|
Consumer Neuroscience
Consumer neuroscience is the combination of consumer research with modern neuroscience. The goal of the field is to find neural explanations for consumer behaviors in individuals both with or without disease. Consumer research Consumer research has existed for more than a century and has been well established as a combination of sociology, psychology, and anthropology, and popular topics in the field revolve around consumer decision-making, advertising, and brand management, branding. For decades, however, consumer researchers had never been able to directly record the internal mental processes that govern consumer behavior; they always were limited to designing experiments in which they alter the external conditions in order to view the ways in which changing variables may affect consumer behavior (examples include changing the packaging or changing a subject’s mood). With the integration of neuroscience with consumer research, it is possible to go directly into the brain to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Research
Marketing research is the systematic gathering, recording, and analysis of qualitative and quantitative data about issues relating to marketing products and services. The goal is to identify and assess how changing elements of the marketing mix impacts customer behavior. This involves employing a data-driven marketing approach to specify the data required to address these issues, then designing the method for collecting information and implementing the data collection process. After analyzing the collected data, these results and findings, including their implications, are forwarded to those empowered to act on them. Market research, marketing research, and marketing are a sequence of business activities; sometimes these are handled informally. The field of ''marketing research'' is much older than that of ''market research''. Although both involve consumers, ''Marketing'' research is concerned specifically with marketing processes, such as advertising effectiveness and salesf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotions
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is no scientific consensus on a definition. Emotions are often reciprocal determinism, intertwined with mood (psychology), mood, temperament, personality psychology, personality, disposition, or creativity. Research on emotion has increased over the past two decades, with many fields contributing, including psychology, medicine, history, sociology of emotions, computer science and philosophy. The numerous attempts to explain the origin, functional accounts of emotion, function, and other aspects of emotions have fostered intense research on this topic. Theorizing about the evolutionary origin and possible purpose of emotion dates back to Charles Darwin. Current areas of research include the neuroscience of emotion, using tools like positron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspense
Suspense is a state of anxiety or excitement caused by mysteriousness, uncertainty, doubt, or undecidedness. In a narrative work, suspense is the audience's excited anticipation about the plot or conflict (which may be heightened by a violent moment, stressful scene, puzzle, mystery, etc.), particularly as it affects a character for whom the audience feels sympathy. However, suspense is not exclusive to narratives. In narratives In literature, films, television, and plays, suspense is a major device for securing and maintaining interest. It may be of several major types: in one, the outcome is uncertain and the suspense resides in the question of ''who, what, or how''; in another, the outcome is inevitable from foregoing events, and the suspense resides in the audience's anxious or frightened anticipation in the question of ''when''. Readers feel suspense when they are deeply curious about ''what'' will happen next, or when they know what is likely to happen but do n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
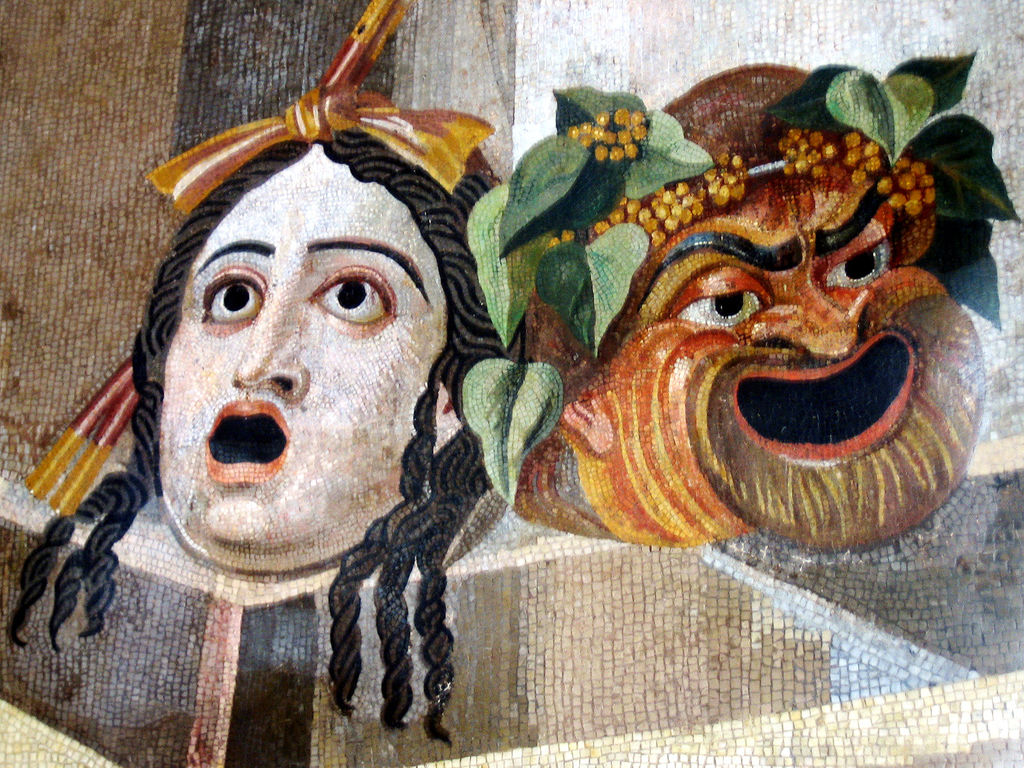
Drama
Drama is the specific Mode (literature), mode of fiction Mimesis, represented in performance: a Play (theatre), play, opera, mime, ballet, etc., performed in a theatre, or on Radio drama, radio or television.Elam (1980, 98). Considered as a genre of poetry in general, the dramatic mode has been contrasted with the Epic poetry, epic and the Lyric poetry, lyrical modes ever since Aristotle's ''Poetics (Aristotle), Poetics'' ()—the earliest work of dramatic theory. The term "drama" comes from a Ancient Greek, Greek word meaning "deed" or "Action (philosophy), act" (Classical Greek: , ''drâma''), which is derived from "I do" (Classical Greek: , ''dráō''). The two masks associated with drama represent the traditional Genre, generic division between Comedy (drama), comedy and tragedy. In English (as was the analogous case in many other European languages), the word ''Play (theatre), play'' or ''game'' (translating the Old English, Anglo-Saxon ''pleġan'' or Latin ''ludus'') wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comedy
Comedy is a genre of dramatic works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. Origins Comedy originated in ancient Greece: in Athenian democracy, the public opinion of voters was influenced by political satire performed by comic poets in Ancient Greek theatre, theaters. The theatrical genre of Greek comedy can be described as a dramatic performance pitting two groups, ages, genders, or societies against each other in an amusing ''agon'' or conflict. Northrop Frye depicted these two opposing sides as a "Society of Youth" and a "Society of the Old". A revised view characterizes the essential agon of comedy as a struggle between a relatively powerless youth and the societal conventions posing obstacles to his hopes. In this struggle, the youth then becomes constrained by his lack of social authority, and is left with little choice but to resort to ruses which e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affective
Affect, in psychology, is the underlying experience of feeling, emotion, attachment, or mood. It encompasses a wide range of emotional states and can be positive (e.g., happiness, joy, excitement) or negative (e.g., sadness, anger, fear, disgust). Affect is a fundamental aspect of human experience and plays a central role in many psychological theories and studies. It can be understood as a combination of three components: emotion, mood (enduring, less intense emotional states that are not necessarily tied to a specific event), and affectivity (an individual's overall disposition or temperament, which can be characterized as having a generally positive or negative affect). In psychology, the term ''affect'' is often used interchangeably with several related terms and concepts, though each term may have slightly different nuances. These terms encompass: emotion, feeling, mood, emotional state, sentiment, affective state, emotional response, affective reactivity, and disposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Waves
Theta waves generate the theta rhythm, a neural oscillation in the brain that underlies various aspects of cognition and behavior, including learning, memory, and spatial navigation in many animals. It can be recorded using various electrophysiological methods, such as electroencephalogram (EEG), recorded either from inside the brain or from electrodes attached to the scalp. At least two types of theta rhythm have been described. The hippocampal theta rhythm is a strong oscillation that can be observed in the hippocampus and other brain structures in numerous species of mammals including rodents, rabbits, dogs, cats, and marsupials. ''"Cortical theta rhythms"'' are low-frequency components of scalp EEG, usually recorded from humans. Theta rhythms can be quantified using quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG) using freely available toolboxes, such as, EEGLAB or the Neurophysiological Biomarker Toolbox (NBT). In rats, theta wave rhythmicity is easily observed in the hip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Wave
Beta waves, or beta rhythm, are neural oscillations (brainwaves) in the brain with a frequency range of between 12.5 and 30 Hz (12.5 to 30 cycles per second). Several different rhythms coexist, with some being inhibitory and others excitory in function. Beta waves can be split into three sections: Low Beta Waves (12.5–16 Hz, "Beta 1"); Beta Waves (16.5–20 Hz, "Beta 2"); and High Beta Waves (20.5–28 Hz, "Beta 3"). Beta states are the states associated with normal waking consciousness. History Beta waves were discovered and named by the German psychiatrist Hans Berger, who invented electroencephalography (EEG) in 1924, as a method of recording electrical brain activity from the human scalp. Berger termed the larger amplitude, slower frequency waves that appeared over the posterior scalp when the subject's eye were closed alpha waves. The smaller amplitude, faster frequency waves that replaced alpha waves when the subject opened their eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Waves
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent ( in phase or constructive) neocortical neuronal electrical activity possibly involving thalamic pacemaker cells. Historically, they are also called "Berger's waves" after Hans Berger, who first described them when he invented the EEG in 1924. Alpha waves are one type of brain waves detected by electrophysiological methods, e.g., electroencephalography (EEG) or magnetoencephalography (MEG), and can be quantified using power spectra and time-frequency representations of power like quantitative electroencephalography (qEEG). They are predominantly recorded over parieto-occipital brain and were the earliest brain rhythm recorded in humans. Alpha waves can be observed during relaxed wakefulness, especially when there is no mental activity. During the eyes-closed condition, alpha waves are prominent at parietal locations. Atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Term Memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to sensory memory, the initial stage, and Short-term memory, short-term or working memory, the second stage, which persists for about 18 to 30 seconds. LTM is grouped into two categories known as explicit memory (declarative memory) and implicit memory (non-declarative memory). Explicit memory is broken down into Episodic memory, episodic and semantic memory, while implicit memory includes procedural memory and emotional conditioning. Stores The idea of separate memories for short- and long-term storage originated in the 19th century. One model of memory developed in the 1960s assumed that all memories are formed in one store and transfer to another store after a small period of time. This model is referred to as the "modal model", most famously detailed by Richard Shiffrin, Shiffrin. The model states that memory is first stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Term Memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recited. The duration of short-term memory (absent rehearsal or active maintenance) is estimated to be on the order of seconds. The commonly cited capacity of 7 items, found in Miller's Law, has been superseded by 4±1 items. In contrast, long-term memory holds information indefinitely. Short-term memory is not the same as working memory, which refers to structures and processes used for temporarily storing and manipulating information. Stores The idea of separate memories for short-term and long-term storage originated in the 19th century. A model of memory developed in the 1960s assumed that all memories are formed in one store and transfer to other stores after a small period of time. This model is referred to as the "modal model", most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
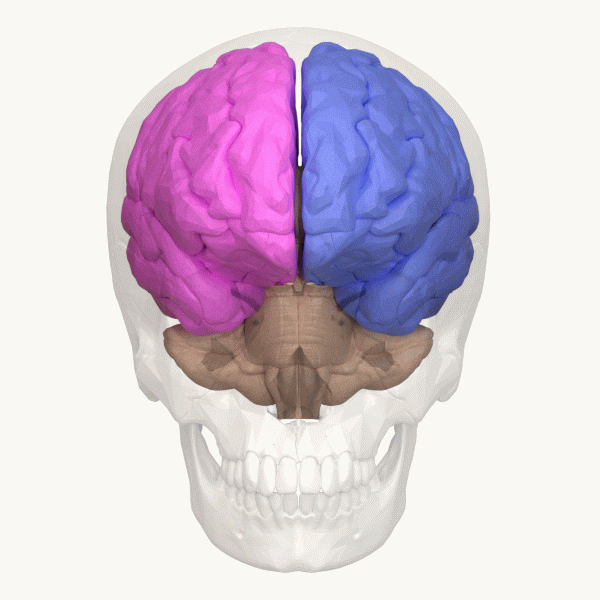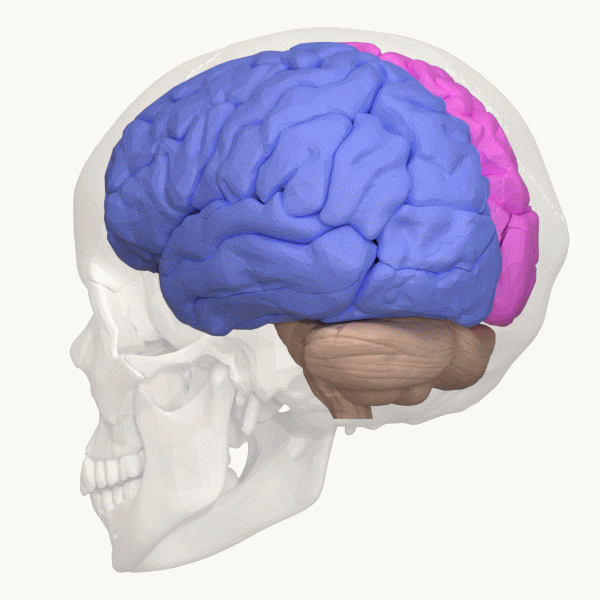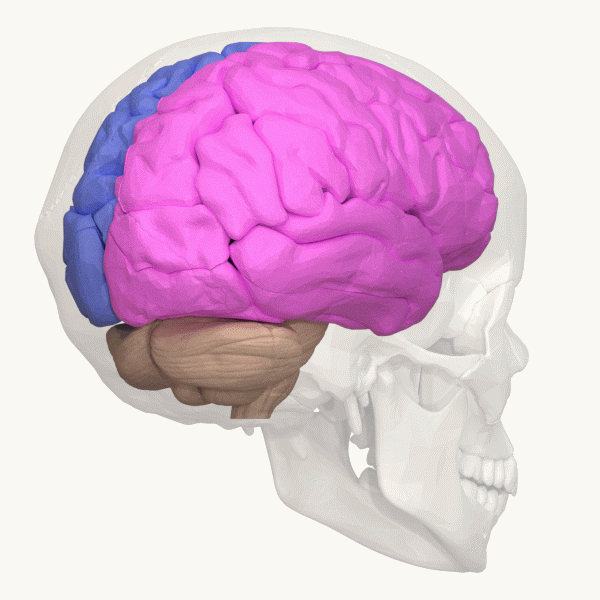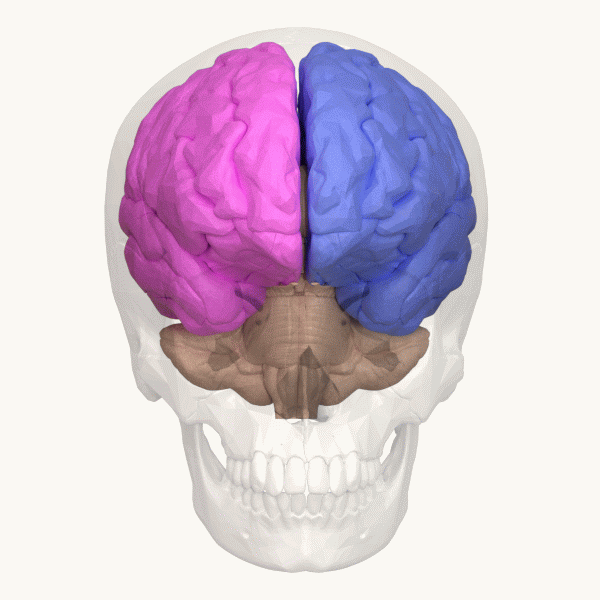
Left Hemisphere
The lateralization of brain function (or hemispheric dominance/ lateralization) is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Both hemispheres exhibit brain asymmetries in both structure and neuronal network composition associated with specialized function. Lateralization of brain structures has been studied using both healthy and split-brain patients. However, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization and each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best example of an establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |