|
Conopophaga Castaneiceps 2
''Conopophaga'' is a genus of birds in the gnateater family. Its members are found in forest and woodland in South America. Taxonomy and species list The genus ''Conopophaga'' was introduced in 1816 by the French ornithologist Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot. The name combines the Ancient Greek ''kōnōps'' meaning "gnat" with ''-phagos'' meaning "-eating". The type species was subsequently designated as the chestnut-belted gnateater by George Robert Gray in 1840. Peters incorrectly gives the page in Gray 1840 as 41. The genus now contains nine species, all with "gnateater" in their common names. Distribution and habitat Gnateaters are birds found in the undergrowth of forest, woodland, and bamboo stands, with most species in the Amazon Basin, the Atlantic Forest, and the East Andean slopes. All are associated with dense thickets. While they are always found near the ground, seldom rising more than 1.5 m up, they also seldom travel or spend much time on the ground itself (tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-cheeked Gnateater
The black-cheeked gnateater (''Conopophaga melanops'') is a species of bird in the family Conopophagidae Endemism, endemic to Brazil. The male is distinguished by its orange crown, black face and white throat, while the female has brown plumage. Taxonomy French naturalist Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot described the black-cheeked gnateater in 1818, giving it the species name ''melanops'' from the Ancient Greek words ''melas'' "black" and ''ops'' "face". The black-cheeked gnateater has three subspecies: *''C. m. perspicillata'' (Hinrich Lichtenstein, Lichtenstein, MHK, 1823) - Bahia and Sergipe (eastern Brazil) *''C. m. melanops'' (Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot, Vieillot, 1818) - southeastern Brazil *''C. m. nigrifrons'' Olivério Pinto, Pinto, 1954 - Paraíba to Alagoas (eastern Brazil) Description Measuring 11.5 cm (4.5 in), the black-cheeked gnateater is a small round bird with a short tail. It exhibits sexual dimorphism, as the male has distinctive coloured plumage and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conopophaga Cearae - Ceara Gnateater
''Conopophaga'' is a genus of birds in the gnateater family. Its members are found in forest and woodland in South America. Taxonomy and species list The genus ''Conopophaga'' was introduced in 1816 by the French ornithologist Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot. The name combines the Ancient Greek ''kōnōps'' meaning "gnat" with ''-phagos'' meaning "-eating". The type species was subsequently designated as the chestnut-belted gnateater by George Robert Gray in 1840. Peters incorrectly gives the page in Gray 1840 as 41. The genus now contains nine species, all with "gnateater" in their common names. Distribution and habitat Gnateaters are birds found in the undergrowth of forest, woodland, and bamboo stands, with most species in the Amazon Basin, the Atlantic Forest, and the East Andean slopes. All are associated with dense thickets. While they are always found near the ground, seldom rising more than 1.5 m up, they also seldom travel or spend much time on the ground itself (though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
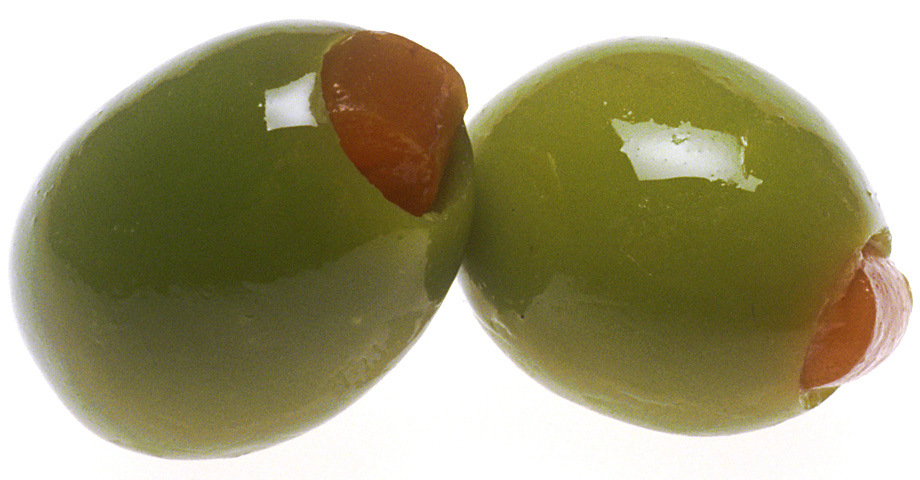
Olive (colour)
Olive is a dark yellowish-green color, like that of unripe or green olives. As a color word in the English language, it appears in late Middle English. Shaded toward gray, it becomes olive drab. Variations Olivine Olivine is the typical color of the mineral olivine. The first recorded use of ''olivine'' as a color name in English was in 1912. Olive drab Olive drab is variously described as a "dull olive-green colour" (''Oxford English Dictionary'');''Oxford English Dictionary'', 5th Edition, 1982 "a shade of greenish-brown" (''Webster's New World Dictionary''); "a dark gray-green" (''MacMillan English dictionary''); "a grayish olive to dark olive brown or olive gray" (''American Heritage Dictionary''); or "A dull but fairly strong gray-green color" (''Collins English Dictionary''). It was widely used as a camouflage color for uniforms and equipment in the armed forces, particularly by the U.S. Army during the Second World War. The first recorded use of ''olive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerated d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest mountain range outsid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Forest
The Atlantic Forest ( pt, Mata Atlântica) is a South American forest that extends along the Atlantic coast of Brazil from Rio Grande do Norte state in the northeast to Rio Grande do Sul state in the south and inland as far as Paraguay and the Misiones Province of Argentina, where the region is known as Selva Misionera. The Atlantic Forest has ecoregions within the following biome categories: seasonal moist and dry broad-leaf tropical forests, tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands, and mangrove forests. The Atlantic Forest is characterized by a high biodiversity and endemism. It was the first environment that the Portuguese colonists encountered over 500 years ago, when it was thought to have had an area of , and stretching an unknown distance inland, making it, back then, the second largest rainforest on the planet, only behind the Amazon rainforest. Over 85% of the original area has been deforested, threatening many plant and animal species with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
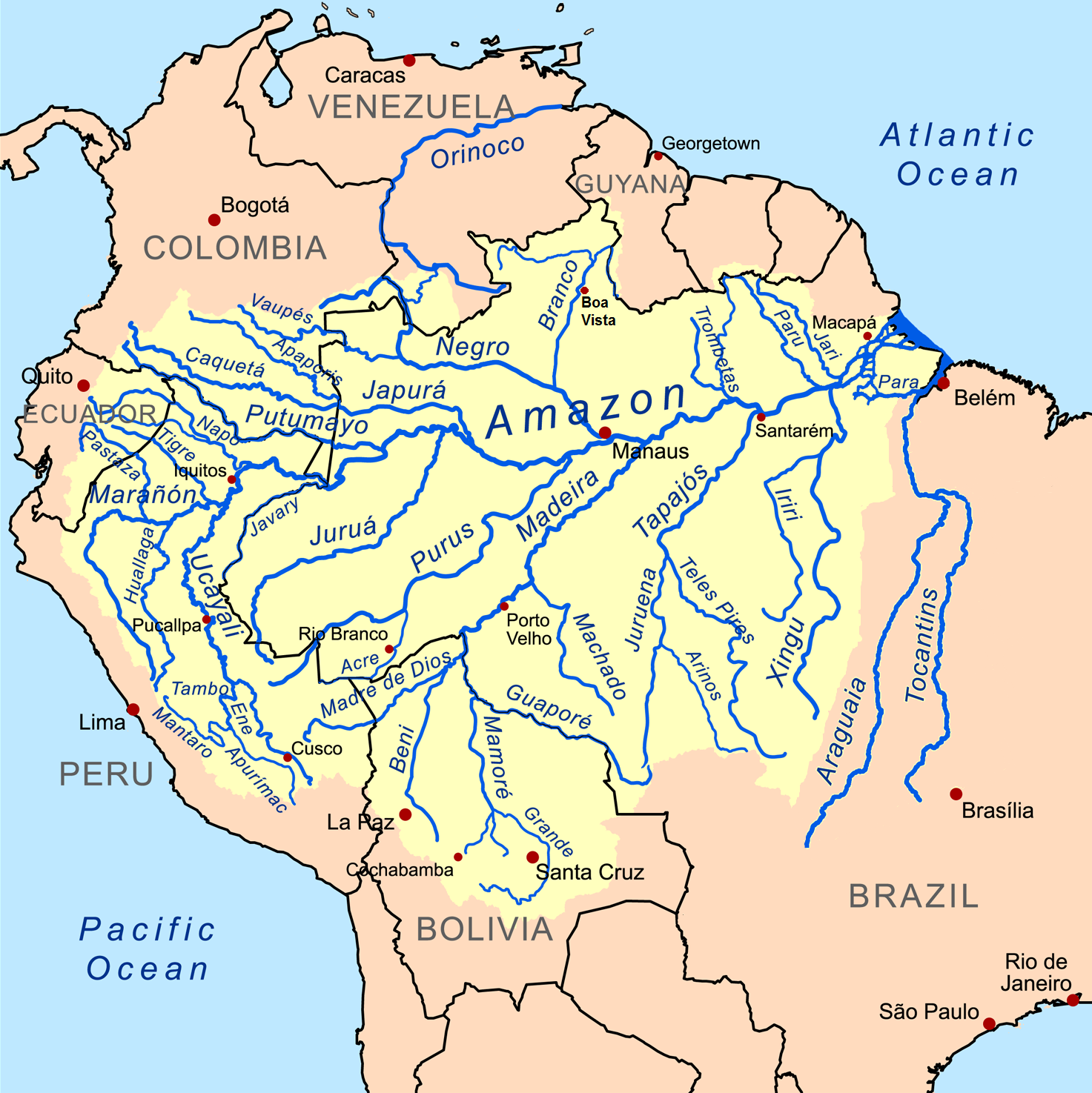
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, but it probably comes from the Dutch or Portuguese language, which originally borrowed it from Malay or Kannada. In bamboo, as in other grasses, the internodal regions of the stem are usually hollow and the vascular bundles in the cross-section are scattered throughout the stem instead of in a cylindrical arrangement. The dicotyledonous woody xylem is also absent. The absence of secondary growth wood causes the stems of monocots, including the palms and large bamboos, to be columnar rather than tapering. Bamboos include some of the fastest-growing plants in the world, due to a unique rhizome-dependent system. Certain species of bamboo can grow within a 24-hour period, at a rate of almost an hour (equivalent to 1 mm every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-bellied Gnateater
The black-bellied gnateater (''Conopophaga melanogaster'') is a species of bird in the family Conopophagidae. It is endemic to Brazil. Taxonomy and systematics The position of the black-bellied gnateater in linear format is unsettled. The International Ornithological Committee (IOC) and the Clements taxonomy place it differently within the gnateater family. Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2019. The eBird/Clements Checklist of Birds of the World: v2019. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved 15 August 2019 The species is monotypic. Description The black-bellied gnateater is long and weighs . The male's entire head and most of the under parts are black, becoming dark gray on the lower belly and crissum (the area around the cloaca). Its upper parts are rich chestnut. There is a long white tuft behind the eye. The female's face and most of the under p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conopophaga Melanogaster - Black-bellied Gnateater (male); Carajás National Forest, Pará, Brazil
''Conopophaga'' is a genus of birds in the gnateater family. Its members are found in forest and woodland in South America. Taxonomy and species list The genus ''Conopophaga'' was introduced in 1816 by the French ornithologist Louis Jean Pierre Vieillot. The name combines the Ancient Greek ''kōnōps'' meaning "gnat" with ''-phagos'' meaning "-eating". The type species was subsequently designated as the chestnut-belted gnateater by George Robert Gray in 1840. Peters incorrectly gives the page in Gray 1840 as 41. The genus now contains nine species, all with "gnateater" in their common names. Distribution and habitat Gnateaters are birds found in the undergrowth of forest, woodland, and bamboo stands, with most species in the Amazon Basin, the Atlantic Forest, and the East Andean slopes. All are associated with dense thickets. While they are always found near the ground, seldom rising more than 1.5 m up, they also seldom travel or spend much time on the ground itself (though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chestnut-crowned Gnateater
The chestnut-crowned gnateater (''Conopophaga castaneiceps'') is a species of bird in the family Conopophagidae. It is found in Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Taxonomy and systematics The position of the chestnut-crowned gnateater in linear format is unsettled. The International Ornithological Committee (IOC) and the Clements taxonomy place it differently within the gnateater family.Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2019. The eBird/Clements Checklist of Birds of the World: v2019. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved August 15, 2019 Four subspecies are recognized, though birds on the western slope of Colombia's Central Andes might be an unnamed taxonWhitney, B. (2020). Chestnut-crowned Gnateater (''Conopophaga castaneiceps''), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)