|
Common Indo-European Religion
Proto-Indo-European mythology is the body of myths and deities associated with the Proto-Indo-Europeans, speakers of the hypothesized Proto-Indo-European language. Although the mythological motifs are not directly attested – since Proto-Indo-European speakers lived in preliterate societies – scholars of comparative mythology have reconstructed details from inherited similarities in mythological concepts found in Indo-European languages, based on the assumption that parts of the Proto-Indo-Europeans' original belief systems survived in the daughter traditions. The Proto-Indo-European pantheon includes a number of securely reconstructed deities, since they are both cognates—linguistic siblings from a common origin—and associated with similar attributes and body of myths: such as , the daylight-sky god; his consort , the earth mother; his daughter , the dawn goddess; his sons the Divine Twins; and and , a solar deity and moon deity, respectively. Some deities, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manu And Yemo
*' and *' are thought to have been a duo in Proto-Indo-European mythology. In the creation myth, Manu kills Yemo as a foundational part of the origin of the universe. is sometimes also interpreted as a primordial hermaphrodite. The comparative analysis of different Indo-European tales has led scholars to reconstruct an original Proto-Indo-European creation myth involving twin brothers, *' ('Man') and *' ('Twin'), as the progenitors of the world and mankind, and a hero named *' ('Third') who ensured the continuity of the original sacrifice. Although some thematic parallels can be made with Ancient Near East (the primordial couple Adam and Eve), and even Polynesian or South American legends, the linguistic correspondences found in descendant cognates of *''Manu'' and *' make it very likely that the myth discussed here has a Proto-Indo-European (PIE) origin. Following a first paper on the cosmogonical legend of Manu and Yemo, published simultaneously with Jaan Puhvel in 1975 (w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creation Myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop through oral traditions and therefore typically have multiple versions." While in popular usage the term ''myth'' often refers to false or fanciful stories, members of cultures often ascribe varying degrees of truth to their creation myths. In the society in which it is told, a creation myth is usually regarded as conveying profound truthsmetaphorically, symbolically, historically, or literally. They are commonly, although not always, considered cosmogonical mythsthat is, they describe the ordering of the cosmos from a state of chaos or amorphousness. Creation myths often share several features. They often are considered sacred accounts and can be found in nearly all known religious traditions. They are all storie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trito (Proto-Indo-European Mythology)
''*Trito'' is a significant figure in Proto-Indo-European mythology, representing the first warrior and acting as a culture hero. He is connected to other prominent characters, such as Manu and Yemo, and is recognized as the protagonist of the myth of the warrior function, establishing the model for all later men of arms. In the legend, Trito is offered cattle as a divine gift by celestial gods, which is later stolen by a three-headed serpent named *'' H₂n̥gʷʰis'' ('serpent'). Despite initial defeat, Trito, fortified by an intoxicating drink and aided by the Sky-Father, or alternatively the Storm-God or ''*H₂nḗr'', 'Man', together they go to a cave or a mountain, and the hero overcomes the monster and returns the recovered cattle to a priest for it to be properly sacrificed. He is now the first warrior, maintaining through his heroic deeds the cycle of mutual giving between gods and mortals. Scholars have interpreted the story of Trito either as a cosmic conflict between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graeco-Aryan
Graeco-Aryan, or Graeco-Armeno-Aryan, is a hypothetical clade within the Indo-European family that would be the ancestor of Hellenic, Armenian, and the Indo-Iranian languages, which spans Southern Europe, Armenian highlands and Southern Asian regions of Eurasia. The Graeco-Armeno-Aryan group supposedly branched off from the parent Indo-European stem by the mid-3rd millennium BC. Relation to the possible homeland In the context of the Kurgan hypothesis, Graeco-Aryan is also known as "Late Proto-Indo-European" or "Late Indo-European" to suggest that Graeco-Aryan forms a dialect group, which corresponds to the latest stage of linguistic unity in the Indo-European homeland in the early part of the 3rd millennium BC. By 2500 BC, Proto-Greek and Proto-Indo-Iranian had separated and moved respectively westward and eastward from the Pontic Steppe. If Graeco-Aryan is a valid group, Grassmann's law may have a common origin in Greek and Sanskrit. However, Grassmann's law in Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
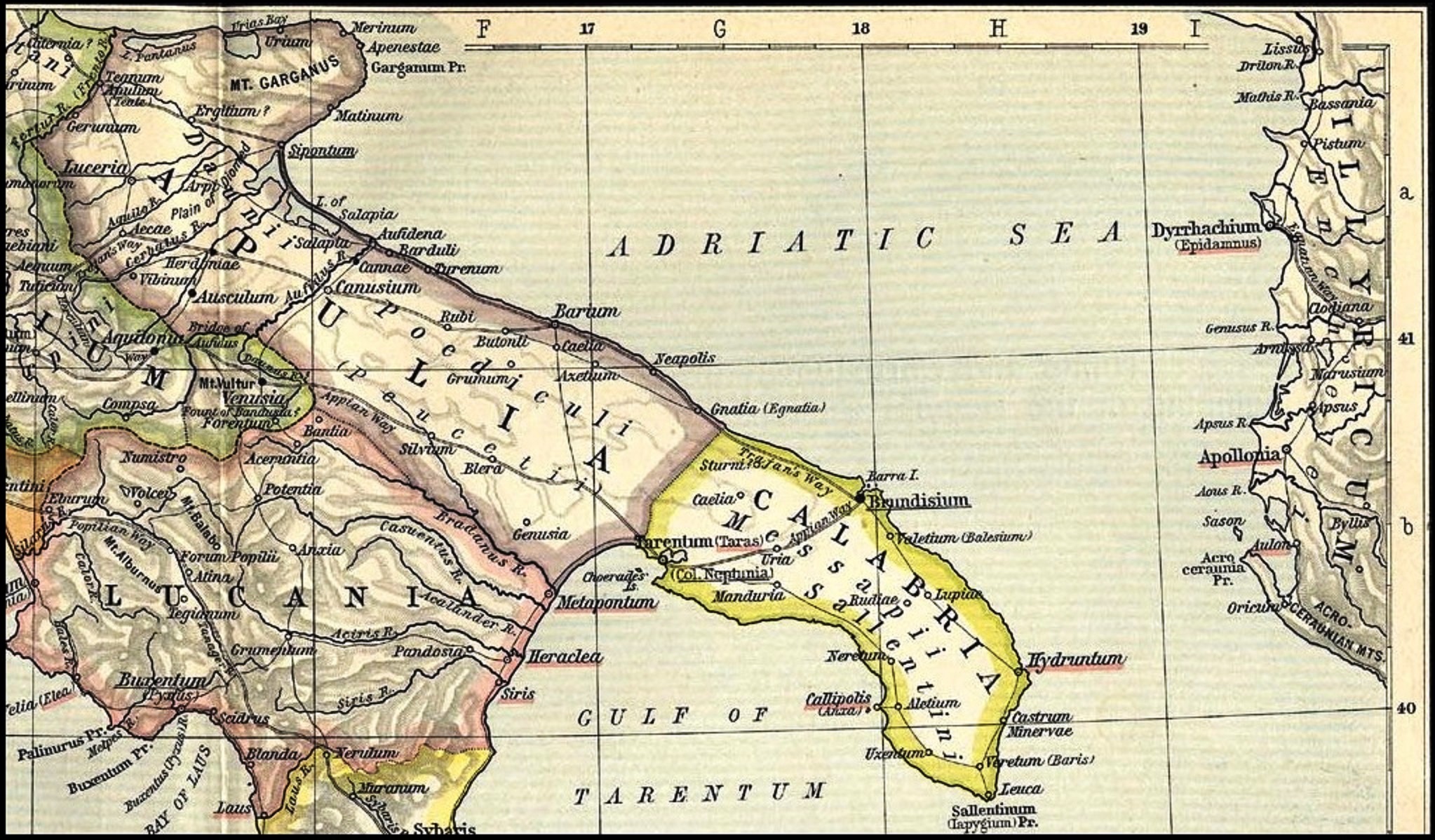
Messapic Language
Messapic (; also known as Messapian; or as Iapygian) is an extinct Indo-European Paleo-Balkanic language of the southeastern Italian Peninsula, once spoken in Salento by the Iapygian peoples of the region: the Calabri and Salentini (known collectively as the Messapians), the Peucetians and the Daunians. Messapic was the pre- Roman, non- Italic language of Apulia. It has been preserved in about 600 inscriptions written in an alphabet derived from a Western Greek model and dating from the mid-6th to at least the 2nd century BC, when it went extinct following the Roman conquest of the region. Name The term 'Messapic' or 'Messapian' is traditionally used to refer to a group of languages spoken by the Iapygians, a "relatively homogeneous linguistic community" of non- Italic-speaking tribes ( Messapians, Peucetians and Daunians) dwelling in the region of Apulia before the Roman conquest. However, some scholars have argued that the term ' Iapygian languages' should be prefer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaulish Language
Gaulish is an extinct Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the west bank of the Rhine). In a wider sense, it also comprises varieties of Celtic that were spoken across much of central Europe (" Noric"), parts of the Balkans, and Anatolia (" Galatian"), which are thought to have been closely related. The more divergent Lepontic of Northern Italy has also sometimes been subsumed under Gaulish. Together with Lepontic and the Celtiberian spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, Gaulish is a member of the geographic group of Continental Celtic languages. The precise linguistic relationships among them, as well as between them and the modern Insular Celtic languages, are uncertain and a matter of ongoing debate because of their spar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetic Language
Venetic ( ) is an extinct Indo-European language, most commonly classified into the Italic subgroup, that was spoken by the Veneti people in ancient times in northeast Italy (Veneto and Friuli) and part of modern Slovenia, between the Po Delta and the southern fringe of the Alps, associated with the Este culture. The language is attested by over 300 short inscriptions dating from the 6th to the 1st century BCE. Its speakers are identified with the ancient people called '' Veneti'' by the Romans and ''Enetoi'' by the Greeks. It became extinct around the 1st century when the local inhabitants assimilated into the Roman sphere. Inscriptions dedicating offerings to Reitia are one of the chief sources of knowledge of the Venetic language. Linguistic classification Venetic is a centum language. The inscriptions use a variety of the Northern Italic alphabet, similar to the Etruscan alphabet. The exact relationship of Venetic to other Indo-European lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather God
A weather god or goddess, also frequently known as a storm god or goddess, is a deity in mythology associated with weather phenomena such as thunder, snow, lightning, rain, wind, storms, tornadoes, and hurricanes. Should they only be in charge of one feature of a storm, they will be called after that attribute, such as a rain god or a lightning/thunder god. This singular attribute might then be emphasized more than the generic, all-encompassing term "storm god", though with thunder/lightning gods, the two terms seem interchangeable. They feature commonly in polytheism, polytheistic religions, especially in Proto-Indo-European mythology, Proto-Indo-European ones. Storm gods are most often conceived of as wielding thunder and/or lightning (some lightning gods' names actually mean "thunder", but since one cannot have thunder without lightning, they presumably wielded both). The ancients didn't seem to differentiate between the two, which is presumably why both the words "lightning bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |