|
Consumer Network
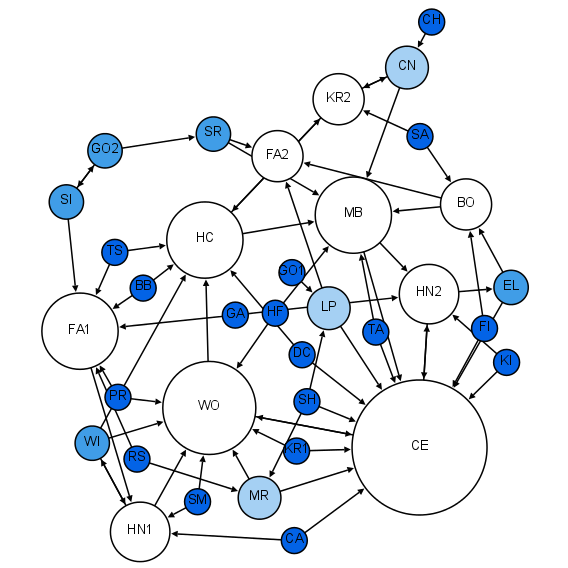
The notion of consumer networks expresses the idea that people's embeddedness in social networks affects their behavior as consumers. Interactions within consumer networks such as information exchange and imitation can affect demand and market outcomes in ways not considered in the neoclassical theory of consumer choice. Economics Economic research on the topic is not ample. In attempts to incorporate consumer networks into standard microeconomic models, some interesting implications have been found concerning market structure, market dynamics and the firm's profit maximizating decision. It has been shown that under certain assumptions the structure of the consumer network can affect market structure.. In certain scenarios, where consumers have a higher inclination to compare their habitually consumed product to that of their acquaintances, the equilibrium market structure can switch from oligopoly to monopoly. In another model, which incorporates small world consumer networks i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Network
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of Dyad (sociology), dyadic ties, and other Social relation, social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities along with a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine dynamics of networks. For instance, social network analysis has been used in studying the spread of misinformation on social media platforms or analyzing the influence of key figures in social networks. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense Graph
In mathematics, a dense graph is a graph in which the number of edges is close to the maximal number of edges (where every pair of vertices is connected by one edge). The opposite, a graph with only a few edges, is a sparse graph. The distinction of what constitutes a dense or sparse graph is ill-defined, and is often represented by 'roughly equal to' statements. Due to this, the way that density is defined often depends on the context of the problem. The graph density of simple graphs is defined to be the ratio of the number of edges with respect to the maximum possible edges. For undirected simple graphs, the graph density is: :D = \frac = \frac For directed, simple graphs, the maximum possible edges is twice that of undirected graphs (as there are two directions to an edge) so the density is: :D = \frac = \frac where is the number of edges and is the number of vertices in the graph. The maximum number of edges for an undirected graph is = \frac2, so the maximal density is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word-of-mouth Marketing
Word-of-mouth marketing (WOMM, WOM marketing, also called word-of-mouth advertising) is the communication between consumers about a product, service, or company in which the sources are considered independent of direct commercial influence that has been actively influenced or encouraged as a marketing effort (e.g. 'seeding' a message in a network rewarding regular consumers to engage in WOM, employing WOM 'agents'). While it is difficult to truly control word of mouth communication, there are three generic avenues to 'manage' word of mouth communication for the purpose of word-of-mouth marketing, including: * Building a strong WOM foundation (building brand loyalty, trust and satisfaction) * Indirect WOM management ( advertisement and other promotional strategies) * Direct WOMM management ( viral marketing and electronic communication) The success of word-of-mouth marketing depends heavily on the nature of the loyalty rewards used. When companies utilize poor incentives to mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Marketing
Viral marketing is a business strategy that uses existing social networks to promote a product mainly on various social media platforms. Its name refers to how consumers spread information about a product with other people, much in the same way that a virus spreads from one person to another. It can be delivered by Word-of-mouth marketing, word of mouth, or enhanced by the network effects of the Internet and mobile networks. The concept is often misused or misunderstood, as people apply it to any successful enough story without taking into account the word "viral". Viral advertising is personal and, while coming from an identified sponsor, it does not mean businesses pay for its distribution. Most of the well-known viral ads circulating online are ads paid by a sponsor company, launched either on their own platform (company web page or social media profile) or on social media websites such as YouTube. Consumers receive the page link from a social media network or copy the entire a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advertising
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a Product (business), product or Service (economics), service. Advertising aims to present a product or service in terms of utility, advantages, and qualities of interest to Consumer, consumers. It is typically used to promote a specific good or service, but there are a wide range of uses, the most common being commercial advertisement. Commercial advertisements often seek to generate increased Consumption (economics), consumption of their products or services through "Branding (promotional), branding", which associates a product name or image with certain qualities in the minds of consumers. On the other hand, ads that intend to elicit an immediate sale are known as Direct marketing, direct-response advertising. Non-commercial entities that advertise more than consumer products or services include Political party, political parties, Interest group, interest groups, Religious organization, religious o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word-of-mouth Marketing
Word-of-mouth marketing (WOMM, WOM marketing, also called word-of-mouth advertising) is the communication between consumers about a product, service, or company in which the sources are considered independent of direct commercial influence that has been actively influenced or encouraged as a marketing effort (e.g. 'seeding' a message in a network rewarding regular consumers to engage in WOM, employing WOM 'agents'). While it is difficult to truly control word of mouth communication, there are three generic avenues to 'manage' word of mouth communication for the purpose of word-of-mouth marketing, including: * Building a strong WOM foundation (building brand loyalty, trust and satisfaction) * Indirect WOM management ( advertisement and other promotional strategies) * Direct WOMM management ( viral marketing and electronic communication) The success of word-of-mouth marketing depends heavily on the nature of the loyalty rewards used. When companies utilize poor incentives to mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Marketing
Viral marketing is a business strategy that uses existing social networks to promote a product mainly on various social media platforms. Its name refers to how consumers spread information about a product with other people, much in the same way that a virus spreads from one person to another. It can be delivered by Word-of-mouth marketing, word of mouth, or enhanced by the network effects of the Internet and mobile networks. The concept is often misused or misunderstood, as people apply it to any successful enough story without taking into account the word "viral". Viral advertising is personal and, while coming from an identified sponsor, it does not mean businesses pay for its distribution. Most of the well-known viral ads circulating online are ads paid by a sponsor company, launched either on their own platform (company web page or social media profile) or on social media websites such as YouTube. Consumers receive the page link from a social media network or copy the entire a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Economics
Experimental economics is the application of experimental methods to study economic questions. Data collected in experiments are used to estimate effect size, test the validity of economic theories, and illuminate market mechanisms. Economic experiments usually use cash to motivate subjects, in order to mimic real-world incentives. Experiments are used to help understand how and why markets and other exchange systems function as they do. Experimental economics have also expanded to understand institutions and the law (experimental law and economics). A fundamental aspect of the subject is design of experiments. Experiments may be conducted in the field or in laboratory settings, whether of individual or group behavior. Variants of the subject outside such formal confines include natural and quasi-natural experiments. Experimental topics One can loosely classify economic experiments using the following topics: * Markets * Games * Evolutionary game theory * Decision making * Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networks (journal)
''Social Networks'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering research on social network theory. The editors-in-chief are Thomas Valente (University of Southern California) and Ulrik Brandes (ETH Zurich). It was established in 1979 and is currently published by Elsevier. Abstracting and indexing ''Social Networks'' is abstracted and indexed in: * Anthropological Index * Anthropological Literature * Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences * Scopus * Social Sciences Citation Index * Sociological Abstracts According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', its 2011 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... was 2.931, ranking it 6th out of 137 journals in the category "Sociology". References External links * {{Authority control Acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or use purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Rights "Consumers, by definition, include us all", said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech, John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading information, adverti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
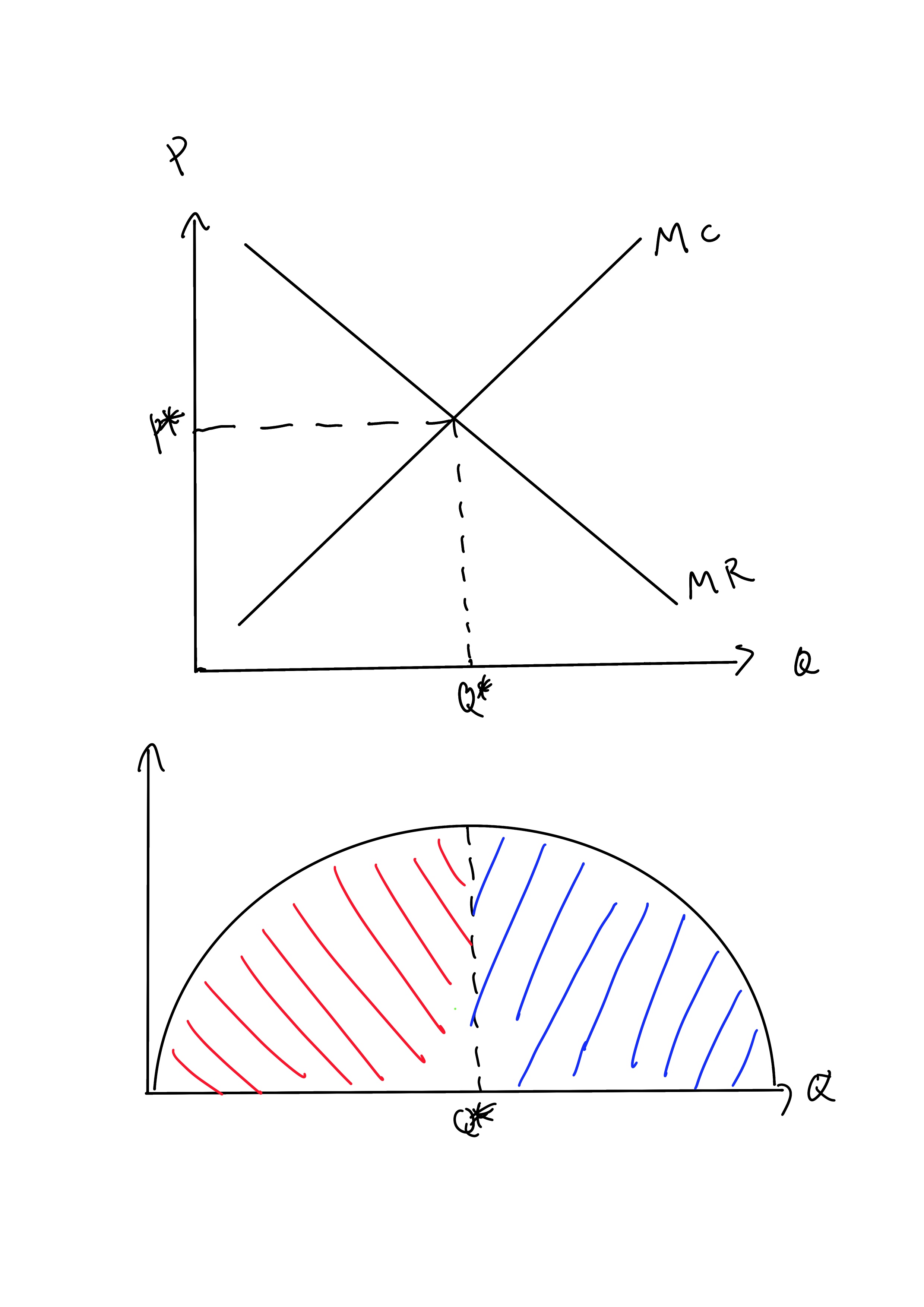
Profit Maximization
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that will lead to the highest possible total profit (or just profit in short). In neoclassical economics, which is currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, the firm is assumed to be a " rational agent" (whether operating in a perfectly competitive market or otherwise) which wants to maximize its total profit, which is the difference between its total revenue and its total cost. Measuring the total cost and total revenue is often impractical, as the firms do not have the necessary reliable information to determine costs at all levels of production. Instead, they take more practical approach by examining how small changes in production influence revenues and costs. When a firm produces an extra unit of product, the additional revenue gained from selling it is called the marginal revenue (\text), and the additional cost to produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, Cognitive network, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential statistics, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |