|
Copier
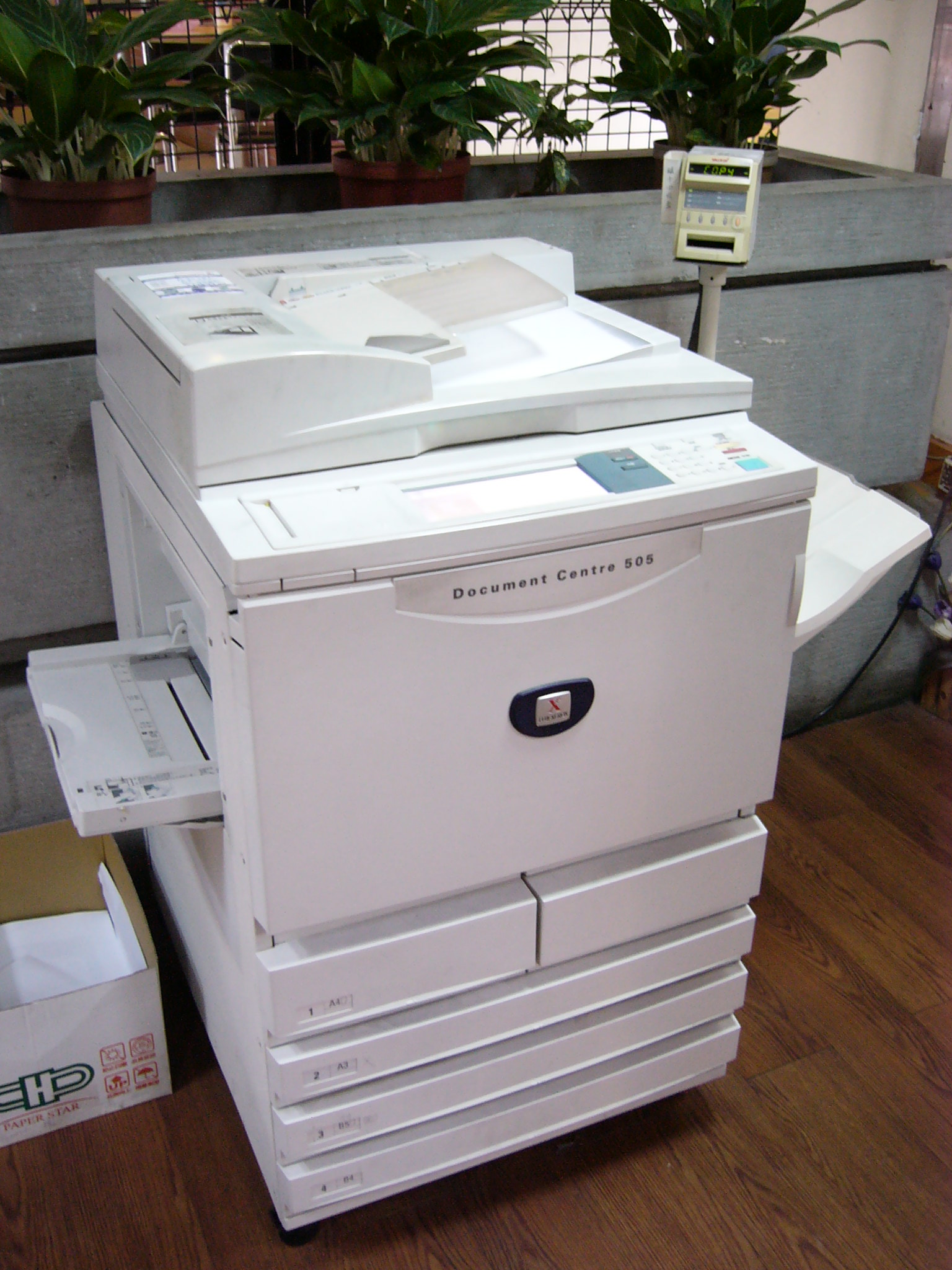
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called ''xerography'', a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles (a powder) onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Commercial xerographic office photocopying gradually replaced copies made by verifax, photostat, carbon paper, mimeograph machines, and other duplicating machines. Photocopying is widely used in the business, education, and government sectors. While there have been predictions that photocopiers will eventually become obsolete as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
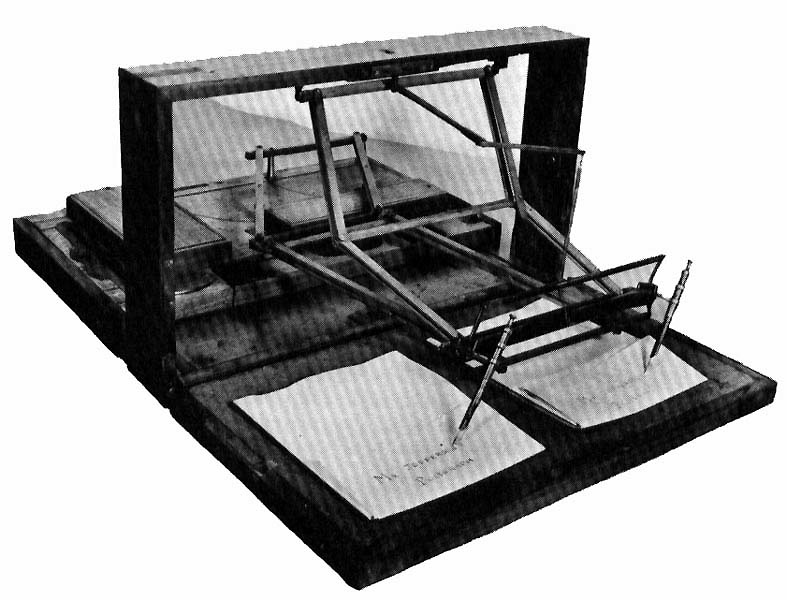
Duplicating Machines
Duplicating machines were the predecessors of modern document-reproduction technology. They have now been replaced by digital duplicators, image scanner, scanners, laser printers, and photocopiers, but for many years they were the primary means of reproducing documents for limited-run distribution. The duplicator was pioneered by Thomas Edison and David Gestetner, with Gestetner dominating the market up until the late 1990s. Like the typewriter, these machines were products of the second phase of the Industrial Revolution which started near the end of the 19th century (also called the Second Industrial Revolution). This second phase brought to mass markets technologies like the small electric motors and the products of industrial chemistry without which the duplicating machines would not have been economical. By bringing greatly increased quantities of paperwork to daily life, the duplicating machine and the typewriter gradually changed the forms of the office desk and transforme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerography
Xerography is a dry photocopying technique. Originally called electrophotography, it was renamed xerography—from the Greek roots , meaning "dry" and , meaning "writing"—to emphasize that unlike reproduction techniques then in use such as cyanotype, the process of xerography used no liquid chemicals. History Xerography was invented by American physicist Chester Carlson, based significantly on contributions by Hungarian physicist Pál Selényi. Carlson applied for and was awarded on October 6, 1942. Carlson's innovation combined electrostatic printing with photography, unlike the dry electrostatic printing process invented by Georg Christoph Lichtenberg in 1778. Carlson's original process was cumbersome, requiring several manual processing steps with flat plates. In 1946, Carlson signed an agreement with Haloid Photographic Company to develop it as a commercial product. Before that year, Carlson had proposed his idea to more than a dozen companies, but none was int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester Carlson
Chester Floyd Carlson (February 8, 1906 – September 19, 1968) was an American physicist, inventor, and patent attorney born in Seattle, Washington. Carlson invented electrophotography (now xerography, meaning "dry writing"), producing a dry copy in contrast to the wet copies then produced by the Photostat process; it is now used by millions of photocopiers worldwide. Early life Carlson's father, Olaf Adolph Carlson, had little formal education, but was described as "brilliant" by a relative. Carlson wrote of his mother, Ellen, that she "was looked up to by her sisters as one of the wisest." When Carlson was an infant, his father contracted tuberculosis, and also later suffered from arthritis of the spine (a common, age-related disease). When Olaf moved the family to Mexico for a seven-month period in 1910, in hopes of gaining riches through what Carlson described as "a crazy American land colonization scheme," Ellen contracted malaria. Because of his parents' illnesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
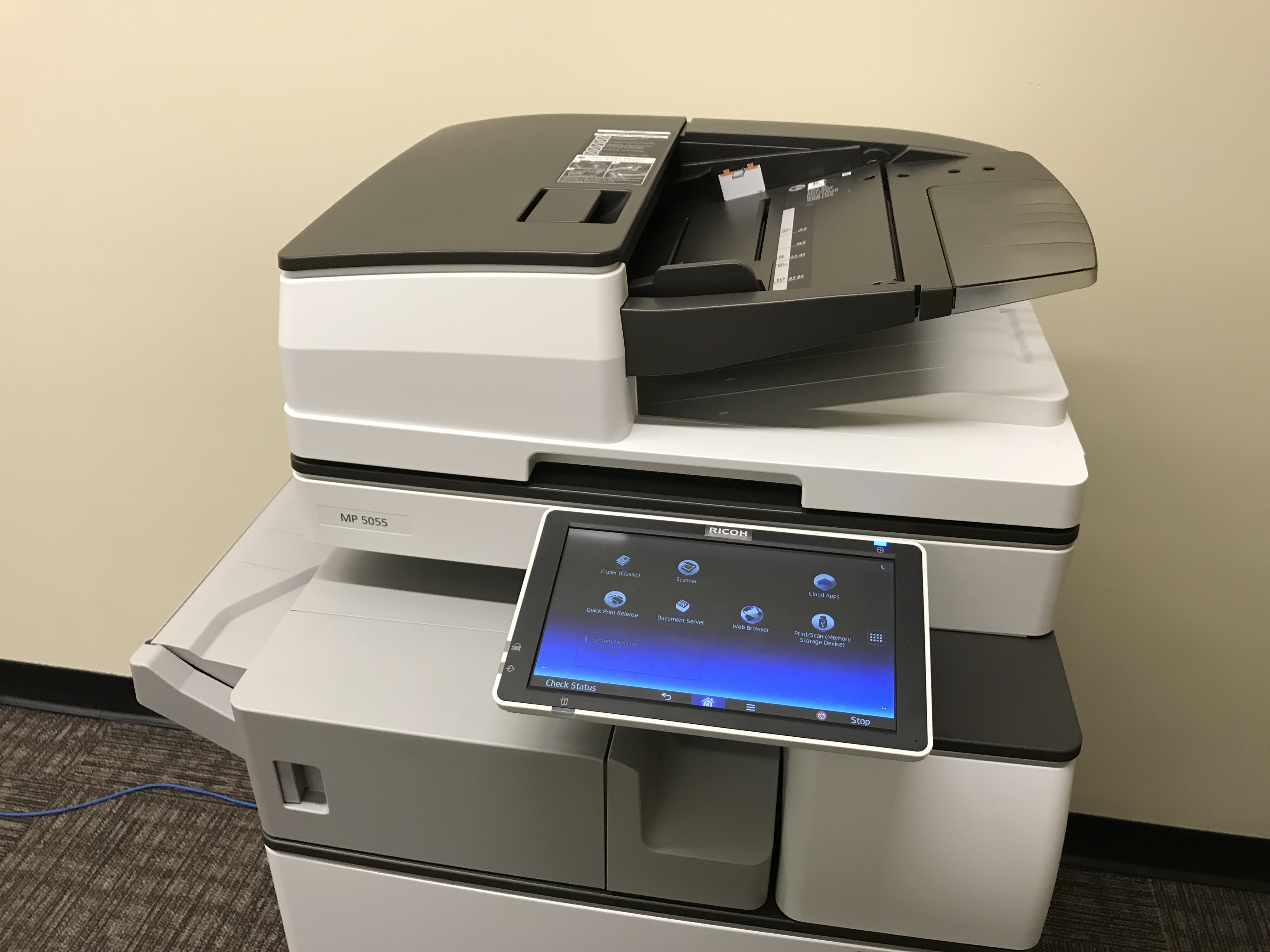
Multi-function Printer
An MFP (multi-function product/printer/peripheral), multi-functional, all-in-one (AIO), or multi-function device (MFD), is an office machine which incorporates the functionality of multiple devices in one, so as to have a smaller footprint in a home or small business setting (the Small office/home office, SOHO market segment), or to provide centralized document management/distribution/production in a large-office setting. A typical MFP may act as a combination of some or all of the following devices: email, fax, photocopier, Printer (computing), printer, Image scanner, scanner. Types of MFPs MFP manufacturers traditionally divided MFPs into various segments. The segments roughly divided the MFPs according to their speed in pages-per-minute (ppm) and duty-cycle/robustness. However, many manufacturers are beginning to avoid the segment definition for their products, as speed and basic functionality alone do not always differentiate the many features that the devices includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toner (printing)
Toner is a Powder (substance), powder mixture used in laser printers and photocopiers to form the text and images on paper, in general through a toner cartridge. Mostly granulated plastic, early mixtures added only carbon powder and iron oxide; now there are mixtures that contain polypropylene, fumed silica, and various minerals for triboelectrification. Toner using plant-derived plastic also exists as an alternative to petroleum plastic. Toner particles are melted by the heat of the Laser Printer#Fusing, fuser, and are thus bonded to the paper. In earlier photocopiers, this low-cost carbon toner was poured by the user from a bottle into a reservoir in the machine. Later copiers, and laser printers from the first 1984 Hewlett-Packard LaserJet#1980s, Hewlett-Packard LaserJet, feed directly from a sealed toner cartridge. Laser toner cartridges for use in color copiers and printers come in sets of cyan, magenta, yellow and black (CMYK), allowing a very large Gamut, color gamut to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photostat
The Photostat machine, or Photostat, was an early Photocopying, projection photocopier created in the 1900s (decade), decade of the 1900s by the Commercial Camera Company, which became the Photostat Corporation. The "Photostat" name, which was originally a trademark of the company, became generic trademark, genericized, and was often used to refer to similar machines produced by the RetinalGraph Company or to wikt:photostat#Noun, any copy made by any such machine. History Background The growth of business during the Industrial Revolution created the need for a more efficient means of transcription than hand copying. Carbon paper was first used in the early 19th century. By the late 1840s copying presses were used to copy outgoing correspondence. One by one, List of duplicating processes, other methods appeared. These included the "manifold writer", developed from Christoph Scheiner's pantograph and used by Mark Twain; copying baths; copying books; and roller copiers. Among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimeograph Machine
A mimeograph machine (often abbreviated to mimeo, sometimes called a stencil duplicator or stencil machine) is a low-cost duplicating machines, duplicating machine that works by forcing ink through a stencil onto paper. The process is called mimeography, and a copy made by the process is a mimeograph. Mimeographs, along with spirit duplicators and hectographs, were common technologies for printing small quantities of a document, as in office work, classroom materials, and church bulletins. For even smaller quantities, up to about five, a typewriter, typist would use carbon paper. Early fanzines were printed by mimeograph because the machines and supplies were widely available and inexpensive. Beginning in the late 1960s and continuing into the 1970s, photocopying gradually displaced mimeographs, spirit duplicators, and hectographs. Origins Use of stencils is an ancient art, butthrough chemistry, papers, and pressestechniques advanced rapidly in the late nineteenth century: P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Scanner
An image scanner (often abbreviated to just scanner) is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object and converts it to a digital image. The most common type of scanner used in the home and the office is the flatbed scanner, where the document is placed on a glass bed. A sheetfed scanner, which moves the page across an image sensor using a series of rollers, may be used to scan one page of a document at a time or multiple pages, as in an automatic document feeder. A handheld scanner is a portable version of an image scanner that can be used on any flat surface. Scans are typically downloaded to the computer that the scanner is connected to, although some scanners are able to store scans on standalone Flash memory, flash media (e.g., memory cards and USB flash drive, USB drives). Modern scanners typically use a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a contact image sensor (CIS) as the image sensor, whereas drum scanners, developed earlier and still used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printer (computing)
A printer is a peripheral machine which makes a durable representation of graphics or text, usually on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers. Different types of printers include 3D printers, inkjet printers, laser printers, and thermal printers. History The first computer printer designed was a mechanically driven apparatus by Charles Babbage for his difference engine in the 19th century; however, his mechanical printer design was not built until 2000. He also had plans for a curve plotter, which would have been the first computer graphics printer if it was built. The first patented printing mechanism for applying a marking medium to a recording medium or more particularly an electrostatic inking apparatus and a method for electrostatically depositing ink on controlled areas of a receiving medium, was in 1962 by C. R. Winston, Teletype Corporation, using continuous inkjet printing. The ink was a red sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verifax Copier
The Kodak verifax is a photo copying approach that uses a wet colloidal diffusion transfer technique patented by Yutzy, H.C. and Yackel, E.C. (1947) The light source is projected to the top crossing the negative being reflected -more or less, according to the color- against the original to be copied exposing the negative. Has a base that contains the recipient with the liquid developer and the exposure timer. Due to its extreme simplicity, the method was commonplace until the late 1960s, when it was surpassed by the popularity of the xerocopies using plain paper. Copies had some chemical smell and lost contrast over time. Diffusion transfer The DT (Diffusion transfer) was widespread in several countries since 1960: * CopyRapid Agfa; * Gevacopy of Gevaert (1950); * Verifax Kodak (1952-1976); * Copyproof (1980?); Other products not specifically intended for copying, but employing a similar PMT technology include: Kodak Ektaflex (1981); Polaroid, sepia (1948), id, White Black (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |