 |
Copolymers
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Graft Polymer
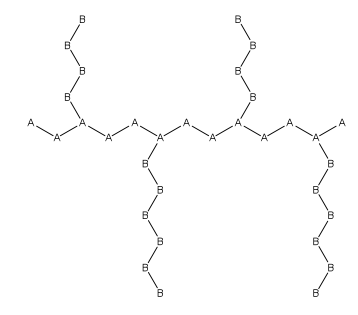
In polymer chemistry, graft polymers are segmented copolymers with a linear backbone of one composite and randomly distributed branches of another composite. The picture labeled "graft polymer" shows how grafted chains of species B are covalently bonded to polymer species A. Although the side chains are structurally distinct from the main chain, the individual grafted chains may be homopolymers or copolymers. Graft polymers have been synthesized for many decades and are especially used as impact resistant materials, thermoplastic elastomers, compatibilizers, or emulsifiers for the preparation of stable blends or alloys. One of the better-known examples of a graft polymer is a component used in high impact polystyrene, consisting of a polystyrene backbone with polybutadiene grafted chains. General properties Graft copolymers are a branched copolymer where the components of the side chain are structurally different than that of the main chain. Graft copolymers containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compound (chemistry), compounds, produces unique physical property, physical properties including toughness, high rubber elasticity, elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form Amorphous solid, amorphous and crystallization of polymers, semicrystalline structures rath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Ethylene-vinyl Acetate
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), also known as poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) (PEVA), is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. The weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 50%, with the remainder being ethylene. There are three different types of EVA copolymer, which differ in the vinyl acetate (VA) content and the way the materials are used. The EVA copolymer which is based on a low proportion of VA (approximately up to 4%) may be referred to as vinyl acetate modified polyethylene. It is a copolymer and is processed as a thermoplastic material – just like low-density polyethylene. It has some of the properties of a low-density polyethylene but increased gloss (useful for film), softness and flexibility. The material is generally considered non-toxic. The EVA copolymer which is based on a medium proportion of VA (approximately 4 to 30%) is referred to as thermoplastic ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer and is a thermoplastic elastomer material. It is not vulca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Chain-growth Polymerization
Chain-growth polymerization (American English, AE) or chain-growth polymerisation (British English, BE) is a polymerization technique where monomer molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. There are a limited number of these active sites at any moment during the polymerization which gives this method its key characteristics. Chain-growth polymerization involves 3 types of reactions : # Initiation: An active species I* is formed by some decomposition of an initiator molecule I # Propagation: The initiator fragment reacts with a monomer M to begin the conversion to the polymer; the center of activity is retained in the adduct. Monomers continue to add in the same way until polymers Pi* are formed with the degree of polymerization i # Termination: By some reaction generally involving two polymers containing active centers, the growth center is deactivated, resulting in dead polymer Introduction In 1953, Paul Flory first classified polymeriza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' ) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point. ABS is a terpolymer made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. The proportions can vary from 15% to 35% acrylonitrile, 5% to 30% butadiene and 40% to 60% styrene. The result is a long chain of polybutadiene crisscrossed with shorter chains of poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile). The nitrile groups from neighboring chains, being polar, attract each other and bind the chains together, making ABS stronger than pure polystyrene. The acrylonitrile also contributes chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, hardness, and rigidity, while increasing the heat deflection temperature. The styrene gives the plastic a shiny, impervious surface, as well as hardness, rigidity, and improved processing ease. The polybutad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Mayo–Lewis Equation
The Mayo–Lewis equation or copolymer equation in polymer chemistry describes the distribution of monomers in a copolymer. It was proposed by Frank R. Mayo and Frederick M. Lewis.''Copolymerization. I. A Basis for Comparing the Behavior of Monomers in Copolymerization; The Copolymerization of Styrene and Methyl Methacrylate'' Frank R. Mayo and Frederick M. Lewis J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1944; 66(9) pp 1594 - 1601; The equation considers a monomer mix of two components M_1\, and M_2\, and the four different reactions that can take place at the reactive chain end terminating in either monomer (M_1^*\, and M_2^*\,) with their reaction rate constants k\,: :M_1^* + M_1 \xrightarrow M_1M_1^* \, :M_1^* + M_2 \xrightarrow M_1M_2^* \, :M_2^* + M_2 \xrightarrow M_2M_2^* \, :M_2^* + M_1 \xrightarrow M_2M_1^* \, The reactivity ratio for each propagating chain end is defined as the ratio of the rate constant for addition of a monomer of the species already at the chain end to the rate constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Monomer
A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. By type: * natural vs synthetic, e.g. glycine vs caprolactam, respectively * polar vs nonpolar, e.g. vinyl acetate vs ethylene, respectively * cyclic vs linear, e.g. ethylene oxide vs ethylene glycol, respectively By type of polymer they form: * those that participate in condensation polymerization * those that participate in addition polymerization Differing stoichiometry causes each class to create its respective form of polymer. : The polymerization of one kind of monomer gives a homopolymer. Many polymers are copolymers, meaning that they are derived from two different monomers. In the case of condensation polymerizations, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |