|
Complex Lasso Proteins
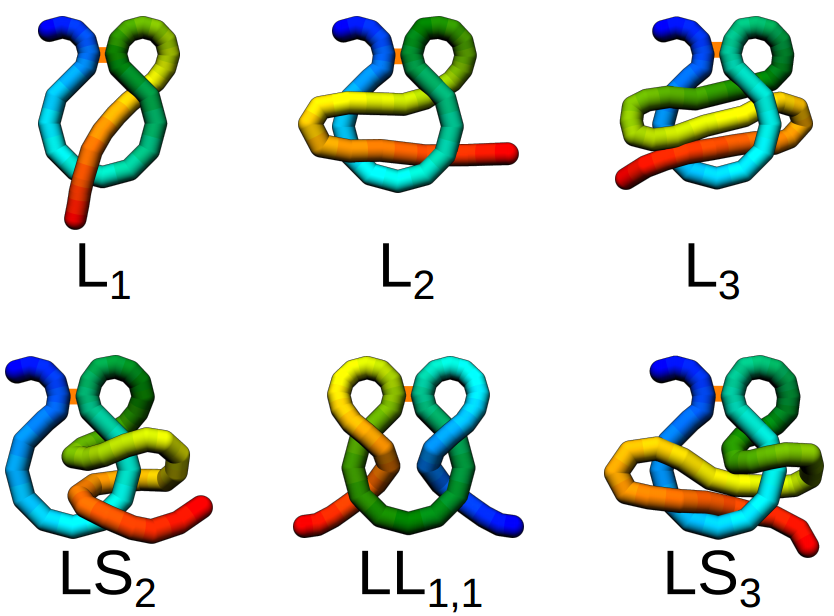
Complex lasso proteins (also called pierced lasso bundles or tadpoles) are proteins in which a covalent loop (portion of the backbone closed with a covalent bridge) is pierced by another piece of the backbone. Subclass of complex lasso proteins are Lasso peptides in which the loop is formed by post-translational amide bridge. Classification of complex lassos Complex lassos can be divided according to the number of piercings through the minimal surface spanned on the covalent loop. In particular, four classes of complex lasso proteins exist: * the Ln class (simple lasso), where one tail pierces the surface n times; * the LSn class (the supercoiling lasso), where one tail pierces the surface n times, winding around the loop; * the LLi,j class (double lasso), where both tails pierce the surface i and j times respectively; * the LSLi,j class, where one tail pierces the surface i times in the supercoiling manner, and the second pierces the surface in the simple manner. Another clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasso Peptide
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs), also known as ribosomal natural products, are a diverse class of natural products of ribosomal origin. Consisting of more than 20 sub-classes, RiPPs are produced by a variety of organisms, including prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea, and they possess a wide range of biological functions. As a consequence of the falling cost of genome sequencing and the accompanying rise in available genomic data, scientific interest in RiPPs has increased in the last few decades. Because the chemical structures of RiPPs are more closely predictable from genomic data than are other natural products (e.g. alkaloids, terpenoids), their presence in sequenced organisms can, in theory, be identified rapidly. This makes RiPPs an attractive target of modern natural product discovery efforts. Definition RiPPs consist of any peptides (i.e. molecular weight below 10 kDa) that are ribosomally-produced and undergo some degree of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the Polymer backbone, main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a Derivative (chemistry), derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl group, acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group. Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary (chemistry), primary, secondary (chemistry), secondary, and tertiary (chemistry), tertiary according to the number of acyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasso Types
A lasso or lazo ( or ), also called reata or la reata in Mexico, and in the United States riata or lariat (from Mexican Spanish lasso for roping cattle), is a loop of rope designed as a restraint to be thrown around a target and tightened when pulled. It is a well-known tool of the Mexican and South American cowboys, which was then adopted from the Mexicans by the cowboys of the United States. The word is also a verb; ''to lasso'' is to throw the loop of rope around something. Etymology The word ''lasso'' seems to have begun to be used as an English word in the early nineteenth century. It may have originated from the Castilian Spanish, Castilian word ''lazo'', which is first attested in the thirteenth century in the sense 'noose, snare', and derives in turn from classical Latin language, Latin ''laqueus'' ('noose, snare, trap, bond, tie'). The rope or lasso used to restrain cattle is also called ''Reata'' or ''La Reata'' in Mexico, which was Anglicized to “Lariat” or “R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimal Surface
In mathematics, a minimal surface is a surface that locally minimizes its area. This is equivalent to having zero mean curvature (see definitions below). The term "minimal surface" is used because these surfaces originally arose as surfaces that minimized total surface area subject to some constraint. Physical models of area-minimizing minimal surfaces can be made by dipping a wire frame into a soap solution, forming a soap film, which is a minimal surface whose boundary is the wire frame. However, the term is used for more general surfaces that may self-intersect or do not have constraints. For a given constraint there may also exist several minimal surfaces with different areas (for example, see minimal surface of revolution): the standard definitions only relate to a local optimum, not a global optimum. Definitions Minimal surfaces can be defined in several equivalent ways in \R^3. The fact that they are equivalent serves to demonstrate how minimal surface theory lies at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlphaFold
AlphaFold is an artificial intelligence (AI) program developed by DeepMind, a subsidiary of Alphabet, which performs predictions of protein structure. It is designed using deep learning techniques. AlphaFold 1 (2018) placed first in the overall rankings of the 13th Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) in December 2018. It was particularly successful at predicting the most accurate structures for targets rated as most difficult by the competition organizers, where no existing template structures were available from proteins with partially similar sequences. AlphaFold 2 (2020) repeated this placement in the CASP14 competition in November 2020. It achieved a level of accuracy much higher than any other entry. It scored above 90 on CASP's global distance test (GDT) for approximately two-thirds of the proteins, a test measuring the similarity between a computationally predicted structure and the experimentally determined structure, where 100 represents a complete matc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knotted Protein
Knotted proteins are proteins whose backbones entangle themselves in a knot. One can imagine pulling a protein chain from both termini, as though pulling a string from both ends. When a knotted protein is “pulled” from both termini, it does not get disentangled. Knotted proteins are very rare, making up only about one percent of the proteins in the Protein Data Bank, and their folding mechanisms and function are not well understood. Although there are experimental and theoretical studies that hint to some answers, systematic answers to these questions have not yet been found. Although number of computational methods have been developed to detect protein knots, there are still no completely automatic methods to detect protein knots without necessary manual intervention due to the missing residues or chain breaks in the X-ray structures or the nonstandard PDB formats. Most of the knots discovered in proteins are deep trefoil (31) knots. Figure eight knots (41), three-twist kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups. In inorganic chemistry, the anion appears in a few rare minerals, but the functional group has tremendous importance in biochemistry. Disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Compounds of the form are usually called ''persulfides'' instead. Organic disulfides Structure Disulfides have a C–S–S–C dihedral angle approaching 90°. The S–S bond length is 2.03 Å in diphenyl disulfide, similar to that in elemental sulfur. Disulfides are usually symmetric but they can also be unsymmetric. Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organosulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopf Link
In mathematics, mathematical knot theory, the Hopf link is the simplest nontrivial link (knot theory), link with more than one component. It consists of two circles linked together exactly once, and is named after Heinz Hopf. Geometric realization A concrete model consists of two unit circles in perpendicular planes, each passing through the center of the other.. See in particulap. 77 This model minimizes the ropelength of the link and until 2002 the Hopf link was the only link whose ropelength was known. The convex hull of these two circles forms a shape called an oloid. Properties Depending on the relative Orientation (geometry), orientations of the two components the linking number of the Hopf link is ±1. The Hopf link is a (2,2)-torus link with the braid word :\sigma_1^2.\, The knot complement of the Hopf link is R × ''S''1 × ''S''1, the Cylinder (geometry), cylinder over a torus. This space has a Geometrization conjecture, locally Euc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis Suppressor
A metastasis suppressor is a protein that acts to slow or prevent metastases (secondary tumors) from spreading in the body of an organism with cancer. Metastasis is one of the most lethal cancer processes. This process is responsible for about ninety percent of human cancer deaths. Proteins that act to slow or prevent metastases are different from those that act to suppress tumor growth. Genes for about a dozen such proteins are known in humans and other animals. Background The treatment of cancer usually aims to destroy and/or stop the growth of the primary tumor. Major improvements in the methods of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy have taken place, but corresponding improvements in patient survival have not always followed. Treatments that focus on the primary cancer typically do not address metastasis. Metastasis suppressors act by different mechanisms than tumor suppressors and do not affect primary tumors. Tumor suppressors, however, also inhibit metastasis, since meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptin
Leptin (from Ancient Greek, Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small"), also known as obese protein, is a protein hormone predominantly made by adipocytes (cells of adipose tissue). Its primary role is likely to regulate long-term Energy homeostasis, energy balance. As one of the major signals of energy status, leptin levels influence appetite, Hunger (physiology), satiety, and motivated behaviors oriented toward the maintenance of energy reserves (e.g., feeding, foraging behaviors). The amount of circulating leptin correlates with the amount of energy reserves, mainly Triglyceride, triglycerides stored in adipose tissue. High leptin levels are interpreted by the brain that energy reserves are high, whereas low leptin levels indicate that energy reserves are low, in the process adapting the organism to Starvation response, starvation through a variety of metabolic, endocrine, neurobiochemical, and behavioral changes. Leptin is coded for by the ''LEP'' gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |