|
Context Sensitive User Interface
A context-sensitive user interface offers the user options based on the state of the active program. Context sensitivity is ubiquitous in current graphical user interfaces, often in context menus. A user-interface may also provide context sensitive feedback, such as changing the appearance of the mouse pointer or cursor, changing the menu color, or with auditory or tactile feedback. Reasoning and advantages of context sensitivity The primary reason for introducing context sensitivity is to simplify the user interface. Advantages include: * Reduced number of commands required to be known to the user for a given level of productivity. * Reduced number of clicks or keystrokes required to carry out a given operation. * Allows consistent behaviour to be pre-programmed or altered by the user. * Reduces the number of options needed on screen at one time. Disadvantages Context sensitive actions may be perceived as dumbing down of the user interface, leaving the operator at a loss as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based user interface, text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation interface, direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and Distributed control system, industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Quick Time Event
In video games, a quick time event (QTE) is a method of context-sensitive gameplay in which the player performs actions on the control device shortly after the appearance of an on-screen instruction/prompt. It allows for limited control of the game character during cut scenes or cinematic sequences in the game. Performing the wrong prompt, mistiming the action, or not performing any action at all results in the character's failure at their task, resulting in a death/failure animation and often an immediate game over or the loss of a life, with some games providing a lesser but significant penalty of sorts instead. The term "quick time event" is attributed to Yu Suzuki, director of the game ''Shenmue'' which used the QTE feature (then called "quick timer events") to a great degree. They allow for the game designer to create sequences of actions that cannot be expressed through the game's standard control scheme, or to constrain the player into taking only one specific action at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ergonomics
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of Psychology, psychological and Physiology, physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goals of human factors engineering are to reduce human error, increase productivity and system availability, and enhance safety, health and comfort with a specific focus on the interaction between the human and equipment. The field is a combination of numerous disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, anthropometry, interaction design, visual design, user experience, and user interface design. Human factors research employs methods and approaches from these and other knowledge disciplines to study human behavior and generate data relevant to previously stated goals. In studying and sharing learning on the design of equipment, devices, and processes that fit the human body and its Cog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Human–computer Interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and computers. HCI researchers observe the ways humans interact with computers and design technologies that allow humans to interact with computers in novel ways. These include visual, auditory, and tactile (haptic) feedback systems, which serve as channels for interaction in both traditional interfaces and mobile computing contexts. A device that allows interaction between human being and a computer is known as a "human–computer interface". As a field of research, human–computer interaction is situated at the intersection of computer science, behavioral sciences, design, media studies, and several other fields of study. The term was popularized by Stuart K. Card, Allen Newell, and Thomas P. Moran in their 1983 book, ''The Psychology of Hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its advertising platform, Yahoo Native. It is operated by the namesake company Yahoo! Inc. (2017–present), Yahoo! Inc., which is 90% owned by Apollo Global Management and 10% by Verizon. Yahoo was established by Jerry Yang and David Filo in January 1994 and was one of the pioneers of the early Internet era in the 1990s. However, its use declined in the 2010s as some of its services were discontinued, and it lost market share to Facebook and Google. Etymology The word "yahoo" is a backronym for "Yet another, Yet Another Hierarchically Organized Oracle" or "Yet Another Hierarchical Officious Oracle". The term "hierarchical" described how the Yahoo database was arranged in layers of subcategories. The term "oracle" was intended to mean "sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Quick Time Event
In video games, a quick time event (QTE) is a method of context-sensitive gameplay in which the player performs actions on the control device shortly after the appearance of an on-screen instruction/prompt. It allows for limited control of the game character during cut scenes or cinematic sequences in the game. Performing the wrong prompt, mistiming the action, or not performing any action at all results in the character's failure at their task, resulting in a death/failure animation and often an immediate game over or the loss of a life, with some games providing a lesser but significant penalty of sorts instead. The term "quick time event" is attributed to Yu Suzuki, director of the game ''Shenmue'' which used the QTE feature (then called "quick timer events") to a great degree. They allow for the game designer to create sequences of actions that cannot be expressed through the game's standard control scheme, or to constrain the player into taking only one specific action at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Principle Of Least Astonishment
In user interface design and software design, the principle of least astonishment (POLA), also known as principle of least surprise, proposes that a component of a system should behave in a way that most users will expect it to behave, and therefore not astonish or surprise users. The following is a corollary of the principle: "If a necessary feature has a high astonishment factor, it may be necessary to redesign the feature." The principle has been in use in relation to computer interaction since at least the 1970s. Although first formalized in the field of computer technology, the principle can be applied broadly in other fields. For example, in writing, a cross-reference to another part of the work or a hyperlink should be phrased in a way that accurately tells the reader what to expect. Origin An early reference to the "Law of Least Astonishment" appeared in the PL/I Bulletin in 1967 (PL/I is a programming language released by IBM in 1966). By the late 1960s, PL/I had becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
DWIM
DWIM (do what I mean) computer systems attempt to anticipate what users intend to do, correcting trivial errors automatically rather than blindly executing users' explicit but potentially incorrect input. Software The term was coined by Warren Teitelman in his DWIM package for BBN Lisp, part of his PILOT system, sometime before 1966.Warren Teitelman, "PILOT: A Step towards Man-Computer Symbiosis", M.I.T. Ph.D. Dissertation, Project MAC MAC-TR-32, September 1966DTIC AD0638446 p. 51Warren Teitelman, "Toward a programming laboratory", in J. N. Buxton and , ''Software Engineering Techniques'', April 1970, a report on a conference sponsored by the NATO Science Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Context Awareness
Context awareness refers, in information and communication technologies, to a capability to take into account the ''situation'' of ''entities'', which may be users or devices, but are not limited to those. ''Location'' is only the most obvious element of this ''situation''. Narrowly defined for mobile devices, context awareness does thus generalize location awareness. Whereas location may determine how certain processes around a contributing device operate, context may be applied more flexibly with mobile users, especially with users of smart phones. Context awareness originated as a term from ubiquitous computing or as so-called pervasive computing which sought to deal with linking changes in the environment with computer systems, which are otherwise static. The term has also been applied to business theory in relation to contextual application design and business process management issues. Qualities of context Various categorizations of context have been proposed in the past. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Combo Box
A combo box is a commonly used graphical user interface A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ... widget (or control). Traditionally, it is a combination of a drop-down list or list box and a single-line editable Text box, textbox, allowing the user to either type a value directly or select a value from the list. The term "combo box" is sometimes used to mean "drop-down list". In both Java and .NET, "combo box" is ''not'' a synonym for "drop-down list". Definition of "drop down list" is sometimes clarified with terms such as "non-editable combo box" (or something similar) to distinguish it from "combo box". See also *Autocomplete *Drop-down list *List box *User interface References External linksList and Combo boxes for Microsoft Access {{Graphical control ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Autotype
Autotype is a function in some computer applications or programs, typically those containing forms, which fills in a field once you have typed in the first few letters. Most of the time, such as in a web browser, the entries that appear in the list depend on the form's name, so as to not propose street names in a last name field or vice versa. Background Autotype can also refer to automatically determining a peripheral's configuration or a program's variables. Autotype is defined as a "true representation of the original" (see O.E.D). The term autotype was coined in the late 19th century and referred to a process for making photographic prints using a carbon process. Many autotype prints were produced and the process was popular well into the 20th century, particularly since autotype prints are very long lasting (it is said that an autotype could last up to 500 years without fading). Autotype may also refer to halftone printing. The term may also apply to the Autotype Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
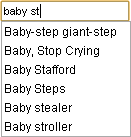 |
Autofill
Autocomplete, or word completion, is a feature in which an application software, application predicts the rest of a word a user is typing. In Android (operating system), Android and iOS smartphones, this is called predictive text. In graphical user interfaces, users can typically press the tab key to accept a suggestion or the down arrow key to accept one of several. Autocomplete speeds up human-computer interactions when it correctly predicts the word a user intends to enter after only a few characters have been typed into a text input field. It works best in domains with a limited number of possible words (such as in command line interpreters), when some words are much more common (such as when addressing an e-mail), or writing structured and predictable text (as in source code editors). Many autocomplete algorithms learn new words after the user has written them a few times, and can suggest alternatives based on the learned habits of the individual user. Definition Origina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |