|
Comes Theodosius
Count Theodosius (; died 376), Flavius Theodosius or Theodosius the Elder (), was a senior military officer serving Valentinian I () and the Western Roman Empire during Late Antiquity. Under his command the Roman army defeated numerous threats, incursions, and usurpations. Theodosius was patriarch of the imperial Theodosian dynasty () and father of the emperor Theodosius the Great (). Appointed '' comes rei militaris per Britannias'' (commander of mobile military forces for the Diocese of the Britains) by Valentinian, Theodosius put down the Great Conspiracy (367–368) and the usurpation of Valentinus. After restoring order in Britain he returned to continental Europe and fought against the Alemanni; as Valentinian's ''magister equitum'' (Master of Horse) he successfully invaded Alemannic territory (371 or 370). In 372 Theodosius led a successful campaign against the Sarmatians. Within the same year Firmus, a Mauritanian prince, rebelled against Roman rule with the help of Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
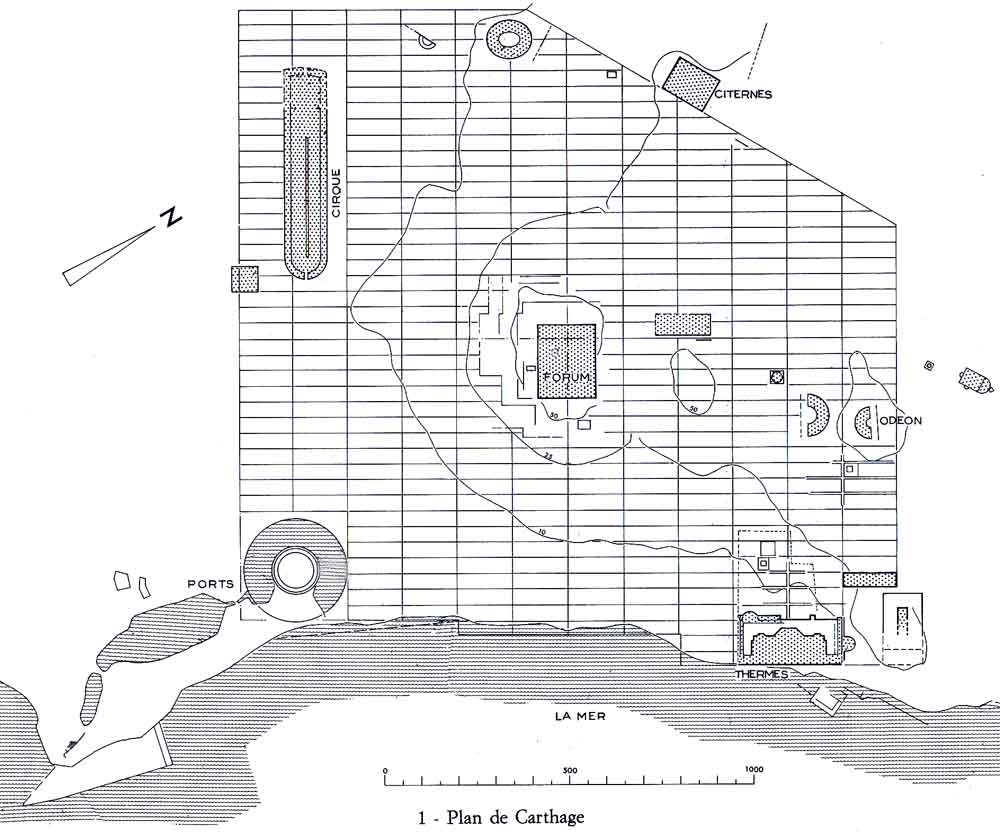
Roman Carthage
Roman Carthage was an important city in ancient Rome, located in modern-day Tunisia. Approximately 100 years after the destruction of Punic Carthage in 146 BC, a new city of the same name (Latin '' Carthāgō'') was built on the same land by the Romans in the period from 49 to 44 BC. By the 3rd century, Carthage had developed into one of the largest cities of the Roman Empire, with a population of several hundred thousand.Likely the fourth city in terms of population during the imperial period, following Rome, Alexandria and Antioch, in the 4th century also surpassed by Constantinople; also of comparable size were Ephesus, Smyrna and Pergamum. Stanley D. Brunn, Maureen Hays-Mitchell, Donald J. Zeigler (eds.), ''Cities of the World: World Regional Urban Development'', Rowman & Littlefield, 2012p. 27/ref> It was the center of the Roman province of Africa, which was a major breadbasket of the empire. Carthage briefly became the capital of a usurper, Domitius Alexander, in 308&nda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firmus (4th-century Usurper)
Firmus (died 375) was a Berber Numidian prince and Roman usurper under Valentinian I. Firmus was the son of the Berber Jubaleni prince Nubel, a powerful Roman military officer, as well as a wealthy Christian. When Nubel died, Firmus killed his half-brother Zammac, who had illegitimately appropriated Nubel's wealth, and became successor to his father. Between 372 and 375, Firmus revolted against the '' comes Africae'' Romanus, who was a supporter of Zammac. The misbehaviour of Romanus, who had neglected protection from African tribes to Roman cities that had refused the payment of bribes, had worsened the situation in Africa Province in the 360s. The revolt of Firmus against Romanus forced Valentinian to take action against both his officer and the African rebel. When Valentinian sent Count Theodosius (father of Theodosius I) to depose Romanus, Firmus initially professed his willingness to compromise, and appeared on the verge of reaching an honorable settlement with Valentinian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, also known as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest Sea lane, shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel aided the United Kingdom in becoming a naval superpower, serving as a natural defence against invasions, such as in the Napoleonic Wars and in the World War II, Second World War. The northern, English coast of the Channel is more populous than the southern, French coast. The major languages spoken in this region are English language, English and French language, French. Names Roman historiography, Roman sources as (or , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulogne-sur-Mer
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; ; ; or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Hauts-de-France, Northern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the Côte d'Opale, a touristic stretch of French coast on the English Channel between Calais and Normandy, and the most visited location in the region after the Lille conurbation. Boulogne is its department's second-largest city after Calais, and the 183rd-largest in France.Téléchargement du fichier d'ensemble des populations légales en 2017 Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques, INSEE It is also the country's largest fishing port, specialising in herring. Boulogne is an ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comitatensis
The ''comitatenses'' and later the ''Palatini (Roman military), palatini'' were the units of the field armies of the late Roman Empire. They were the soldiers that replaced the Legionary, legionaries, who had formed the backbone of the Roman military since the late republic. Organization Units such as the Jovians and Herculians, Joviani and Herculiani had 5,000 soldiers and 726–800 cavalrymen. Many units' sizes would vary. There were three types of units, the heavy infantry, Infantry, medium infantry, and light infantry. The ''comitatenses'' were the heavy infantry. The auxiliaries, ''auxilia palatina'', and the ''peltasts'' were the medium infantry, and the ''psiloi'' were the light infantry. ''Comitatenses'' regiments consisted of 1,024 soldiers. ''Comitatenses'' legions could consist of 6,000 to 7,000 soldiers. Some of these soldiers would be lightly armed, while others would be heavily armed. During a battle the army would divide into 3-4 divisions. The army might use a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. This material culture was found throughout Gaul and as far east as modern-day southern Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary. Warbands led by the Gaul Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennos Battle of the Allia, sacked Rome in 387 BC, becoming the only time Rome was conquered by a foreign enemy in 800 years. However, Gallia Cisalpina was conquered by the Romans in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comes Rei Militaris
''Comes'' (plural ''comites''), translated as count, was a Roman title, generally linked to a comitatus or comital office. The word ''comes'' originally meant "companion" or "follower", deriving from "''com-''" ("with") and "''ire''" ("go"). The special lasting meaning derives from the position of a follower within a ''comitatus'', which was a retinue, or group of followers, such as those of magnates. In some instances these were sufficiently large and/or formal to justify specific denomination, such as a "''cohors amicorum''". The word ''comes'' is the origin of the much later terms for counts within the medieval nobility, and counties as their territorial jurisdictions. Ancient Roman religion ''Comes'' was a common epithet or title that was added to the name of a hero or god in order to denote relation with another god. The coinage of Roman Emperor Constantine I declared him "''comes''" to Sol Invictus ("Unconquered Sun") ''qua'' god. Imperial Roman curial titles and of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). Written in Latin and known as the '' Res gestae'', his work chronicled the history of Rome from the accession of Emperor Nerva in 96 to the death of Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Only the sections covering the period 353 to 378 survive. Biography Ammianus was born in the East Mediterranean, possibly in Syria or Phoenicia, around 330, into a noble family of Greek origin. Since he calls himself ''Graecus'' ( Greek), he was most likely born in a Greek-speaking area of the empire. His native language was Greek, but he also knew Latin. The surviving books of his history cover the years 353 to 378. Ammianus began his career as a military officer in the Praetorian Guard, where he gained firsthand exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . Especially in earlier medieval periods the term often implied not only a certain status, but also that the ''count'' had specific responsibilities or offices. The etymologically related English term " county" denoted the territories associated with some countships, but not all. The title of ''count'' is typically not used in England or English-speaking countries, and the term ''earl'' is used instead. A female holder of the title is still referred to as a ''countess'', however. Origin of the term The word ''count'' came into English from the French ', itself from Latin '—in its accusative form ''comitem''. It meant "companion" or "attendant", and as a title it indicated that someone was delegated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinian II
Valentinian II (; 37115 May 392) was a Roman emperor in the western part of the Roman Empire between AD 375 and 392. He was at first junior co-ruler of his half-brother, then was sidelined by a usurper, and finally became sole ruler after 388, albeit with limited ''de facto'' powers. A son of emperor Valentinian I and empress Justina, he was raised to the imperial office at the age of four by military commanders upon his father's death. Until 383, Valentinian II remained a junior partner to his older half-brother Gratian in ruling the Western empire, while the East was governed by his uncle Valens until 378 and Theodosius I from 379. When the usurper emperor Magnus Maximus killed Gratian in 383, the court of Valentinian II in Milan became the locus of confrontations between adherents to Nicene and Arian Christianity. In 387, Maximus invaded Italy, spurring Valentinian II and his family to escape to Thessalonica where they successfully sought Theodosius's aid. Theodosius def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratian
Gratian (; ; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian was raised to the rank of ''Augustus'' as a child and inherited the West after his father's death in 375. He nominally shared the government with his infant half-brother Valentinian II, who was also acclaimed emperor in Pannonia on Valentinian's death. The East was ruled by his uncle Valens, who was later succeeded by Theodosius I. Gratian subsequently led a campaign across the Rhine, attacked the Lentienses, and forced the tribe to surrender. That same year, the eastern emperor Valens was killed fighting the Goths at the Battle of Adrianople, which led to Gratian elevating Theodosius to replace him in 379. Gratian favoured Nicene Christianity over traditional Roman religion, issuing the Edict of Thessalonica, refusing the office of '' pontifex maximus'', and removing the Altar of Victory from the Roman Senate's Curia Julia. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |