|
Constantine Paparregopoulus
Constantine Paparrigopoulos (; 1815 – 14 April 1891) was a Greek historian, who is considered the founder of modern Greek historiography. He is the founder of the concept of historical continuity of Greece from antiquity to the present, establishing the tripartite division of Greek history in ancient, medieval and modern, and sought to set aside the prevailing views at the time that the Byzantine Empire was a period of decadence and degeneration. Paparrigopoulos introduced this division in his teaching at the University of Athens. His main work is the multi-volume ''History of the Greek Nation'' (), covering the history of the Greeks from ancient to modern times, and notably including the Greek Middle Ages as part of the national history of Greece. He is also known for vigorously countering the theories of Jakob Philipp Fallmerayer regarding the racial origins of the Greeks. He was the first historian who managed to demonstrate that Fallmerayer's theory was false. Life Paparr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odessa
ODESSA is an American codename (from the German language, German: ''Organisation der ehemaligen SS-Angehörigen'', meaning: Organization of Former SS Members) coined in 1946 to cover Ratlines (World War II aftermath), Nazi underground escape-plans made at the end of World War II by a group of ''SS'' officers with the aim of facilitating secret escape routes, and any directly ensuing arrangements. The concept of the existence of an actual ODESSA organisation has circulated widely in fictional Spy fiction, spy novels and movies, including Frederick Forsyth's best-selling 1972 thriller ''The Odessa File''. The escape-routes have become known as "Ratlines (World War II), ratlines". Known goals of elements within the ''SS'' included allowing ''SS'' members to escape to Argentina or to the Middle East under false passports. Although an unknown number of wanted Nazis and war criminals escaped Germany and often Europe, most experts deny that an organisation called ODESSA ever existed. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlos Karolidis
Pavlos Karolidis or Karolides (, c. 1849 – 26 July 1930) was a Greek historian who lived in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Life Karolidis was born in 1849 in the village of Androniki (, now a suburb of Kayseri) in Cappadocia. His father Konstantinos Karolidis or Karloglou was a wealthy landowner and wheat merchant. Like many Cappadocian Greeks, Karolidis' first language was Ottoman Turkish, but he was educated at Greek schools, including two of the premier Greek institutions of the Ottoman Empire, the Great School of the Nation in Constantinople and the Evangelical School of Smyrna. In 1867 he enrolled in the School of Philosophy of the University of Athens, and in 1870 he went to Germany on a scholarship. He studied at the universities of Munich, Strasbourg and Tübingen and was awarded his doctorate in 1872. On his return from Germany, he initially taught in the Greek high schools of Pera and Chalcedon. In 1876 he went to Smyrna to teach at the Evangeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorians
The Dorians (; , , singular , ) were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Greeks, Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans (tribe), Achaeans, and Ionians). They are almost always referred to as just "the Dorians", as they are called in the earliest literary mention of them in the ''Odyssey'', where they already can be found inhabiting the island of Crete. They were diverse in way of life and social organization, varying from the populous trade center of the city of Ancient Corinth, Corinth, known for its ornate style in art and architecture, to the isolationist, military state of Sparta; and yet, all Hellenes knew which localities were Dorian and which were not. Dorian states at war could more likely, but not always, count on the assistance of other Dorian states. Dorians were distinguished by the Doric Greek dialect and by characteristic social and historical traditions. In the 5th century BC, Dorians and Ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the Corinth (municipality), municipality of Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It is the capital of Corinthia. It was founded as Nea Korinthos (), or New Corinth, in 1858 after an earthquake destroyed the existing settlement of Corinth, which had developed in and around the site of the ancient city. History Corinth derives its name from Ancient Corinth, a city-state of antiquity. The site was occupied from before 3000 BC. Ancient Greece Historical references begin with the early 8th century BC, when ancient Corinth began to develop as a commercial center. Between the 8th and 7th centuries, the Bacchiad family ruled Corinth. Cypselus overthrew the Bacchiad f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The unificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
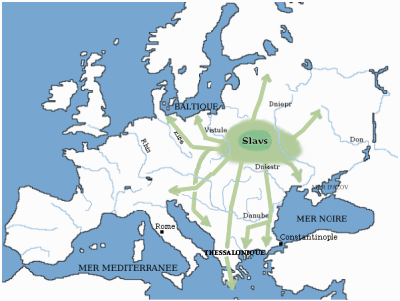
Slavic People
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitrios Paparrigopoulos
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning "devoted to goddess Demeter". Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumitru, Demitri, Dhimitër, Dimitrije and Zmicier, in addition to other forms (such as Russian Dmitry) descended from it. Nicknames include Demmie, Dimmie, Demi, Jim, Jimmy, Jimmie, Metry, Metrie, Mimmie, Demetri, Dmitri, Mitică, Mitya and Dima. Demetrius and its variations may refer to the following: Real people Ancient *Demetrius of Alopece, 4th century BC Greek sculptor noted for his realism *Demetrius of Phalerum ( – BC) *Demetrius (somatophylax), somatophylax of Alexander the Great (d. 330 BC) *Demetrius I of Macedon (337–283 BC), called ''Poliorcetes'', son of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, King of Macedonia 294–288 BC *Demetrius the Fair (Demetrius the Handsome, Demetrius of Cyrene) (285 BC-249/250 BC) - Hellenistic king of Cyrene *Demetrius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gortyna, Arcadia
Gortyna (), is a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Megalopoli, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 116.205 km2. Its seat was in the village Karytaina. The name of the municipality was taken from the ancient city of Gortys. Subdivisions The municipal unit Gortyna is subdivided into the following communities (constituent villages in brackets): * Atsicholos *Karytaina (Karytaina, Kalyvakia, Karvounari) *Katsimpalis * Kotili (Kotili, Palatos, Strongylo) * Kourounios *Kyparissia * Mavria * Sarakini (Sarakini, Kryonero, Palaiokastro) * Vlachorraptis * Zoni Population Ancient Gortys The ancient city Gortys was located in the valley of the river Lousios. It reputedly was founded by Gortys, son of Stymphalus, a legendary king of Arcadia. When Megalopolis was founded in the 4th century BC, many inhabitants moved to the new city, but Gortys was still inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nationality
Nationality is the legal status of belonging to a particular nation, defined as a group of people organized in one country, under one legal jurisdiction, or as a group of people who are united on the basis of culture. In international law, nationality is a legal identification establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction over the person and affords the person the protection of the state against other states. The rights and duties of nationals vary from state to state,Weis, Paul''Nationality and Statelessness in International Law''. BRILL; 1979 ited 19 August 2012 . p. 29–61. and are often complemented by citizenship law, in some contexts to the point where citizenship is synonymous with nationality. However, nationality differs technically and legally from citizenship, which is a different legal relationship between a person and a country. The noun "national" can include both citizens and non-citizens. The mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Capodistria
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (; February 1776 –27 September 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias, was a Greek statesman who was one of the most distinguished politicians and diplomats of 19th-century Europe. Kapodistrias's involvement in politics began as a minister of the Septinsular Republic in the early 19th century. He went on to serve as the foreign minister of the Russian Empire from 1816 until his abdication in 1822, when he became increasingly active in supporting the Greek War of Independence that broke out a year earlier. After a long and distinguished career in European politics and diplomacy, he was elected as the first head of state of independent Greece at the 1827 Third National Assembly at Troezen and served as the governor of Greece between 1828 and 1831. For his significant contribution during his governance, he is recognised as the founder of the modern Greek state, and the architect of Greek independence. Background and early caree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |