|
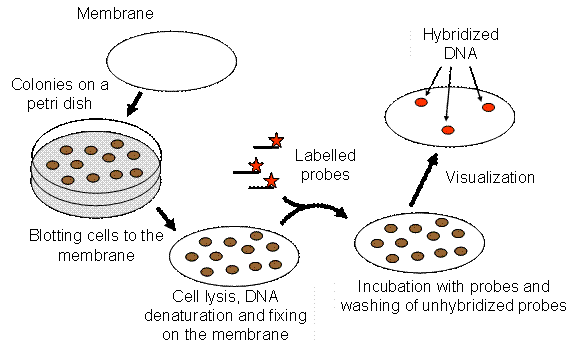
Colony Hybridization
Colony hybridization is a method of selecting bacterial colonies with desired genes through a straightforward cloning and transfer process. The genes of interest have been added to a bacterial plasmid previously through recombination, allowing genes from other organisms to be analyzed within a bacterial colony. The overall process involves a transfer of genetic material from one medium to another, typically using nitrocellulose filter paper, with the intended goal of identifying and isolating a specific gene. Radiographed RNA is used to find the desired sequence within the new bacterial colony and essentially "light it up" so that the sequence can be identified for transfer. The most common purpose of colony hybridization is to verify that a certain DNA sequence was able to successfully enter into a new cell, meaning that the cells being analyzed through this method are the result of recombination between a specific piece of DNA and a bacterial plasmid. This method was discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blot Hybridization
Blot may refer to: Surname *Guillaume Blot (born 1985), French racing cyclist *Harold W. Blot (born 1938), served as United States Deputy Chief of Staff for Aviation *Jean-François Joseph Blot (1781–1857), French soldier and politician *Yvan Blot (1948–2018), French conservative political figure, founder and president of the Club de l'Horloge *Jean Blot (1923–2019), French writer, translator, and senior civil servant of Russian origin * (born 1983), French judoka Other *Blot (biology), method of transferring proteins, DNA, RNA or a protein onto a carrier *Blót, a sacrifice to the gods or other beings in Germanic paganism and Germanic neopaganism **Blot (album), ''Blot'' (album), a 2003 album by Einherjer, referring to the Germanic practice *''The Blot'', a 1921 silent film *Another name of a trick-taking card game Belot *Blot (Transformers), a character from the Transformers franchise *Ink blots, as used in the Rorschach test * Blot (1994 film), ''Blot'' (1994 film), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining at least two fragments from two different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, and differ only in the nucleotide sequence within that identical overall structure. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA, because they can be made of material from two different species, like the mythical chimera. R-DNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA may be joined to ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss '' Physcomitrella patens''. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells. The two major types of growth media are those used for cell culture, which use specific cell types derived from plants or animals, and those used for microbiological culture, which are used for growing microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi. The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths and agar plates; specialized media are sometimes required for microorganism and cell culture growth. Some organisms, termed fastidious organisms, require specialized environments due to complex nutritional requirements. Viruses, for example, are obligate intracellular parasites and require a growth medium containing living cells. Types The most common growth me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Grunstein
Michael Grunstein (born 1946, in Romania) is a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Biological Chemistry at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. The only surviving child of Holocaust survivors, he obtained his Bachelor of Science degree from McGill University in Montreal, and his PhD from the University of Edinburgh, Scotland. He did his post-doctoral training at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California, where he invented the colony hybridization screening technique for recombinant DNAs in David Hogness' laboratory. After coming to UCLA in 1975, Grunstein pioneered the genetic analysis of histones in yeast and showed for the first time that histones are regulators of gene activity in living cells. His laboratory's studies provided inspiration for the eukaryotic histone code and underlie the modern study of epigenetics. His work, which "catapulted the field forward", was recognized in 2018 with the Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research. Honors and awards *200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hogness
David Swenson Hogness (November 17, 1925 – December 24, 2019) was an American biochemist, geneticist, and developmental biologist and emeritus professor at the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California. Life Hogness spent most of his youth in Chicago, the son of Thorfin R. Hogness and Phoebe S. Hogness. His parents were both children of immigrants and graduates of the University of Minnesota; his father later received a PhD in chemistry from the University of California at Berkeley, taught at Berkeley and in 1930 joined the faculty at the University of Chicago. After service in the Navy, David Hogness acquired his bachelor's degree in chemistry in 1949 at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech); and in 1952, his PhD in biology and chemistry. As a postdoctoral fellow, he worked with a scholarship of the National Research Council with Jacques Monod at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, and with a grant from the National Science Foundation at the New Yor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrocellulose
Nitrocellulose (also known as cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, pyroxylin and flash string, depending on form) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid. One of its first major uses was as guncotton, a replacement for gunpowder as propellant in firearms. It was also used to replace gunpowder as a low-order explosive in mining and other applications. In the form of collodion it was also a critical component in an early photographic emulsion, the use of which revolutionized photography in the 1860s. Production The process uses a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to convert cellulose into nitrocellulose. The quality of the cellulose is important. Hemicellulose, lignin, pentosans, and mineral salts give inferior nitrocelluloses. In precise chemical terms, nitrocellulose is not a nitro compound, but a nitrate ester. The glucose repeat unit (anhydroglucose) within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysis
Lysis ( ) is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ''lysate''. In molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell biology laboratories, cell cultures may be subjected to lysis in the process of purifying their components, as in protein purification, DNA extraction, RNA extraction, or in purifying organelles. Many species of bacteria are subject to lysis by the enzyme lysozyme, found in animal saliva, egg white, and other secretions. Phage lytic enzymes (lysins) produced during bacteriophage infection are responsible for the ability of these viruses to lyse bacterial cells. Penicillin and related β-lactam antibiotics cause the death of bacteria through enzyme-mediated lysis that occurs after the drug causes the bacterium to form a defective cell wall. If the cell wall is completely lost and the penicillin was used on gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid Hybridization
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to: *Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom * Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA Nucleus may also refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Astronomy *Active galactic nucleus in astronomy *Comet nucleus, the solid, central part of a comet Biology * Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA *Nucleus (neuroanatomy), a cluster of cell bodies of neurons in the central nervous system *Nucleus that forms in the eye in nuclear sclerosis (early cataracts) *''Nucleus'', a scientific journal concerned with the cell nucleus; published by Taylor & Francis *Nucleus, a small colony of honeybees, induced to raise a new queen by the beekeeper Computer systems * Nucleus (operating system), sometimes a synonym for kernel * Nucleus CMS, a weblog system * Nucleus RTOS, a real-time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoradiography
An autoradiograph is an image on an X-ray film or nuclear emulsion produced by the pattern of decay emissions (e.g., beta particles or gamma rays) from a distribution of a radioactive substance. Alternatively, the autoradiograph is also available as a digital image (digital autoradiography), due to the recent development of scintillation gas detectors or rare earth phosphorimaging systems. The film or emulsion is apposed to the labeled tissue section to obtain the autoradiograph (also called an autoradiogram). The ''auto-'' prefix indicates that the radioactive substance is within the sample, as distinguished from the case of historadiography or microradiography, in which the sample is marked using an external source. Some autoradiographs can be examined microscopically for localization of silver grains (such as on the interiors or exteriors of cells or organelles) in which the process is termed micro-autoradiography. For example, micro-autoradiography was used to examine wheth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |