian Timocrates to bribe the other Greek city states into declaring war on Sparta. Thebes rose up in 395 BC, eventually encouraging others to join in what became known as the Corinthian War. Persia was now on friendly terms with Athens and Pharnabazus permitted their disgraced general Conon to command his fleet of Phoenician and Cypriot ships in attacks that culminated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes II
Arses (; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( ; ), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II () and his mother was Parysatis. Soon after his accession, Artaxerxes II faced opposition from his younger brother Cyrus the Younger, who assembled an army composed of troops from his Lydian and Ionians, Ionian satrapies as well as Greek mercenaries in his bid for the throne. The forces of the brothers clashed at Battle of Cunaxa, Cunaxa in 401 BC, which resulted in the defeat and death of Cyrus. Following this, Artaxerxes II had to contend with several other revolts; a revolt by Evagoras I () in Cyprus between 391–380 BC, by the Phoenicians in , and most importantly, the revolts by the western satraps (known as the Great Satraps' Revolt) in the 360s and 350s BC, led by distinguished figures such as Datames, Ariobarzanes of Phrygia, Ariobarzanes, and Autophradates. The rulers of the Parthian Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (''Symmachia (alliance), symmachia'') of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies". While Sparta excelled as Greece's greatest power on land, Athens turned to the seas becoming the dominant naval power of the Ancient Greece, Greek world. Following Sparta's withdrawal from the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cnidus
The Battle of Cnidus () was a military operation conducted in 394 BC by the Achaemenid Empire against the Spartan fleet during the Corinthian War. A fleet under the joint command of Pharnabazus and former Athenian admiral, Conon, destroyed the Spartan fleet led by the inexperienced Peisander, ending Sparta's brief bid for naval supremacy. The battle outcome was a significant boost for the anti-Spartan coalition that resisted Spartan hegemony in the course of the Corinthian War. Prelude In 394 BC, King Agesilaus II of Sparta and his army were recalled from Ionia to help fight the Corinthian War. The Spartan fleet, under Peisander, also began a return to Greece, sailing out from its harbor at Cnidus with eighty-five triremes. The "Greek" vanguard of the Achaemenid fleet, referred to as such only due to its consisting of Greek mercenaries, was commanded by Conon, while the Persian satrap Pharnabazus led the main body of the forces, a Phoenician fleet from the Chersonese, to op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Coronea (394 BC)
The Battle of Coronea in 394 BC, also Battle of Coroneia, took place during the Corinthian War, in which the Spartans and their allies under King Agesilaus II defeated a force of Thebans and Argives that was attempting to block their march back into the Peloponnese. It ranks among the deadliest of the Hoplite battles, despite its comparative obscurity, when matched up against more famous battles like the Battle of Delium in 424, and the Battle of Mantinea in 362. Prelude The Corinthian War began in 395 BC when Thebes, Argos, Corinth, and Athens, with Persian support and funding, united to oppose Spartan intervention in Locris and Phocis. At the start of the war, Agesilaus was in Ionia, campaigning against the Persians. When hostilities opened, he was recalled with his forces, and began an overland march through Thrace and central Greece back to the Peloponnese. Entering Boeotia, he was opposed by a force composed primarily of Thebans, allied Boeotians, and Argives. Agesilaus's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancient Greece, Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet (built with Persian subsidies) finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. The first phase (431–421 BC) was named the Ten Years War, or the Archidamian War, after the Spartan king Archidamus II, who invaded Attica several times with the full hoplite army of the Peloponnesian League, the alliance network dominated by Sparta (then known as Lacedaemon). The Long Walls of Athens rendered this strategy ineffective, while the superior navy of the Delian League (Athens' all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Corinth
Corinth ( ; ; ; ) was a city-state (''polis'') on the Isthmus of Corinth, the narrow stretch of land that joins the Peloponnese peninsula to the mainland of Greece, roughly halfway between Ancient Athens, Athens and Sparta. The modern city of Corinth is located approximately northeast of the ancient ruins. Since 1896, systematic archaeological investigations of the Corinth Excavations by the American School of Classical Studies at Athens have revealed large parts of the ancient city, and recent excavations conducted by the Greek Ministry of Culture have brought to light important new facets of antiquity. For Christianity, Christians, Corinth is well known from the two letters from Paul the Apostle in the New Testament, the First Epistle to the Corinthians and the Second Epistle to the Corinthians. Corinth is also mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles as part of Paul the Apostle's missionary travels. In addition, the second book of Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias' ''Descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus (; ; 440 – 388 BC) was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a primary leader of the ultimately successful democratic resistance to the coup. As general, he was responsible for recalling the controversial nobleman Alcibiades from exile, and the two worked together extensively over the next several years. In 411 and 410, Thrasybulus was in command along with Alcibiades and others at several critical Athenian naval victories. After Athens' defeat in the Peloponnesian War, Thrasybulus led the democratic resistance to the new oligarchic government, known as the Thirty Tyrants, imposed by the victorious Spartans upon Athens. In 404 BC, he commanded a small force of exiles that invaded the Spartan-ruled Attica and, in successive battles, first defeated a Spartan garrison and then the forces of the oligarchy. In the wake of these vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iphicrates
Iphicrates (; ) was an Athenian general, who flourished in the earlier half of the 4th century BC. He is credited with important infantry reforms that revolutionized ancient Greek warfare by regularizing light-armed peltasts. Cornelius Nepos wrote that Iphicrates was such a leader, that he was not only comparable to the first commanders of his own time, but no one even of the older generals could be set above him. He had a deep knowledge of military tactics, he often had the command of armies and he never miscarried in an undertaking by his own fault. He was always eminent for invention and excellence that he not only introduced much that was new into the military art, but made many improvements in what existed before. Biography The son of a shoemaker of the deme of Rhamnous, he was later married to the daughter of the Thracian King Cotys I and had a son with her. His son was named Menestheus (Μενεσθεύς), after the legendary King of Athens during the Trojan War. Ip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnabazus II
Pharnabazus II (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', ; ruled 413-374 BC) was a Achaemenid Empire, Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I of Phrygia, Pharnabazus I, and great-grandson of Artabazos I of Phrygia, Artabazus I. He and his male ancestors, forming the Pharnacid dynasty, had governed the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia from its headquarters at Dascylium since 478 BC. He married Apama, daughter of Artaxerxes II of Persia, and their son Artabazus of Phrygia, Artabazus also became a satrap of Phrygia. According to some accounts, his granddaughter Barsine may have become Alexander the Great's concubine. According to research by Theodor Nöldeke, he was descended from Otanes, one of the associates of Darius the Great, Darius in the murder of Smerdis. Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia War with Sparta against Athens (c.413-404 BC) Athens was the dominant power in the Aegean Sea, Aege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |