|
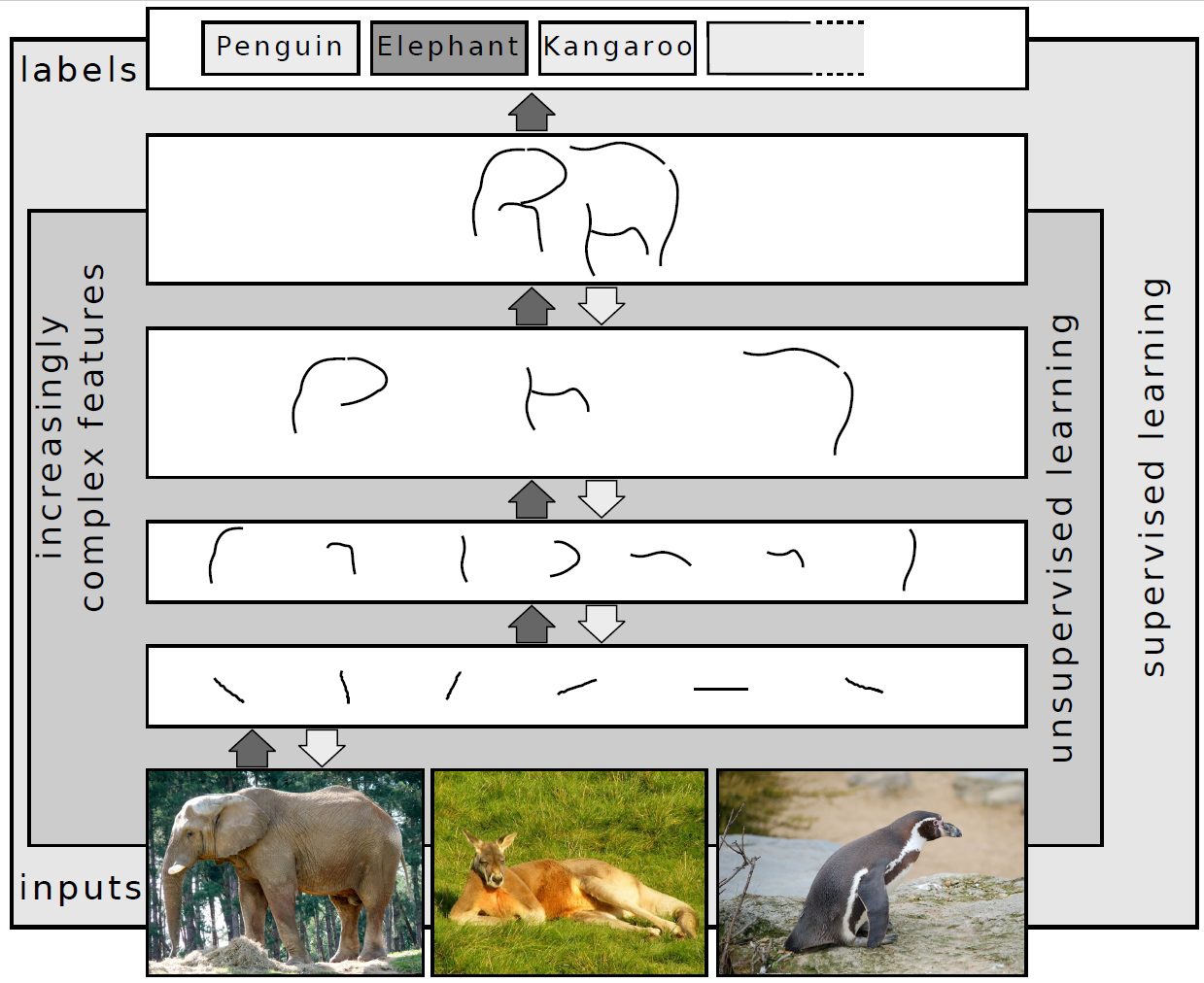
Convolutional Deep Belief Network
In computer science, a convolutional deep belief network (CDBN) is a type of deep artificial neural network composed of multiple layers of convolutional restricted Boltzmann machines stacked together. Alternatively, it is a hierarchical generative model for deep learning, which is highly effective in image processing and object recognition, though it has been used in other domains too. The salient features of the model include the fact that it scales well to high-dimensional images and is translation-invariant.{{cite web, last=Coviello, first=Emanuele, title=Convolutional Deep Belief Networks, url=http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~dasgupta/254-deep/emanuele.pdf CDBNs use the technique of probabilistic max-pooling to reduce the dimensions in higher layers in the network. Training of the network involves a pre-training stage accomplished in a greedy layer-wise manner, similar to other deep belief networks. Depending on whether the network is to be used for discrimination or generative tasks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software). Computer science is generally considered an area of academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of repositories ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be Supervised learning, supervised, Semi-supervised learning, semi-supervised or Unsupervised learning, unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as #Deep_neural_networks, deep neural networks, deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformer (machine learning model), Transformers have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, Climatology, climate science, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
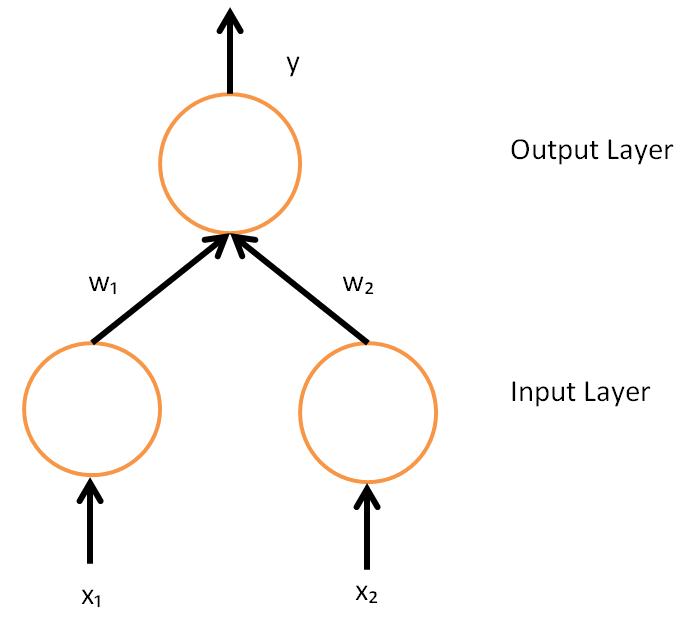
Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a ''weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolutional Neural Network
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of artificial neural network (ANN), most commonly applied to analyze visual imagery. CNNs are also known as Shift Invariant or Space Invariant Artificial Neural Networks (SIANN), based on the shared-weight architecture of the convolution kernels or filters that slide along input features and provide translation- equivariant responses known as feature maps. Counter-intuitively, most convolutional neural networks are not invariant to translation, due to the downsampling operation they apply to the input. They have applications in image and video recognition, recommender systems, image classification, image segmentation, medical image analysis, natural language processing, brain–computer interfaces, and financial time series. CNNs are regularized versions of multilayer perceptrons. Multilayer perceptrons usually mean fully connected networks, that is, each neuron in one layer is connected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restricted Boltzmann Machine
A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is a generative stochastic artificial neural network that can learn a probability distribution over its set of inputs. RBMs were initially invented under the name Harmonium by Paul Smolensky in 1986, and rose to prominence after Geoffrey Hinton and collaborators invented fast learning algorithms for them in the mid-2000. RBMs have found applications in dimensionality reduction, classification, collaborative filtering, feature learning, topic modellingRuslan Salakhutdinov and Geoffrey Hinton (2010)Replicated softmax: an undirected topic model ''Neural Information Processing Systems'' 23. and even many body quantum mechanics. They can be trained in either supervised or unsupervised ways, depending on the task. As their name implies, RBMs are a variant of Boltzmann machines, with the restriction that their neurons must form a bipartite graph: a pair of nodes from each of the two groups of units (commonly referred to as the "visible" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Model
In statistical classification, two main approaches are called the generative approach and the discriminative approach. These compute classifiers by different approaches, differing in the degree of statistical modelling. Terminology is inconsistent, but three major types can be distinguished, following : # A generative model is a statistical model of the joint probability distribution P(X, Y) on given observable variable ''X'' and target variable ''Y'';: "Generative classifiers learn a model of the joint probability, p(x, y), of the inputs ''x'' and the label ''y'', and make their predictions by using Bayes rules to calculate p(y\mid x), and then picking the most likely label ''y''. # A discriminative model is a model of the conditional probability P(Y\mid X = x) of the target ''Y'', given an observation ''x''; and # Classifiers computed without using a probability model are also referred to loosely as "discriminative". The distinction between these last two classes is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three- dimensional, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Recognition
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different view points, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades. Approaches based on CAD-like object models * Edge detection * Primal sketch * Marr, Mohan and Nevatia * Lowe * Olivier Faugeras Recognition by parts * Generalized cylinders (Thomas Binford) * Geons (Irving Biederman) * Dickinson, Forsyth and Ponce Appearance-based methods * Use example images (called templates or exemplars) of the objects to perform recognition * Objects look different u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greedy Algorithm
A greedy algorithm is any algorithm that follows the problem-solving heuristic of making the locally optimal choice at each stage. In many problems, a greedy strategy does not produce an optimal solution, but a greedy heuristic can yield locally optimal solutions that approximate a globally optimal solution in a reasonable amount of time. For example, a greedy strategy for the travelling salesman problem (which is of high computational complexity) is the following heuristic: "At each step of the journey, visit the nearest unvisited city." This heuristic does not intend to find the best solution, but it terminates in a reasonable number of steps; finding an optimal solution to such a complex problem typically requires unreasonably many steps. In mathematical optimization, greedy algorithms optimally solve combinatorial problems having the properties of matroids and give constant-factor approximations to optimization problems with the submodular structure. Specifics Greedy algo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Belief Network
In machine learning, a deep belief network (DBN) is a generative graphical model, or alternatively a class of deep neural network, composed of multiple layers of latent variables ("hidden units"), with connections between the layers but not between units within each layer. When trained on a set of examples without supervision, a DBN can learn to probabilistically reconstruct its inputs. The layers then act as feature detectors. After this learning step, a DBN can be further trained with supervision to perform classification. DBNs can be viewed as a composition of simple, unsupervised networks such as restricted Boltzmann machines (RBMs) or autoencoders, where each sub-network's hidden layer serves as the visible layer for the next. An RBM is an undirected, generative energy-based model with a "visible" input layer and a hidden layer and connections between but not within layers. This composition leads to a fast, layer-by-layer unsupervised training procedure, where contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backpropogation
In machine learning, backpropagation (backprop, BP) is a widely used algorithm for training feedforward artificial neural networks. Generalizations of backpropagation exist for other artificial neural networks (ANNs), and for functions generally. These classes of algorithms are all referred to generically as "backpropagation". In fitting a neural network, backpropagation computes the gradient of the loss function with respect to the weights of the network for a single input–output example, and does so efficiently, unlike a naive direct computation of the gradient with respect to each weight individually. This efficiency makes it feasible to use gradient methods for training multilayer networks, updating weights to minimize loss; gradient descent, or variants such as stochastic gradient descent, are commonly used. The backpropagation algorithm works by computing the gradient of the loss function with respect to each weight by the chain rule, computing the gradient one laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a '' weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |