|
Conservation Area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural or cultural values. Protected areas are those areas in which human presence or the exploitation of natural resources (e.g. firewood, non-timber forest products, water, ...) is limited. The term "protected area" also includes marine protected areas and transboundary protected areas across multiple borders. As of 2016, there are over 161,000 protected areas representing about 17 percent of the world's land surface area (excluding Antarctica). For waters under national jurisdiction beyond inland waters, there are 14,688 Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), covering approximately 10.2% of coastal and marine areas and 4.12% of global ocean areas. In contrast, only 0.25% of the world's oceans beyond national jurisdiction are covered by MPAs. In recent years, the 30 by 30 initiative has targeted to protect 30% of ocean territory and 30% of land territory worldwide by 2030; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas By Percentage Per Country
Protection is any measure taken to guard something against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark (botany), bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like Scale (anatomy), scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from Predation, predators, with some animals having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global 200
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature ( WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none. The WWF assigns a conservation status to each ecoregion in the Global 200: critical or endangered; vulnerable; and relatively stable or intact. Over half of the ecoregions in the Global 200 are rated endangered. Background The WWF has identified 867 terrestrial ecoregions across the Earth's land surface, as well as freshwater and marine ecoregions. The goal of this classification system is to ensure that the full range of ecosystems wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregions
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecology, ecological and Geography, geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural community (ecology), communities and species. The biodiversity of flora (plants), flora, fauna (animals), fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Ecoregions are also known as "ecozones" ("ecological zones"), although that term may also refer to biogeographic realms. Three caveats are appropriate for all bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Biodiversity Areas
Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA) are geographical regions that have been determined to be of international importance in terms of biodiversity conservation, using globally standardized criteria published by the IUCN as part of a collaboration between scientists, conservation groups, and government bodies across the world. The purpose of Key Biodiversity Areas is to identify regions that are in need of protection by governments or other agencies. KBAs extend the Important Bird Area (IBA) concept to other taxonomic groups and are now being identified in many parts of the world. Examples of types of KBAs include Important Plant Areas (IPAs), Ecologically and Biologically Significant Areas (EBSAs) in the High Seas, Alliance for Zero Extinction (AZE) sites, Prime Butterfly Areas, Important Mammal Areas and Important Sites for Freshwater Biodiversity, with prototype criteria developed for freshwater molluscs and fish and for marine systems. The determination of KBAs often brings sites onto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliance For Zero Extinction
Formed in 2000 and launched globally in 2005, the Alliance for Zero Extinction (AZE) comprises 100 non-governmental biodiversity conservation organizations working to prevent species extinctions by identifying and safeguarding sites where species evaluated to be Endangered or Critically Endangered under International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) criteria only exist at one location on Earth."Zero Extinction - Home." Zero Extinction - Home. N.p., n.d. Web. 3 July 2012 AZE members work to rebuild populations of endangered and critically endangered species through efforts to eliminate human threats such as commercial exploitation, disease and the introduction of invasive species. AZE provides expertise on biodiversity goals for the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and assists party nations in integrating protection of AZE sites and species into National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAP).Ainsworth, David. "Alliance for Zero Extinction and the Convention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centres Of Plant Diversity
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity * Central tendency, measures of the central tendency (center) in a set of data Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin ** Center (community), Wisconsin * Center Township (other) * Centre Township (other) * Centre Avenue (other) * Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Bird Areas
An Endemic Bird Area (EBA) is an area of land identified by BirdLife International as being important for habitat-based bird conservation because it contains the habitats of restricted-range bird species (''see below for definition''), which are thereby endemic to them. An EBA is formed where the distributions of two or more such restricted-range species overlap. Using this guideline, 218 EBAs were identified when Birdlife International established its Biodiversity project in 1987. accessed 10 May 2011 A secondary EBA comprises the range of only one restricted-range species, or an area which is only the partial breeding range of a range-restricted species. EBAs contain about 93% of the world's restricted-range bird species, as well as supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Areas
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations. IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International. There are over 13,000 IBAs worldwide. These sites are small enough to be entirely conserved and differ in their character, habitat or ornithological importance from the surrounding habitat. In the United States the program is administered by the National Audubon Society. Often IBAs form part of a country's existing protected area network, and so are protected under national legislation. Legal recognition and protection of IBAs that are not within existing protected areas varies within different countries. Some countries have a National IBA Conservation Strategy, whereas in others protection is completely lacking. History In 1985, following a specific request from the European Economic Community, Birdlife International dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than one-fifth of Earth's terrestrial area and contain about 50% of the world's species. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity for both marine and terrestrial taxa. Since Abiogenesis, life began on Earth, six major mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The Phanerozoic aeon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the Cambrian explosion. In this period, the majority of Multicellular organism, multicellular Phylum, phyla first appeared. The next 400 mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
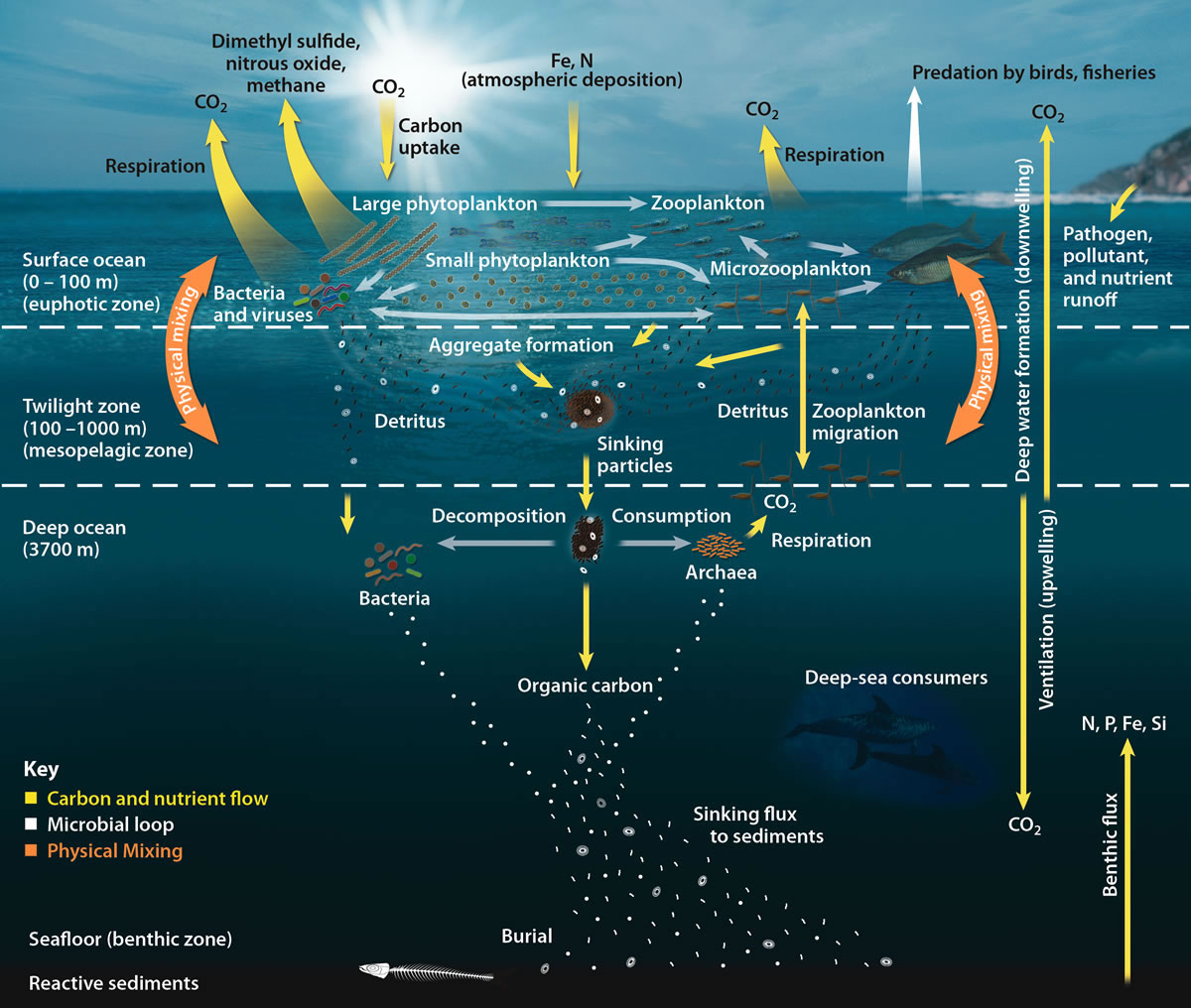
Biological Pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated process which results in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |