|
Coppergate Helmet
The Coppergate Helmet (also known as the York Helmet) is an eighth-century Anglo-Saxon helmet found in York, England. It was discovered in May 1982 during excavations for the Jorvik Viking Centre at the bottom of a pit that is thought to have once been a well. The helmet is one of six Anglo-Saxon helmets known to have survived to the present day, and is by far the best preserved. It shares its basic form with the helmet found at Wollaston (1997), joining that find and those at Benty Grange (1848), Sutton Hoo (1939), Shorwell (2004) and Staffordshire (2009), as one of the "crested helmets" that flourished in England and Scandinavia from the sixth through to the eleventh centuries. It is now in the collections of the Yorkshire Museum. Description Construction The construction of the helmet is complex. Apart from the neck guard the basic form is shared by the contemporaneous Pioneer Helmet, a sparsely decorated fighting piece, and consists of four parts: an iron skull cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a York Minster, minster, York Castle, castle and York city walls, city walls, all of which are Listed building, Grade I listed. It is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of the wider City of York district. It is located north-east of Leeds, south of Newcastle upon Tyne and north of London. York's built-up area had a recorded population of 141,685 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census. The city was founded under the name of Eboracum in AD 71. It then became the capital of Britannia Inferior, a province of the Roman Empire, and was later the capital of the kingdoms of Deira, Northumbria and Jórvík, Scandinavian York. In the England in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages it became the Province of York, northern England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Roman Ridge Helmet
The Late Roman ridge helmet was a type of combat helmet of Late Antiquity used by soldiers of the Late Roman army. It was characterized by the possession of a bowl made up of two or four parts, united by a longitudinal ridge. Origins In the late 3rd century, a complete break in Roman helmet design occurred. Previous Roman helmet types, based ultimately on Celtic designs, were replaced by new forms derived from helmets developed in the Sassanid Empire. A closely related form to the Roman ridge helmets is represented by a single helmet from Dura Europos which is of similar construction, but has a much higher-vaulted skull. It probably belonged to a Sassanid warrior of the 3rd century. This reinforces the evidence for a Sassanid origin of this type of helmet. Two main forms of helmet construction were adopted by the Romans at much the same time: the ridge helmet, described here, and the Spangenhelm, which was likely adopted from the Sarmatians. The earliest confirmed example of a Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of York
The University of York (abbreviated as or ''York'' for Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a public Collegiate university, collegiate research university in York, England. Established in 1963, the university has expanded to more than thirty departments and centres, covering a wide range of subjects. South-east of the city of York, the university campus is about in size. The original campus, Campus West, incorporates the York Science Park and the Science Learning Centres, National Science Learning Centre, and its wildlife, campus lakes and greenery are prominent. In May 2007 the university was granted permission to build an extension to its main campus, on arable land just east of the nearby village of Heslington. The second campus, Campus East, opened in 2009 and now hosts five colleges and three departments as well as conference spaces, a sports village and a business startup company, start-up 'incubator'. The institution also leases King's Manor in York city centre. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borthwick Institute For Archives
The Borthwick Institute for Archives is the specialist archive service of the University of York, York, England. It is one of the biggest archive repositories outside London. The Borthwick was founded in 1953 as The Borthwick Institute of Historical Research. It was originally based at St Anthony's Hall, a fifteenth-century guild hall on Peasholme Green, in central York. Since 2005 it has been based in a purpose-built building, situated adjacent to the JB Morrell Library on the University of York's Heslington West campus. This new building was made possible due to a grant of £4.4 million by the Heritage Lottery Fund and designed by Leach Rhodes Walker and Buro Happold. Archivists and directors Five archivists have headed the Borthwick Institute, all serving under their predecessors. The title was changed from "Director" to "Keeper of Archives" in 2005 and was further expanded to "Keeper of Archives & Special Collections" in 2019. *Canon John Stanley Purvis – 1953–1963 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slag
The general term slag may be a by-product or co-product of smelting (pyrometallurgical) ores and recycled metals depending on the type of material being produced. Slag is mainly a mixture of metal oxides and silicon dioxide. Broadly, it can be classified as ferrous (co-products of processing iron and steel), ferroalloy (a by-product of ferroalloy production) or non-ferrous/ base metals (by-products of recovering non-ferrous materials like copper, nickel, zinc and phosphorus). Within these general categories, slags can be further categorized by their precursor and processing conditions (e.g., blast furnace slags, air-cooled blast furnace slag, granulated blast furnace slag, basic oxygen furnace slag, and electric arc furnace slag). Slag generated from the EAF process can contain toxic metals, which can be hazardous to human and environmental health. Due to the large demand for ferrous, ferralloy, and non-ferrous materials, slag production has increased throughout the years des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antler
Antlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the Cervidae (deer) Family (biology), family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally found only on males, with the exception of Reindeer, reindeer/caribou. Antlers are Moulting, shed and regrown each year and function primarily as objects of sexual attraction and as Weapon (biology), weapons. Etymology Antler comes from the Old French ''antoillier ''(see present French : "Andouiller", from'' ant-, ''meaning before,'' oeil, ''meaning eye and'' -ier'', a suffix indicating an action or state of being) possibly from some form of an unattested Latin word ''*anteocularis'', "before the eye" (and applied to the word for "branch" or "horn (anatomy), horn"). Structure and development Antlers are unique to cervids. The ancestors of deer had tusks (long upper canine tooth, canine teeth). In most species, antlers appear to replace t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
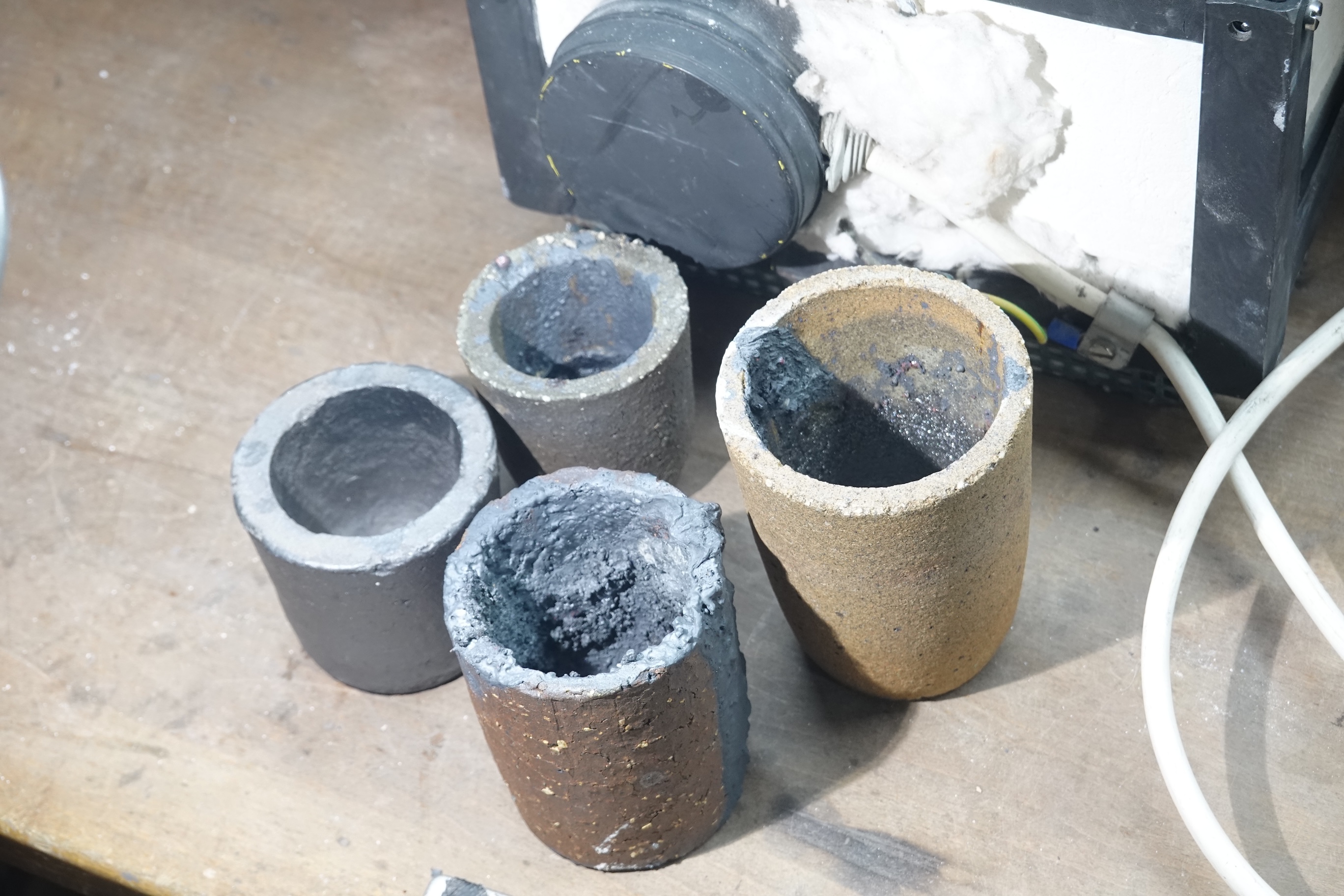
Crucible
A crucible is a container in which metals or other substances may be melted or subjected to very high temperatures. Although crucibles have historically tended to be made out of clay, they can be made from any material that withstands temperatures high enough to melt or otherwise alter its contents. History Typology and chronology The form of the crucible has varied through time, with designs reflecting the process for which they are used, as well as regional variation. The earliest crucible forms derive from the sixth/fifth millennium B.C. in Eastern Europe and Iran. Chalcolithic Crucibles used for copper smelting were generally wide shallow vessels made from clay that lacks refractory properties which is similar to the types of clay used in other ceramics of the time. During the Chalcolithic period, crucibles were heated from the top by using blowpipes.Hauptmann A., 2003, ''Developments in copper Metallurgy During the Fourth and Third Millennia B.C. at Feinan'', Jordan, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butter Churn
A butter churn is a device used to convert cream into butter, a process known as churning. This is done through a mechanical process, frequently via a pole inserted through the lid of the churn, or via a crank used to turn a rotating device inside the churn. Etymology The word ''butter'' is believed by some to derive from the Greek word ''bou-tyron'', the approximate meaning of which is 'cow cheese'. Others believe it came from the Scythian culture, as the ancient Greeks tended to herd sheep and goats, whose milk is not as good for butter making as cow milk, which the Scythians primarily herded. The word ''churn'' is from the Old English ''ċyrin'' 'to churn'. This is probably derived from the Old English ''cyrnel'' 'kernel', due to the appearance of butter grains after milk has been churned. The butter churn gave its name and rough form to the milk churn, which is used to transport milk, not churn it. History The use of butter is mentioned in biblical works and the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beater (weaving)
A beater or batten, is a weaving tool designed to push the weft yarn securely into place. In small hand weaving such as Inkle weaving and tablet weaving the beater may be combined with the shuttle into a single tool. In rigid heddle looms the beater is combined with the heddles. Beaters appear both in a hand-held form, and as an integral part of a loom. Hand beaters must have enough mass to force the weaving into place, so they come in a variety of weights and sizes. Some may have lead inserts to provide additional heft for a smaller beater, and some are made entirely from metal. Loom beaters typically take the form of a bar mounted across the loom. The actual beating is done by a metal insert known as a reed, which contains a number of slots, known as dents, which the warp threads pass through. This is the more common form, as floor looms and mechanized looms both use a beater with a reed. File:Salish Baton.JPG, Coast Salish sword beater, North American west coast File:Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
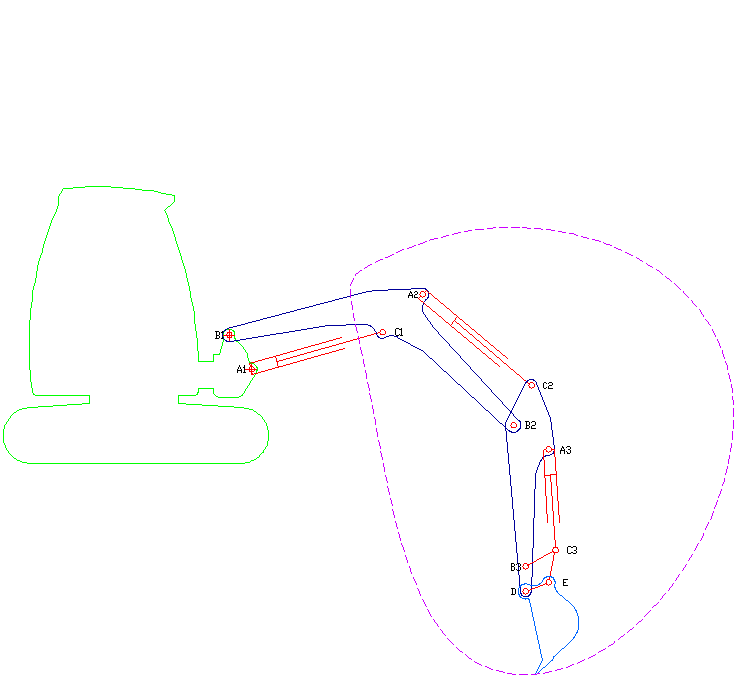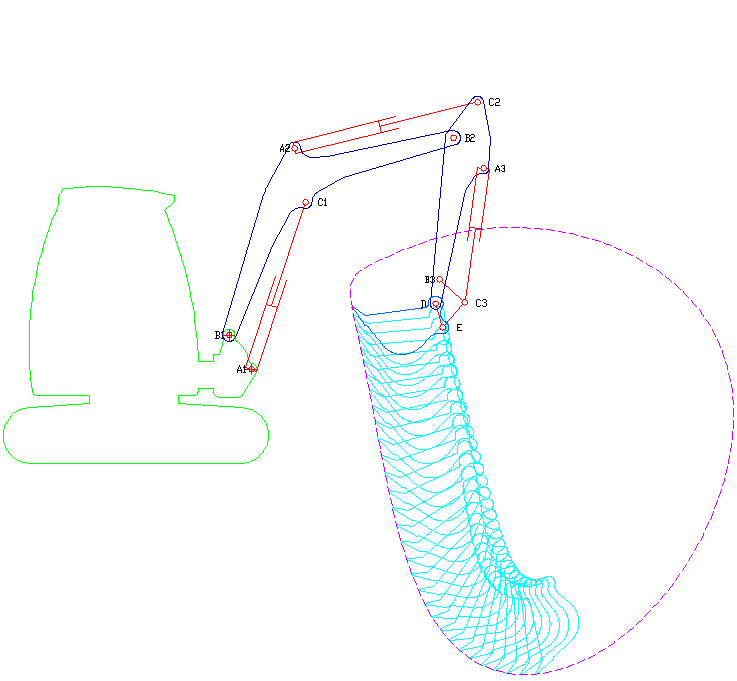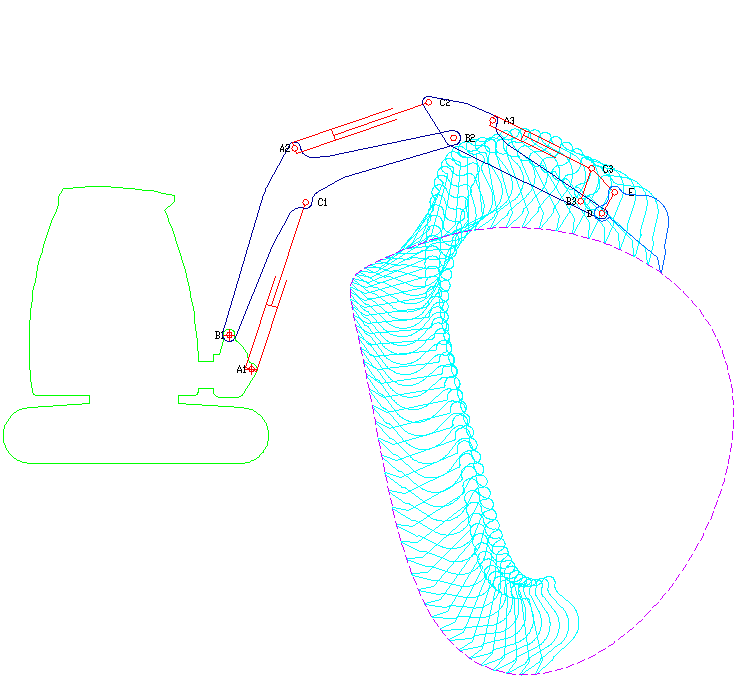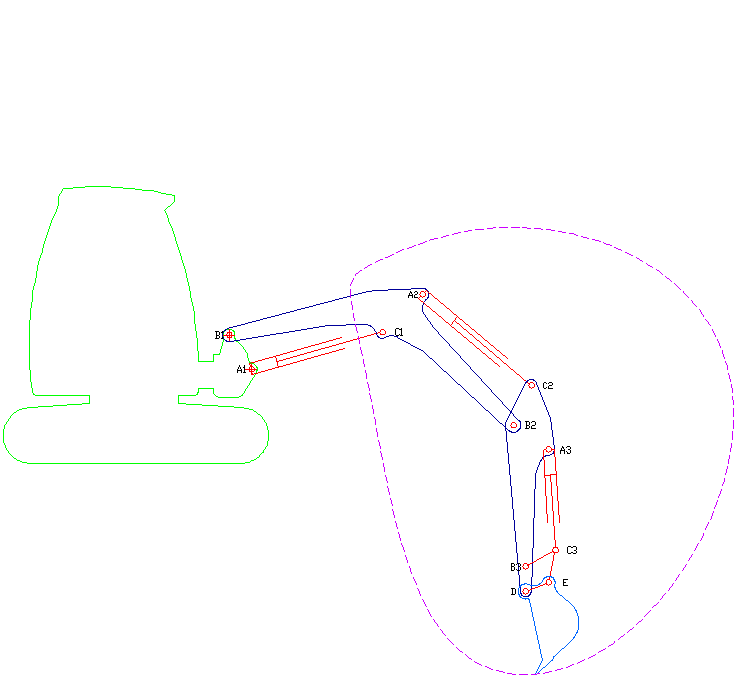
Excavator
Excavators are heavy equipment (construction), heavy construction equipment primarily consisting of a backhoe, boom, dipper (or stick), Bucket (machine part), bucket, and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The modern excavator's house sits atop an undercarriage with Caterpillar track, tracks or wheels, being an evolution of the steam shovel (which itself evolved into the power shovel when steam was replaced by diesel and electric power). All excavation-related movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors, which replaced winches, chains, and steel ropes. Another principle change was the direction of the digging action, with modern excavators pulling their buckets toward them like a dragline rather than pushing them away to fill them the way the first powered shovels did. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, scoopers, mechanical shovels, or 360-degree ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watching Brief
In British archaeology a watching brief is a method of preserving archaeological remains by record in the face of development threat. An archaeologist is employed by the developer to monitor the excavation of foundation and service trenches, landscaping and any other intrusive work the developer undertakes to give the archaeologist sufficient time to identify and record any archaeological finds and features; however, the arrangement is rarely satisfactory for either party. It is both intellectually and physically difficult to identify archaeological features in narrow foundation trenches and the potential delay to a project can also be difficult for a developer to incorporate into a development programme. Prior evaluation through trial trenching can overcome these problems by having the archaeology examined and removed or preserved before groundworks commence. Defined by the Chartered Institute for Archaeologists (CIfA) as: “…a formal programme of observation and investigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppergate Shopping Centre
Coppergate Shopping Centre is a shopping centre in York in North Yorkshire, England. It is named after Coppergate, one of York's medieval streets ("gate" coming from the Old Norse ''gata'', or street). The Coppergate Centre is home to York's Brollywalk from around April to November each year, with a new display of umbrellas installed each month the length of Coppergate Walk. The first Brollywalk was installed in August 2017, and themes have included rainbow umbrellas for York Pride, floral umbrellas, Union Jack umbrellas, brollies with ribbons and many more, making this street a favourite for Instagrammers. Each October, the umbrellas are replaced with broomsticks and ghosts. History Prior to the development of the shopping centre, archaeologists started digging on the site, which had been the Cravens confectionery factory. Between 1976–81, York Archaeological Trust unearthed remains of 10th-century Viking-age buildings from the Viking city of Jorvik. The remains lay in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |