|
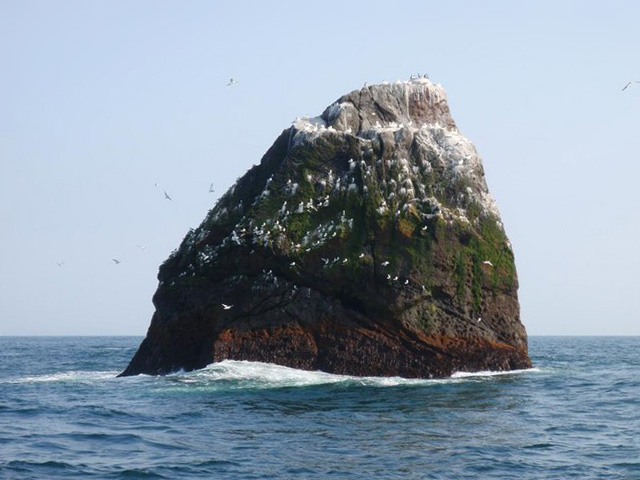
Conception Island, Bahamas
Conception Island is an islet located in the Bahamas. It is and reaches above sea level. It is an important rookery for nesting seabirds and hatching site for green turtles. It is uninhabited and protected as part of the Conception Island National Park. In 2015, a species of Boidae, boa called the Conception Bank silver boa (''Chilabothrus argentum'') was found to occur here; the new species is endemic to Conception as well as its satellite islets. See also * Geography of the Bahamas References External links * Diving at Conception Island Uninhabited islands of the Bahamas {{bahamas-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse colonization of North America, Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an Age of Discovery, age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucayan Archipelago
The Lucayan Archipelago, also known as the Bahamian Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The archipelago is in the western North Atlantic Ocean, north of Cuba and the other Antillean Islands, and east and south-east of Florida. William Keegan writes: "Modern political considerations aside, the islands form a single archipelago with common geological, ecological, and cultural roots." Though it is generally considered part of the Caribbean region, the Lucayan Archipelago is not geographically located within the Caribbean Sea. Countries and territories * The Bahamas * Turks and Caicos Islands (United Kingdom) The Mouchoir Bank, the Silver Bank, and the Navidad Bank are a submerged continuation of the archipelago, to the southeast of the Turks and Caicos Islands. Mouchoir Bank is disputed between the Turks and Caicos Islands and Dominican Republic; Silver Bank and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. It comprises more than 3,000 islands, cays and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and north-west of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida and east of the Florida Keys. The capital and largest city is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes the Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama islands were inhabited by the Arawak and Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan- speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the "New World" in 1492 when he landed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Time Zone
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 U.S. states, states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico. * Eastern Standard Time (EST) is five hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−05:00). Observed during standard time (late autumn/winter in the United States and Canada). * Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) is four hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−04:00). Observed during daylight saving time (spring/summer/early autumn in the United States and Canada). On the second Sunday in March, at 2:00 a.m. EST, clocks are advanced to 3:00 a.m. EDT, creating a 23-hour day. On the first Sunday in November, at 2:00 a.m. EDT, clocks are moved back to 1:00 a.m. EST, which results in a 25-hour day. History The boundaries of the Eastern Time Zone have moved westward since the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) took over time-zone management from railroads in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islet
An islet ( ) is generally a small island. Definitions vary, and are not precise, but some suggest that an islet is a very small, often unnamed, island with little or no vegetation to support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanent or tidal (i.e. surfaced reef or seamount); and may exist in the sea, lakes, rivers or any other sizeable bodies of water. Definition As suggested by its origin ''islette'', an Old French diminutive of "isle", use of the term implies small size, but little attention is given to drawing an upper limit on its applicability. The World Landforms website says, "An islet landform is generally considered to be a rock or small island that has little vegetation and cannot sustain human habitation", and further that size may vary from a few square feet to several square miles, with no specific rule pertaining to size. Other terms * Ait (/eɪt/, like eight) or eyot (/aɪ(ə)t, eɪt/), a small island. It is espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. It comprises more than 3,000 islands, cays and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and north-west of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida and east of the Florida Keys. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Nassau, The Bahamas, Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes the Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama islands were inhabited by the Arawak and Lucayan people, Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-Taino language, speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Above Sea Level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of a location's vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) in reference to a vertical datum based on a historic mean sea level. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric height. The zero level varies in different countries due to different reference points and historic measurement periods. Climate change and other forces can cause sea levels and elevations to vary over time. Uses Elevation or altitude above sea level is a standard measurement for: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Mining infrastructure, particularly underground. * Flying objects such as airplanes or helicopters below a Transition Altitude defined by local regulations. Units and abbreviations Elevation or altitude is generally expressed as "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, or " feet above mean sea level" in United States customary and imperial units. Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conception Island National Park
The Conception Island National Park is a protected area in the Bahamas. The island lies between Cat Island to the north and Rum Cay to the south. The vegetation consists of mangrove communities, with typical strand vegetation, and the island is visited by green turtles, sea birds and migrating birds. The park The park has a land area of and a maximum altitude of . It is administered by the Bahamas National Trust. Washington Irving identified Conception Island as the site of one of Christopher Columbus' landfalls during his 1492 voyage, but this early theory was not supported by other historians and writers (either at the time or subsequently), who identified different claimant islands as the site of Columbus's landfall. Wilcomb E. Washburn, "Landfall Controversy" in ''The Christopher Columbus Encyclopedia'', Vol. 1 (ed. Silvio A. Bedin: Simon & Schuster, 1992). Flora and fauna The island has an extensive area of mangrove-dominated habitat and typical strandline vegetation. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boidae
The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a family of nonvenomous snakes primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anaconda of South America being the heaviest and second-longest snake known; in general, adults are medium to large in size, with females usually larger than the males. Six subfamilies comprising 14-15 genera and 54-67 species are currently recognized. Description Like the pythons, boas have elongated supratemporal bones. The quadrate bones are also elongated, but not as much, while both are capable of moving freely so when they swing sideways to their maximum extent, the distance between the hinges of the lower jaw is greatly increased.Parker, H.W.; Grandison, A.G.C. 1977. ''Snakes – A Natural History''. Second Edition. British Museum (Natural History) and Cornell University Press. 108 pp. 16 plates. LCCCN 76-54625. (cloth), (paper). Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
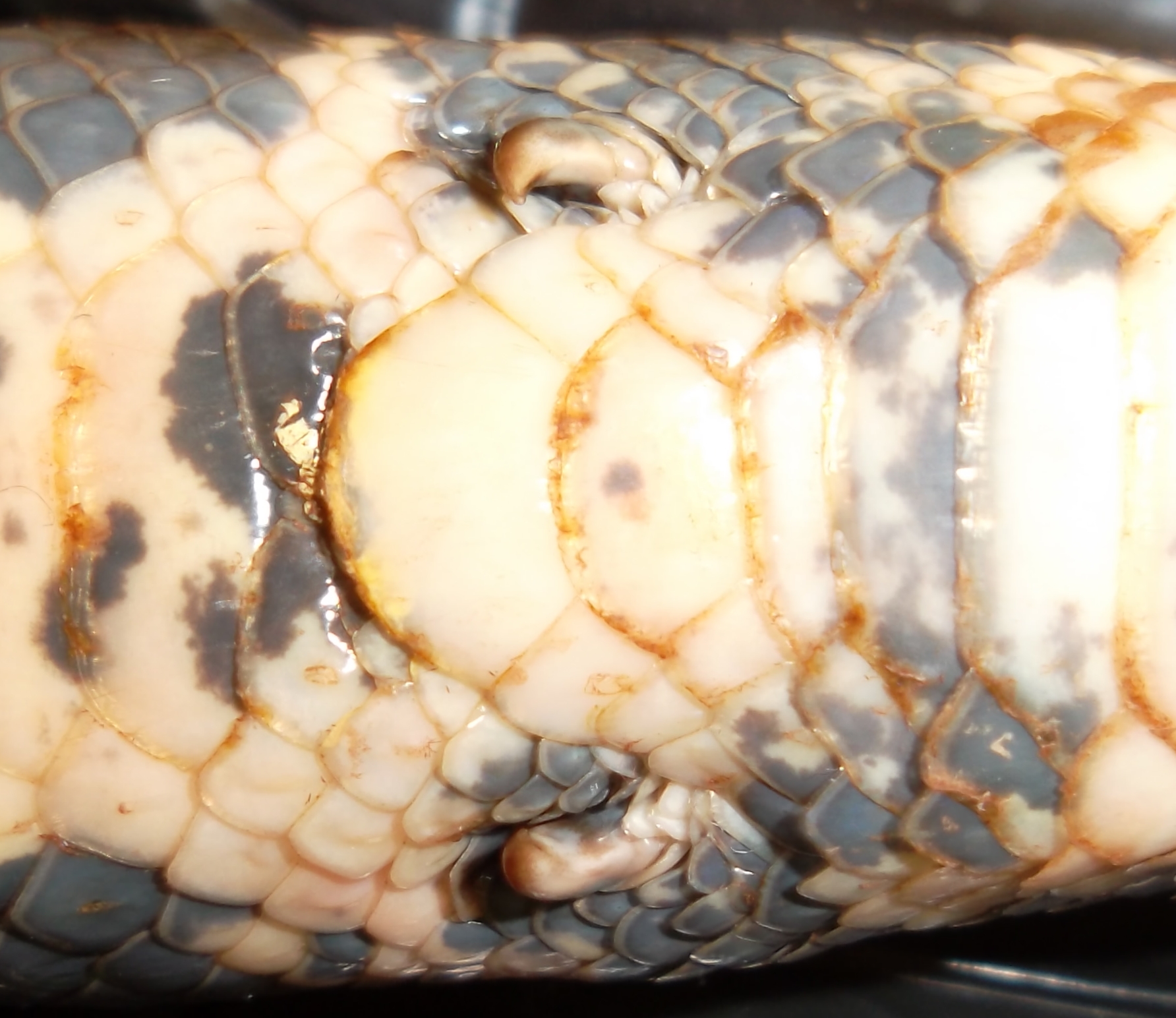
Conception Bank Silver Boa
The Conception Bank silver boa (''Chilabothrus argentum''), also known as the Conception Bank boa or silver boa, is a species of boa described in May 2016 by a team of researchers from Harvard University led by Dr. R. Graham Reynolds. It is only known from the Conception Island Bank in the Bahamas. It is the first known discovery of a West Indian boa species in 73 years. It is named for its unique silver color and the fact that the first specimen was found in a silver palm. It is the most endangered boa in the world, with fewer than 150 individuals in an area of just 5 hectares. Description Conception Bank silver boas have silver to tan dorsal background coloration, with or without scattered dark brown scales. Ventral scales are pure cream-white. Juveniles undergo ontogenetic color change, from a light brownish-orange coloration with heavy patterning as neonates to the adult coloration around 400-500 mm snout-vent length. They measure in snout–vent length and weigh . Tail le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of The Bahamas
The Bahamas are a group of about 700 islands and cays in the western Atlantic Ocean, of which only between 30 and 40 are inhabited. The largest of the islands is Andros Island, located north of Cuba and southeast of Florida. The Bimini islands are to its northwest. To the North is the island of Grand Bahama, home to the second-largest city in the country, Freeport. The island of Great Abaco is to its east. In the far south is the island of Great Inagua, the second-largest island in the country. Other notable islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, and Mayaguana. Nassau is the capital and largest city, located on New Providence. The islands have a tropical savannah climate, moderated by the Gulf Stream. The total size is . Due to the many widespread islands it has the 41st largest Exclusive Economic Zone of . The islands are surface projections of two oceanic Bahama Banks - the Little Bahama Bank and the Great Bahama Bank. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |