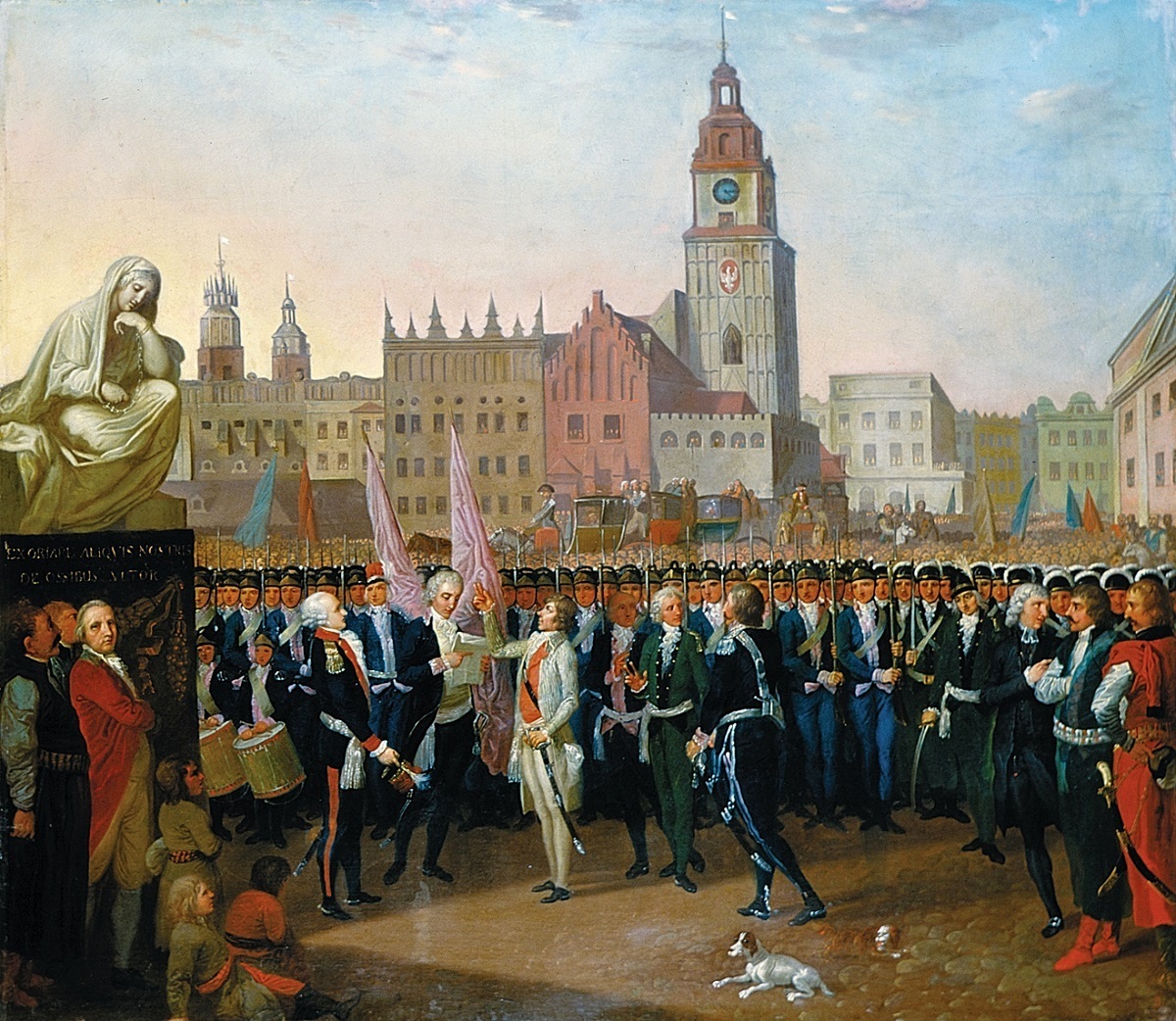|
Copper-Roof Palace
The Copper-Roof Palace ( pl, pałac Pod Blachą) is an 18th-century palace in Warsaw, Poland. It takes its name (which is less precisely phrased in the original Polish) from the copper roof, a rarity in the first half of the 18th century. Since 1989 the palace has been a branch of the Royal Castle Museum. The palace is contiguous with Warsaw's Royal Castle, and down a slope from Castle Square and Warsaw's Old Town. Beneath the palace, a 17th-century lodge still exists. History The original patrician house of Wawrzyniec Reffus was built in 1651–1656. After its 1657 destruction by the army of George II Rákóczi, it was completely remodeled in 1698–1701 for Jerzy Dominik Lubomirski. Lubomirski built on a southern wing, perpendicular to the rest of the structure, and expanded the western elevation. Soon after, the palace came to be called ''Palais Martin'' after Lubomirski's grandson. In 1720 the palace was rebuilt with the addition of a second, northern wing; and the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those simply content to believe they were living in an unprecedented "G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebuilt Buildings And Structures In Poland
''Rebuilt'' is the second and final studio album by the American girl group Girlicious. The album was released on November 22, 2010, by Universal Music Canada. The album draws from the dance-pop genre while infusing hints of R&B. Production initially started in 2009, after former member Tiffanie Anderson parted citing personal differences between the girls. The album has sparked four singles and one promotional single; The first being, "Over You" which was released on January 5, 2010. The song reached number fifty-two on the Canadian Hot 100. "Maniac" was released on April 6, 2010 as the album's second single. The song peaked lower than its previous single reaching number seventy-four. "Drank" was released on July 20, 2010 to Canada and to the United States as a promotional song for "Rebuilt" as well as being included on ''Jersey Shore''s album soundtrack. The album's third single entitled "2 In The Morning" reached a peak of thirty-five giving the group their highest-charting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rococo Architecture In Warsaw
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and ''trompe-l'œil'' frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement. The Rococo style began in France in the 1730s as a reaction against the more formal and geometric Louis XIV style. It was known as the "style Rocaille", or "Rocaille style". It soon spread to other parts of Europe, particularly northern Italy, Austria, southern Germany, Central Europe and Russia. It also came to influence the other arts, particularly sculpture, furniture, silverware, glassware, painting, music, and theatre. Although originally a secular style primarily used for interiors of private residences, the Rococo had a spiritual aspect to it which led to its widespread use i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaces In Warsaw
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which housed the Imperial residences. Most European languages have a version of the term (''palais'', ''palazzo'', ''palacio'', etc.), and many use it for a wider range of buildings than English. In many parts of Europe, the equivalent term is also applied to large private houses in cities, especially of the aristocracy; often the term for a large country house is different. Many historic palaces are now put to other uses such as parliaments, museums, hotels, or office buildings. The word is also sometimes used to describe a lavishly ornate building used for public entertainment or exhibitions such as a movie palace. A palace is distinguished from a castle while the latter clearly is fortified or has the style of a fortification, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses Completed In 1730
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library At The Royal Castle, Warsaw
The Royal Library in Warsaw (Polish: ''Biblioteka Królewska w Warszawie'') is a large building adjacent to the Royal Castle in Warsaw, Poland. It was built between 1779 and 1783 according to design of Dominik Merlini and Jan Chrystian Kamsetzer in order to accommodate the royal collection of books belonging to King Stanisław August Poniatowski, the last King of sovereign Poland. The Library is an elongated building of total dimensions 56 x 9 m, with 15 windows along the entrance hall, and a terrace at the top. The library initially held about 7,500 items, which grew to about 20,000 volumes in 1795. After the King's death in 1798 the whole collection was sold to Tadeusz Czacki, who bequeathed it to the Liceum Krzemienieckie. Following the collapse of the 1830 November Uprising against the Russian occupation, by order of Tsar Nicholas I of Russia, the library was seized and transported to Kiev where it formed the brand new University Library.Agnieszka Kania, Monika BryzekLibra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Royal Castle In Warsaw
The Royal Castle in Warsaw was a seat of the Sejm and Senate of the first Rzeczpospolita and also an official residence of the monarchs in Warsaw. It contained the offices of a number of political institutions, arranged around a central courtyard. The castle is a symbol of Polish statehood and history. Its origins date back almost seven centuries and the design of its present structure has evolved in stages since the fourteenth century. (The actual structure is a mid-20th-century reconstruction of the original castle, which was mostly demolished by German occupiers during World War II.) Castle in the Middle Ages In the 1339 the Papal Legate in Warsaw heard a case brought by the King of Poland, Kazimierz the Great, against the German Teutonic Order. He claimed that they had illegally seized a slice of Polish territory — Pomerania and the Kujawy region. The documents in this case are the earliest written testimony to the existence of Warsaw. At that time a fortified town su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriental Rug
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in " Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export. Oriental carpets can be pile woven or flat woven without pile, using various materials such as silk, wool, and cotton. Examples range in size from pillows to large, room-sized carpets, and include carrier bags, floor coverings, decorations for animals, Islamic prayer rugs ('Jai'namaz'), Jewish Torah ark covers ('' parochet''), and Christian altar covers. Since the High Middle Ages, oriental rugs have been an integral part of their cultures of origin, as well as of the European and, later on, the North American culture. Geographically, oriental rugs are made in an area referred to as the “Rug Belt”, which stretches from Morocco across North Africa, the Middle East, and into Central Asia and northern India. It includes countries such as northern China, Tibet, Turkey, Iran, the Maghreb in the west, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardo Bellotto
Bernardo Bellotto (c. 1721/2 or 30 January 172117 November 1780), was an Italian urban landscape painter or ''vedutista'', and printmaker in etching famous for his ''vedute'' of European cities – Dresden, Vienna, Turin, and Warsaw. He was the student and nephew of the renowned Giovanni Antonio Canal Canaletto and sometimes used the latter's illustrious name, signing himself as Bernardo Canaletto. In Germany and Poland, Bellotto called himself by his uncle's name, Canaletto. This caused some confusion, however Bellotto’s work is more sombre in color than Canaletto's and his depiction of clouds and shadows brings him closer to Dutch painting. Bellotto's style was characterized by elaborate representation of architectural and natural vistas, and by the specific quality of each place's lighting. It is plausible that Bellotto, and other Venetian masters of '' vedute'', may have used the camera obscura in order to achieve superior precision of urban views. Life Bellotto was bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Partition Of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polish–Lithuanian national sovereignty until 1918. The partition was the result of the Kościuszko Uprising and was followed by a number of Polish uprisings during the period. Background Following the First Partition of Poland in 1772, in an attempt to strengthen the significantly weakened Commonwealth, King Stanisław August Poniatowski put into effect a series of reforms to enhance Poland's military, political system, economy, and society. These reforms reached their climax with the enactment of the May Constitution in 1791, which established a constitutional monarchy with separation into three branches of government, strengthened the bourgeoisie and abolished many of the nobility's privileges as well as many of the old laws of serfd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1866 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." In Frederick the Great and the Rise of Prussia, 9–10. 3rd ed. Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |