|
Colorimetric
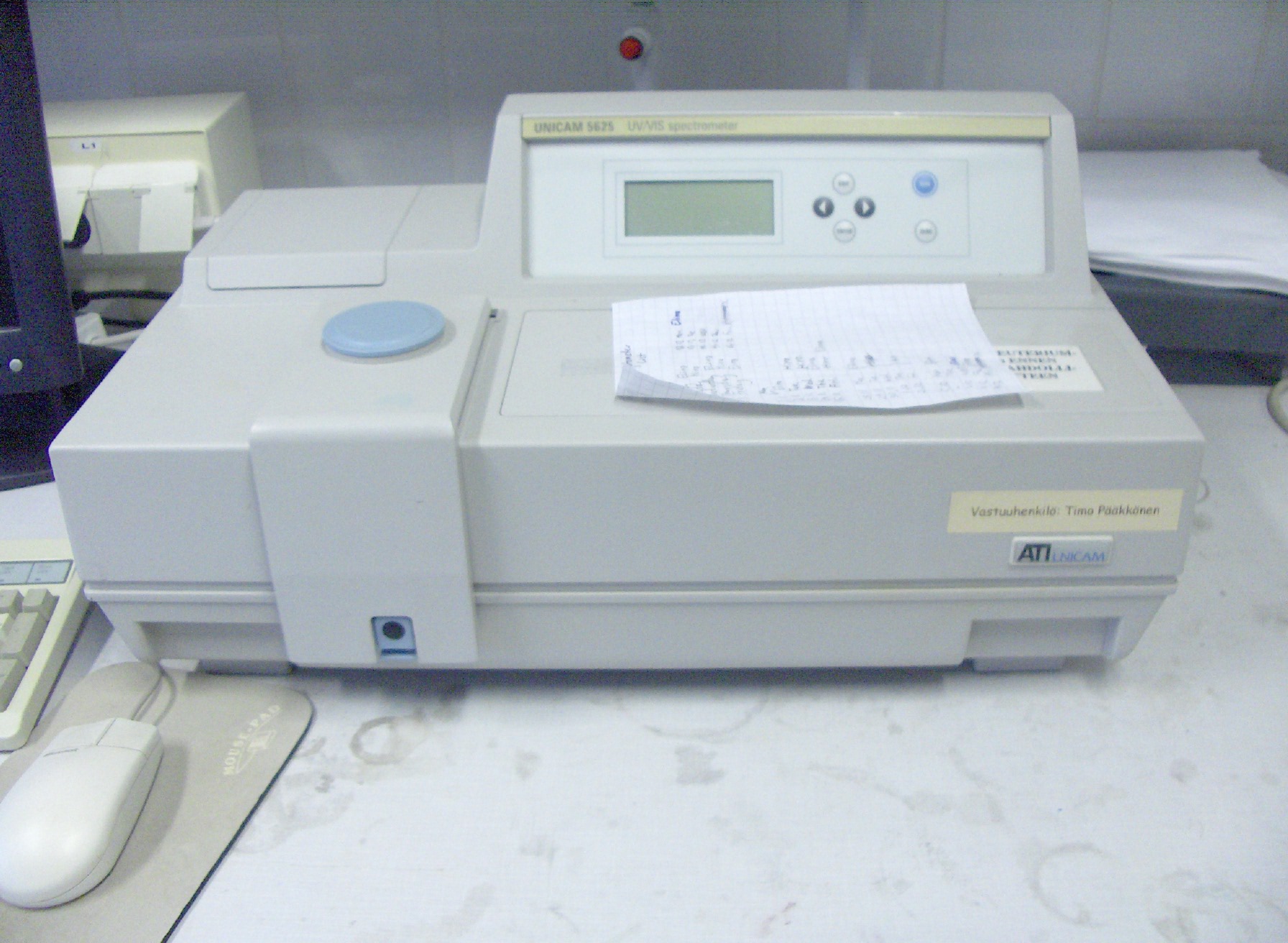
Colorimetry is "the science and technology used to quantify and describe physically the human color perception". It is similar to spectrophotometry, but is distinguished by its interest in reducing spectra to the physical correlates of color perception, most often the CIE 1931 XYZ color space tristimulus values and related quantities. History The Duboscq colorimeter was invented by Jules Duboscq in 1870. Instruments Colorimetric equipment is similar to that used in spectrophotometry. Some related equipment is also mentioned for completeness. * A tristimulus colorimeter measures the tristimulus values of a color. * A spectroradiometer measures the absolute spectral radiance (intensity) or irradiance of a light source. * A spectrophotometer measures the spectral reflectance, transmittance, or relative irradiance of a color sample. * A ''spectrocolorimeter'' is a spectrophotometer that can ''calculate'' tristimulus values. * A densitometer measures the degree of lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristimulus
In 1931, the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) published the CIE 1931 color spaces which define the relationship between the visible spectrum and human color vision. The CIE color spaces are mathematical models that comprise a "standard observer", which is a static idealization of the color vision of a normal human. A useful application of the CIEXYZ colorspace is that a mixture of two colors in some proportion lies on the straight line between those two colors. One disadvantage is that it is not perceptually uniform. This disadvantage is remedied in subsequent color models such as CIELUV and CIELAB, but these and modern color models still use the CIE 1931 color spaces as a foundation. The CIE (from the French name " Commission Internationale de l'éclairage" - International Commission on Illumination) developed and maintains many of the standards in use today relating to colorimetry. The CIE color spaces were created using data from a series of experiments, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
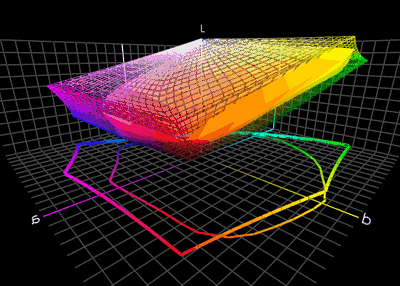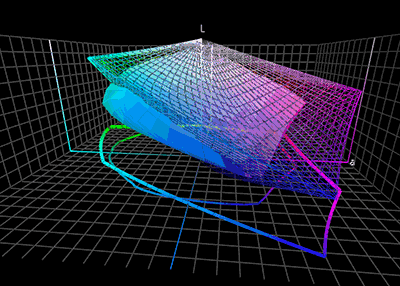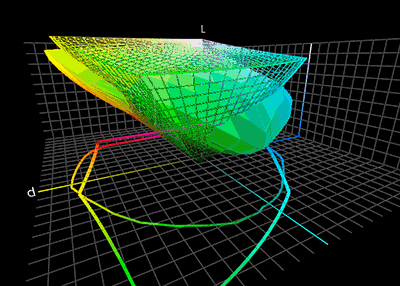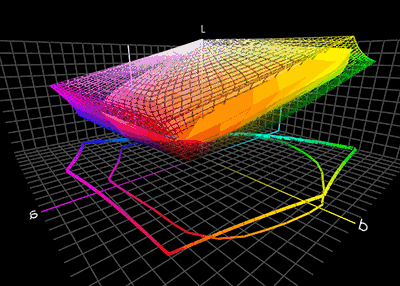
Color Translation
Color management is the process of ensuring consistent and accurate colors across various devices, such as monitors, printers, and cameras. It involves the use of color profiles, which are standardized descriptions of how colors should be displayed or reproduced. Color management is necessary because different devices have different color capabilities and characteristics. For example, a monitor may display colors differently than a printer can reproduce them. Without color management, the same image may appear differently on different devices, leading to inconsistencies and inaccuracies. To achieve color management, a color profile is created for each device involved in the color workflow. This profile describes the device's color capabilities and characteristics, such as its color gamut (range of colors it can display or reproduce) and color temperature. These profiles are then used to translate colors between devices, ensuring consistent and accurate color reproduction. Colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIE 1931 Color Space
In 1931, the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) published the CIE 1931 color spaces which define the relationship between the visible spectrum and human color vision. The CIE color spaces are mathematical models that comprise a "standard observer", which is a static idealization of the color vision of a normal human. A useful application of the CIEXYZ colorspace is that a mixture of two colors in some proportion lies on the straight line between those two colors. One disadvantage is that it is not perceptually uniform. This disadvantage is remedied in subsequent color models such as CIELUV and CIELAB, but these and modern color models still use the CIE 1931 color spaces as a foundation. The CIE (from the French name " Commission Internationale de l'éclairage" - International Commission on Illumination) developed and maintains many of the standards in use today relating to colorimetry. The CIE color spaces were created using data from a series of experiments, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as spectrophotometers, that can measure the intensity of a light beam at different wavelengths. Although spectrophotometry is most commonly applied to ultraviolet, Visible spectrum, visible, and infrared radiation, modern spectrophotometers can interrogate wide swaths of the electromagnetic spectrum, including x-ray, ultraviolet, Visible spectrum, visible, infrared, or microwave wavelengths. Overview Spectrophotometry is a tool that hinges on the quantitative analysis of molecules depending on how much light is absorbed by colored compounds. Important features of spectrophotometers are spectral bandwidth (the range of colors it can transmit through the test sample), the percentage of sample transmission, the logarithmic range of sample absorptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICC Profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the device source or target color space and a ''profile connection space'' (PCS). This PCS is either CIELAB (L*a*b*) or CIEXYZ. Mappings may be specified using tables, to which interpolation is applied, or through a series of parameters for transformations. Every device that captures or displays color can be profiled. Some manufacturers provide profiles for their products, and there are several products that allow an end-user to generate their own color profiles, typically through the use of a tristimulus colorimeter or a spectrophotometer (sometimes called a spectrocolorimeter). The ICC defines the format precisely but does not define algorithms or processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristimulus Colorimeter
A tristimulus colorimeter, colloquially shortened to ''colorimeter'' or ''colourimeter'', is used in digital imaging to profile and calibrate output devices. It takes a limited number of wideband spectral energy readings along the visible spectrum by using filtered photodetectors; e.g. silicon photodiodes. A colorimeter with the known value of absolute error allows measuring (x,y)-chromaticity coordinates in red, green, blue and white colors. Measured values are used for calculation of LCD profile coefficients. Originally, three glass filters whose transmittance spectra mimicked the CIE color matching functions (shown below) were employed. A filter bank may be used to decompose the individual color matching functions if more accuracy is desired. A camera or colorimeter is said to be ''colorimetric'' if it satisfies the by (1868–1945) (also called the "Maxwell–Ives criterion"), reducing observer metamerism color errors, if the product of the spectral responsivity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Integration
In analysis, numerical integration comprises a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral. The term numerical quadrature (often abbreviated to quadrature) is more or less a synonym for "numerical integration", especially as applied to one-dimensional integrals. Some authors refer to numerical integration over more than one dimension as cubature; others take "quadrature" to include higher-dimensional integration. The basic problem in numerical integration is to compute an approximate solution to a definite integral :\int_a^b f(x) \, dx to a given degree of accuracy. If is a smooth function integrated over a small number of dimensions, and the domain of integration is bounded, there are many methods for approximating the integral to the desired precision. Numerical integration has roots in the geometrical problem of finding a square with the same area as a given plane figure ('' quadrature'' or ''squaring''), as in the quadrature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromaticity
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance. Chromaticity consists of two independent parameters, often specified as '' hue'' (''h'') and ''colorfulness'' (''s''), where the latter is alternatively called ''saturation'', ''chroma'', ''intensity'', or '' excitation purity''. This number of parameters follows from trichromacy of vision of most humans, which is assumed by most models in color science. Quantitative description In color science, the white point of an illuminant or of a display is a neutral reference characterized by a chromaticity; all other chromaticities may be defined in relation to this reference using polar coordinates. The ''hue'' is the angular component, and the ''purity'' is the radial component, normalized by the maximum radius for that hue. ''Purity'' is roughly equivalent to the term '' saturation'' in the HSV color model. The property '' hue'' is as used in general color theory and in specific c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Calibration
The aim of color calibration is to measure and/or adjust the color response of a device (input or output) to a known state. In International Color Consortium (ICC) terms, this is the basis for an additional color characterization of the device and later profiling. In non-ICC workflows, calibration sometimes refers to establishing a known relationship to a standard color space in one go. The device that is to be calibrated is sometimes known as a ''calibration source''; the color space that serves as a standard is sometimes known as a ''calibration target''. Color calibration is a requirement for all devices taking an active part in a color management, color-managed workflow and is used by many industries, such as television production, gaming, photography, engineering, chemistry, medicine, and more. Information flow and output distortion Input data can come from device sources like digital cameras, image scanners, or any other measuring devices. Those inputs can be either mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRT Phosphors
CRT or Crt most commonly refers to: * Cathode-ray tube, a display * Critical race theory, an academic framework of analysis CRT may also refer to: Law * Charitable trust#charitable remainder trust, Charitable remainder trust, United States * Civil Resolution Tribunal, Canada * Columbia River Treaty, Canada–US, 1960s Science, technology, and mathematics Medicine and biology * Calreticulin, a protein *Capillary refill time, for blood to refill capillaries *Cardiac resynchronization therapy and CRT defibrillator (CRT-D) *Central venous catheter#Catheter-related thrombosis, Catheter-related thrombosis, the development of a blood clot related to long-term use of central venous catheters *Certified Respiratory Therapist *Chemoradiotherapy, chemo- and radiotherapy combined * Cognitive Retention Therapy, for dementia * Corneal Refractive Therapy, in optometrics * CRT (genetics), a gene cluster Social sciences * Cognitive reflection test, in psychology * Current reality tree (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
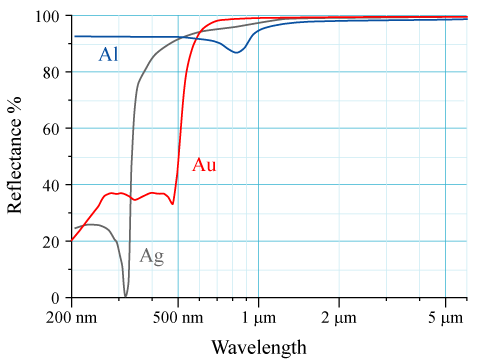
Reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in Reflection (physics), reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |