|
Common Moorhen
The common moorhen (''Gallinula chloropus''), also known as the waterhen, is a bird species in the Rail (bird), rail family (Rallidae). It is distributed across many parts of the Old World, across Africa, Europe, and Asia. It lives around well-vegetated marshes, ponds, canals and other wetlands. The species is not found in the polar regions or many tropical rainforests; generally it is one of the commonest Old World rail species, together with the Eurasian coot in some regions. Taxonomy The common moorhen was Species description, formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. He placed it in the genus ''Fulica (genus), Fulica'' and coined the binomial nomenclature, binomial name ''Fulica chloropus''. The common moorhen is now one of five extant species placed in the genus ''Gallinula'' that was introduced in 1760 by the French zoologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson. The genus name is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
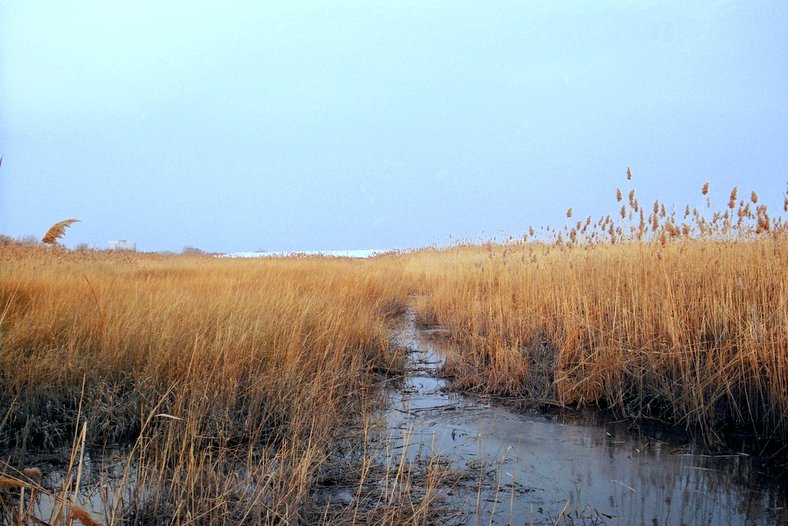
Habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as Biophysical environment, environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and Luminous intensity, light intensity. Biotic index, Biotic factors include the availability of food and the presence or absence of Predation, predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, habitat generalist species are able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species require a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of Habitat (ecology), habitat found in upland (geology), upland areas in temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands and the biomes of montane grasslands and shrublands, characterised by low-growing vegetation on Soil pH, acidic soils. Moorland today generally means uncultivated hill land (such as Dartmoor in South West England), but also includes low-lying wetlands (such as Sedgemoor, also South West England). It is closely related to heath, although experts disagree on the exact distinction between these types of vegetation. Generally, moor refers to Highland (geography), highland and high rainfall areas, while heath refers to lowland zones which are more likely to be the result of human activity. Moorland habitats are found mainly in Tropics, tropical Africa, Northern Europe, northern and western Europe, and South America. Most of the world's moorlands are diverse ecosystems. In the extensive moorlands of the tropics, biodiversity can be extremely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in general, the word can be used for any low-lying and seasonally waterlogged terrain. In Europe and in agricultural literature low-lying meadows that require draining and embanked polderlands are also referred to as marshes or marshland. Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dusky Moorhen
The dusky moorhen (''Gallinula tenebrosa'') is a bird species in the rail family and is one of the eight extant species in the moorhen genus. It occurs in India, Australia, New Guinea, Borneo and Indonesia. It is often confused with the purple swamphen and the Eurasian coot due to similar appearance and overlapping distributions. They often live alongside birds in the same genus, such as the Tasmanian nativehen and the common moorhen. Taxonomy John Gould described the dusky moorhen in 1846 from a skin collected along the Murray River in South Australia. Its species name is derived from the Latin ''tenebrosa'' "dark". Charles Lucien Bonaparte described ''Gallinula haematopus'' in 1856, but this is now a ''nomen nudum''. Gregory Mathews described two subspecies that have been synonymized—''magnirostris'' from Western Australia and ''subfrontata'' from New South Wales. Three subspecies are recognised: subspecies ''frontata'' from southeastern Borneo, the Sunda Islands, Timor a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristan Da Cunha
Tristan da Cunha (), colloquially Tristan, is a remote group of volcano, volcanic islands in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is one of three constituent parts of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, with its own constitution. The territory consists of the inhabited island Tristan da Cunha, which has a diameter of roughly and an area of ; the wildlife reserves of Gough Island and Inaccessible Island; and the smaller, uninhabited Nightingale Islands. , the main island had 250 permanent inhabitants, who all carry British Overseas Territories citizenship. The other islands are uninhabited, except for the South African personnel of a weather station on Gough Island. As there is no airstrip on the island, the only way of travelling to or from Tristan is by ship. There are six-day journeys from Cape Town, South Africa, and some cruises offered departing from Ushuaia, Argentina. History Discovery The islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gough Moorhen
The Gough moorhen (''Gallinula comeri'') is a medium-sized, almost flightless bird that is similar to the common moorhen (''Gallinula chloropus''), but is smaller, stockier, and has shorter wings. The bird has a distinctive yellow-tipped red bill and red frontal shield. Its first account was written in 1888 by the polar explorer George Comer, whom the specific name ''comeri'' commemorates. This bird is found only on two remote islands in the South Atlantic. The Gough moorhen was originally endemic to Gough Island, but in 1956 was introduced to Tristan da Cunha, an island in the same archipelago which was formerly home of the now extinct Tristan moorhen (''Galinula nesiotis''). On the basis of DNA sequencing of both recently collected and historical material from both of the archipelago's moorhen species, Groenenberg ''et al'' (2008) concluded that the genetic distances between ''G. nesiotis'' and ''G. comeri'' are of at least the same size as those found between subspecie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristan Moorhen
The Tristan moorhen or Tristan gallinule (''Gallinula nesiotis'') is an extinct species of flightless rail endemic to the South Atlantic island of Tristan da Cunha. It was very similar to the Gough moorhen of Gough Island, located to the southeast. The once abundant Tristan moorhen had become rare by 1873, and by the end of 19th century it was extinct as a result of hunting, predation by introduced species (rats, cats and pigs) and habitat destruction by fire. A handful of taxidermied specimens of the Tristan moorhen have been preserved. In 1956 the closely related Gough moorhen ''G. comeri'' was introduced to Tristan da Cunha, under the then belief it was a reintroduction of the same species. On the basis of DNA sequencing of both recently collected and historical material from both species, Groenenberg ''et al'' (2008) concluded that the genetic distances between ''G. nesiotis'' and ''G. comeri'' are of at least the same size as those found between subspecies of ''G. chloropu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16th century, the term "New World" has been used to describe the Western Hemisphere, often referred to as the Americas. Since the 18th century, it has come to represent the United States, which was initially colonial British America until it established independence following the American Revolutionary War. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term arose in the early 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |