|
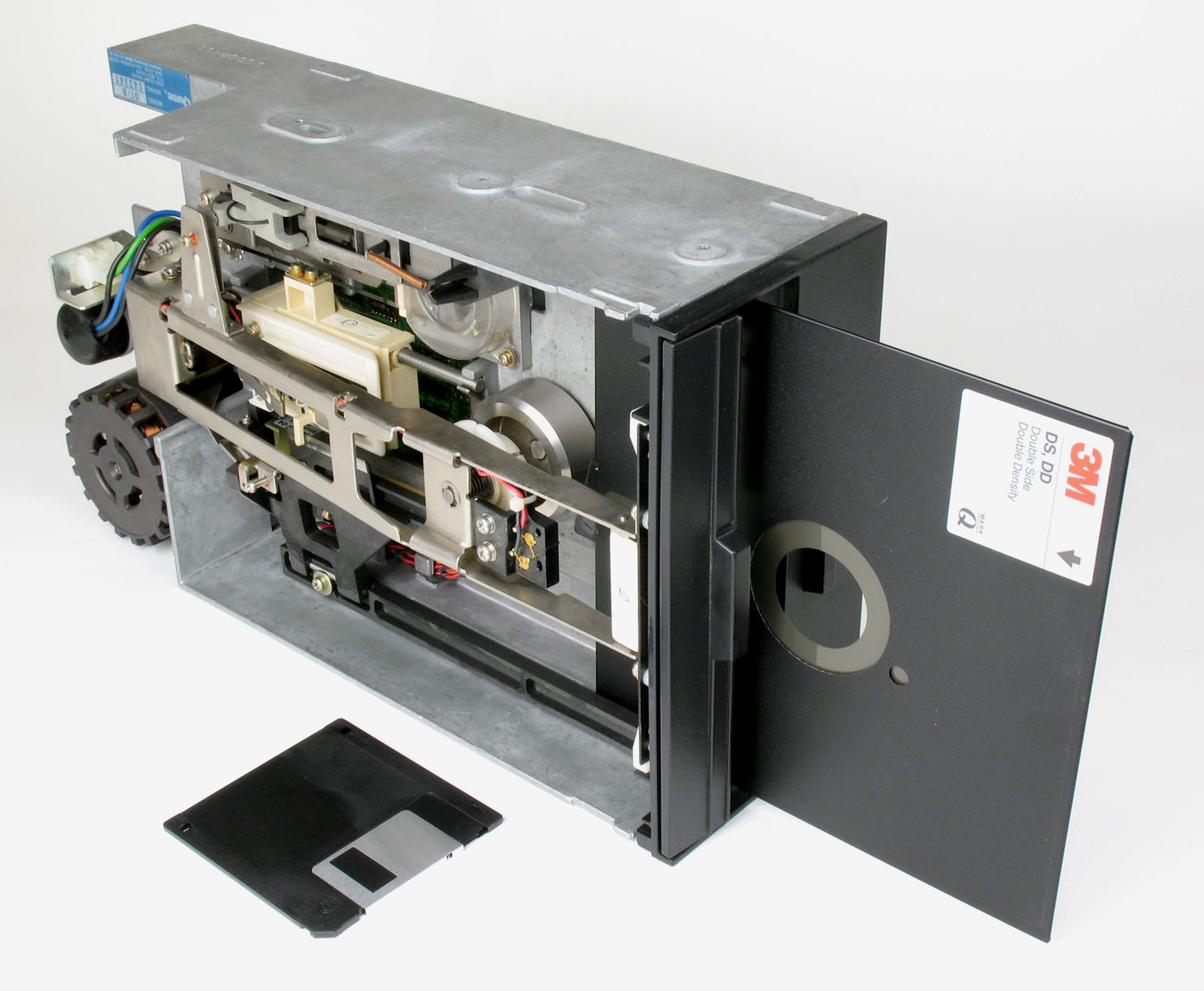
Commodore 1551
The Commodore 1551 (originally introduced as the SFS 481) is a floppy disk drive for the Commodore Plus/4 home computer. It resembles a charcoal-colored Commodore 1541 and plugs into the cartridge port, providing faster access than the C64/1541 combination. Commodore reportedly planned an interface to allow use of the 1551 with the C64, but it was never released. Aside from faster access, the drive is very similar to the 1541. Like the 1541, it is a single-sided 170-kilobyte drive for 5¼" disks, with each disk split into 664 256-byte blocks available for user data plus 19 blocks for DOS data and directory; the file system makes each block its own cluster. Hardware The disk drive uses group coded recording and contains an MOS Technology 6510T processor as a disk controller. The 6510T is a specialized version of the 6510 processor used in the C64, and it is only used in the 1551. The DOS limits the number of files per disk to 144 regardless of the number of free blocks on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for Computer data storage, digital information. The International System of Units (SI) defines the prefix ''kilo-, kilo'' as a multiplication factor of 1000 (103); therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information science and technology, International Electrotechnical Commission (2008). The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. In some areas of information technology, particularly in reference to random-access memory capacity, ''kilobyte'' instead often refers to 1024 (210) bytes. This arises from the prevalence of sizes that are powers of two in modern digital memory architectures, coupled with the coincidence that 210 differs from 103 by less than 2.5%. The kibibyte is defined as 1024 bytes, avoiding the ambiguity issues of the ''kilobyte''.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodore International
Commodore International Corporation was a home computer and electronics manufacturer with its head office in The Bahamas and its executive office in the United States founded in 1976 by Jack Tramiel and Irving Gould. It was the successor company to Commodore Business Machines (Canada) Ltd., established in 1958 by Tramiel and Manfred Kapp. Commodore International (CI), along with its U.S. subsidiary Commodore Business Machines, Inc. (CBM), was a significant participant in the development of the home computer industry, and at one point in the 1980s was the world's largest in the industry. The company released its first home computer, the Commodore PET, in 1977; it was followed by the VIC-20, the first ever computer to reach one million units of sales. In 1982, the company developed and marketed the world's best selling computer, the Commodore 64; its success made Commodore one of the world's largest personal computer manufacturers, with sales peaking in the last quarter of 1983 at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Centre For Computing History
The Centre for Computing History is a computer museum in Cambridge, England, established to create a permanent public exhibition telling the story of the Information Age. Overview The museum acts as a repository for vintage computers and related artefacts. The museum is open Wednesdays through to Sundays from 10am to 5pm in term time and 7 days a week during school holidays. On display are key items from the early era of computers (and even before) from ageing comptometers through the Altair 8800 to the ZX Spectrum and Apple II. The museum also holds vintage games consoles, peripherals, vintage software, software and an extensive collection of computer manuals, magazines and other literature. It is home to the Megaprocessor, an enormous version of a computer chip designed by James Newman. History and status The centre is a Charitable organization, registered educational charity. It is funded by a combination of sponsors from local businesses and private individuals. Venture ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
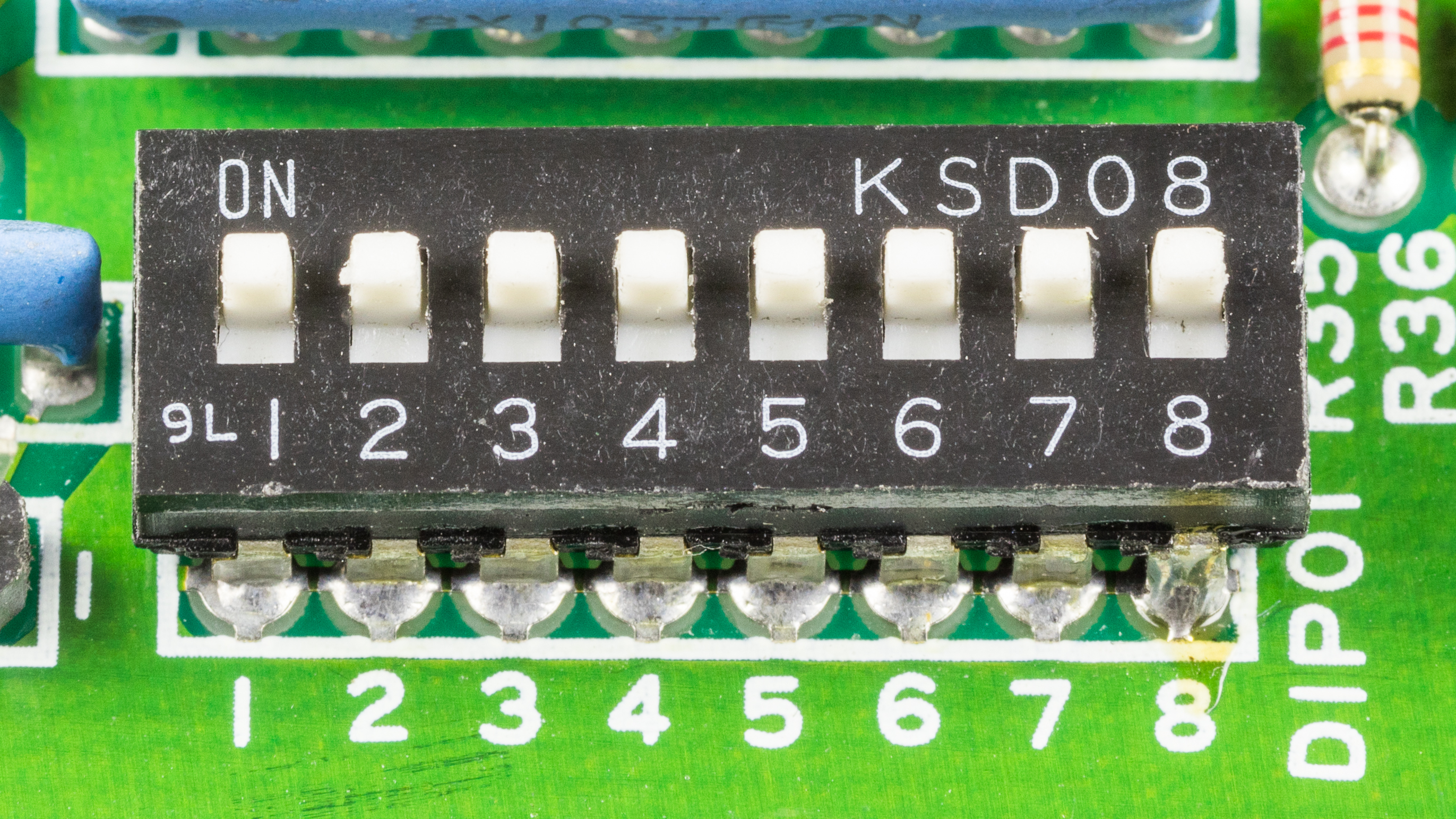
DIP Switch
A DIP switch is a manual electric switch that is packaged with others in a group in a standard dual in-line package (DIP). The term may refer to each individual switch, or to the unit as a whole. This type of switch is designed to be used on a printed circuit board along with other electronics, electronic components and is commonly used to customize the behavior of an electronic device for specific situations. DIP switches are an alternative to jumper (computing), jumper blocks. Their main advantages are that they are quicker to change and there are no parts to lose. History US patent 3621157, filed in 1970 by Pierre Schwab,U.S. Patent 3621157. "Miniature switch with multiple cam-operated switch contacts", filed June 1, 1970. is the earliest known DIP switch patent, which discloses a rotary style DIP switch. US patent 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Controller
A disk controller is a controller circuit that enables a CPU to communicate with a hard disk, floppy disk or other kind of disk drive. It also provides an interface between the disk drive and the bus connecting it to the rest of the system.{{Cite book , url=https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/955038 , access-date=2023-10-18 , date=2001 , doi=10.1109/ICCD.2001.955038 , s2cid=3084914 , language=en-US , last1=Jeppesen , first1=J. , last2=Allen , first2=W. , last3=Anderson , first3=S. , last4=Pilsl , first4=M. , title=Proceedings 2001 IEEE International Conference on Computer Design: VLSI in Computers and Processors. ICCD 2001 , chapter=Hard disk controller: The disk drive's brain and body , pages=262–267 , isbn=0-7695-1200-3 Early disk controllers were identified by their storage methods and data encoding. They were typically implemented on a separate controller card. Modified frequency modulation (MFM) controllers were the most common type in small computers, used for bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as the Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words of 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48, or 60 bits, corresponding t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in the Guinness World Records as the highest-selling single computer model of all time, with independent estimates placing the number sold between 12.5 and 17 million units. Volume production started in early 1982, marketing in August for . Preceded by the VIC-20 and Commodore PET, the C64 took its name from its of RAM. With support for multicolor sprite (computer graphics), sprites and a custom chip for waveform generation, the C64 could create superior visuals and audio compared to systems without such custom hardware. The C64 dominated the low-end computer market (except in the UK, France and Japan, lasting only about six months in Japan) for most of the later years of the 1980s. For a substantial period (1983–1986), the C64 had betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOS Technology 6510
300px, Internals of a Commodore 64 showing the 6510 CPU (40-pin DIP, lower left). The chip on the right is the 6581 SID. The production week/year (WWYY) of each chip is given below its name. The MOS Technology 6510 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by MOS Technology. It is a modified form of the very successful 6502. The 6510 is widely used in the Commodore 64 (C64) home computer and its variants. It is also used in the Seagate ST-251 MFM hard disk. The primary change from the 6502 is the addition of an 8-bit general purpose I/O port, although 6 I/O pins are available in the most common version of the 6510. In addition, the address bus can be made tri-state and the CPU can be halted cleanly. Use In the C64, the extra I/O pins of the processor are used to control the computer's memory map by bank switching, and for controlling three of the four signal lines of the Datasette tape recorder (the electric motor control, key-press sensing and write data lines; the read data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a single, non-technical user. These computers were a distinct market segment that typically cost much less than business, scientific, or engineering-oriented computers of the time, such as those running CP/M or the IBM PC, and were generally less powerful in terms of computer memory, memory and expandability. However, a home computer often had better video display controller, graphics and sound than contemporary business computers. Their most common uses were word processing, playing video games, and computer programming, programming. Home computers were usually sold already manufactured in stylish metal or plastic enclosures. However, some home computers also came as commercial electronic kits, like the ZX80, Sinclair ZX80, which were both h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |