|
Collision Domain
A collision domain is a network segment (connected by a shared medium or through repeaters) where simultaneous data transmissions collide with one another as a result of more than one device attempting to send a packet on the network segment at the same time. The collision domain applies particularly in wireless networks, but also affected early versions of Ethernet. Members of a collision domain may be involved in collisions with one another. Devices outside the collision domain do not have collisions with those inside. A channel access method dictates that only one device in the collision domain may transmit at any one time, and the other devices in the domain listen to the network and refrain from transmitting while others are already transmitting in order to avoid collisions. Because only one device may be transmitting at any one time, total network bandwidth is shared among all devices on the collision domain. Collisions also decrease network efficiency in a collision domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Segment
A network segment is a portion of a computer network. The nature and extent of a segment depends on the nature of the network and the device or devices used to interconnect end stations. Ethernet According to the defining IEEE 802.3 standards for Ethernet, a network segment is an ''electrical connection'' between networked devices using a shared medium. In the original 10BASE5 and 10BASE2 Ethernet varieties, a segment would therefore correspond to a single coax cable and all devices tapped into it. At this point in the evolution of Ethernet, multiple network segments could be connected with repeaters (in accordance with the 5-4-3 rule for 10 Mbit Ethernet) to form a larger collision domain. With twisted-pair Ethernet, electrical segments can be joined using repeaters or repeater hubs as can other varieties of Ethernet. This corresponds to the extent of an OSI layer 1 network and is equivalent to the collision domain. The 5-4-3 rule applies to this collision domain. Usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in small office/home office, home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, restaurants, hotels, libraries, and airports. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term "''Wi-Fi Certified''" to products that successfully complete Interoperability Solutions for European Public Administrations, interoperability certification testing. Non-compliant hardware is simply referred to as WLAN, and it may or may not work with "''Wi-Fi Certified''" devices. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Coordination Function
Point Coordination Function (PCF) is a media access control (MAC) technique used in IEEE 802.11 based WLANs, including Wi-Fi. It resides in a point coordinator also known as access point (AP), to coordinate the communication within the network. The AP waits for PIFS duration rather than DIFS duration to grasp the channel. PIFS is less than DIFS duration and hence the point coordinator always has the priority to access the channel. The PCF is located directly above the distributed coordination function (DCF), in the IEEE 802.11 MAC Architecture. Channel access in PCF mode is centralized and hence the point coordinator sends CF-Poll frame to the PCF capable station to permit it to transmit a frame. In case the polled station does not have any frames to send, then it must transmit null frame. Due to the priority of PCF over DCF, stations that only use DCF might not gain access to the medium. To prevent this, a repetition interval has been designed to cover both (Contention free) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Multimedia Extensions
Wireless Multimedia Extensions (WME), also known as Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM), is a Wi-Fi Alliance interoperability certification, based on the IEEE 802.11e standard. It provides basic Quality of service (QoS) features to IEEE 802.11 networks. WMM prioritizes traffic according to four Access Categories (AC): voice (AC_VO), video (AC_VI), best effort (AC_BE), and background (AC_BK). However, it does not provide guaranteed throughput. It is suitable for well-defined applications that require QoS, such as Voice over IP (VoIP) on Wi-Fi phones ( VoWLAN). WMM replaces the Wi-Fi DCF distributed coordination function for CSMA/CA wireless frame transmission with Enhanced Distributed Coordination Function (EDCF). EDCF, according to version 1.1 of the WMM specifications by the Wi-Fi Alliance, defines Access Categories labels AC_VO, AC_VI, AC_BE, and AC_BK for the Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) parameters that are used by a WMM-enabled station to control how long it sets its Tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
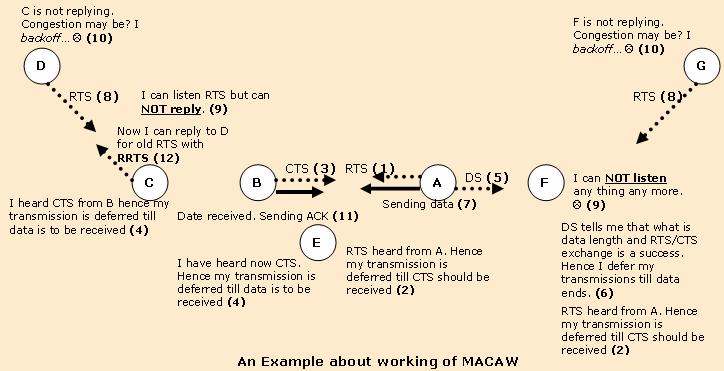
Multiple Access With Collision Avoidance For Wireless
Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance for Wireless (MACAW) is a slotted medium access control (MAC) protocol widely used in ad hoc networks. Furthermore, it is the foundation of many other MAC protocols used in wireless sensor networks (WSN). The IEEE 802.11 RTS/CTS mechanism is adopted from this protocol. It uses ''RTS-CTS-DS-DATA-ACK'' frame sequence for transferring data, sometimes preceded by an ''RTS-RRTS'' frame sequence, in view to provide solution to the hidden node problem. Although protocols based on MACAW, such as S-MAC, use carrier sense in addition to the RTS/CTS mechanism, MACAW does not make use of carrier sense. Principles of operation Assume that node A has data to transfer to node B. Node A initiates the process by sending a ''Request to Send'' frame (RTS) to node B. The destination node (node B) replies with a ''Clear To Send'' frame (CTS). After receiving CTS, node A sends data. After successful reception, node B replies with an acknowledgement frame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Node Problem
In wireless networking, the hidden node problem or hidden terminal problem occurs when a Node (networking), node can communicate with a wireless access point (AP), but cannot directly communicate with other nodes that are communicating with that AP. This leads to difficulties in medium access control sublayer since multiple nodes can send data packets to the AP simultaneously, which creates interference at the AP resulting in no packet getting through. Although some loss of packets is normal in wireless networking, and the higher layers will resend them, if one of the nodes is transferring a lot of large packets over a long period, the other node may get very little goodput. Practical protocol solutions exist to the hidden node problem. For example, IEEE 802.11 RTS/CTS, Request To Send/Clear To Send (RTS/CTS) mechanisms where nodes send short packets to request permission of the access point to send longer data packets. As responses from the AP are seen by all the nodes, the node ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier-sense Multiple Access With Collision Avoidance
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) in computer networking, is a link layer multiple access method in which carrier sensing is used. Under CSMA/CA, nodes attempt to avoid collisions by beginning transmission only after the channel is sensed to have no traffic. When they do transmit, nodes transmit frames in their entirety. This technique is primarily used in wireless networks, where the alternative with collision detection CSMA/CD is not possible due to wireless transmitters de-sensing (turning off) their receivers during packet transmission. CSMA/CA is unreliable due to the hidden node problem. Details Collision avoidance is used to improve the performance of the CSMA method by attempting to divide the channel somewhat equally among all transmitting nodes within the collision domain. # Carrier Sense: prior to transmitting, a node first listens to the shared medium (such as listening for wireless signals in a wireless network) to determine whet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless LAN
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network (LAN) within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building. This gives users the ability to move around within the area and remain connected to the network. Through a Gateway (telecommunications), gateway, a WLAN can also provide a connection to the wider Internet. Wireless LANs based on the IEEE 802.11 standards are the most widely used computer networks in the world. These are commonly called Wi-Fi, which is a trademark belonging to the Wi-Fi Alliance. They are used for home and small office networks that link together laptop computers, printer (computing), printers, smartphones, Web TVs and gaming devices through a Wireless router, wireless network router, which in turn may link them to the Internet. Hotspot (Wi-Fi), Hotspots provided by routers at restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, libraries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wifi Hidden Station Problem
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in small office/home office, home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, restaurants, hotels, libraries, and airports. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term "''Wi-Fi Certified''" to products that successfully complete Interoperability Solutions for European Public Administrations, interoperability certification testing. Non-compliant hardware is simply referred to as WLAN, and it may or may not work with "''Wi-Fi Certified''" devices. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. The first standard for faster 10 Gigabit Ethernet was approved in 2002. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented Physical layer, physical and Data link layer, link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to . The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Duplex
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow for simultaneous communication in both directions between two connected parties or to provide a reverse path for the monitoring and remote adjustment of equipment in the field. There are two types of duplex communication systems: full-duplex (FDX) and half-duplex (HDX). In a full-duplex system, both parties can communicate with each other simultaneously. An example of a full-duplex device is plain old telephone service; the parties at both ends of a call can speak and be heard by the other party simultaneously. The earphone reproduces the speech of the remote party as the microphone transmits the speech of the local party. There is a two-way communication channel between them, or more strictly speaking, there are two communication channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |