|
Colegio Mayor De San Ildefonso
The ''Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso'' (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso'') is a historic college and building located in Alcalá de Henares, Spain. It was declared ''Bien de Interés Cultural'' in 1914. Construction The college was built by Francisco Jiménez de Cisneros, Cardinal Cisneros, who commissioned architect Pedro de Gumiel, designing it in the Purism (Spanish architecture), purism style. The foundation stone was laid in 1499, the Saint Ildefonsus` Chapel was completed in 1510; in 1516 began construction of the ''Paraninfo'' (Auditorium) and in 1537 Rodrigo Gil de Hontañón designed the main façade. Although most of the work had been carried out by 1617 when Juan Gómez de Mora redesigned the courtyard (Thomas of Villanova's courtyard), the construction was not finished until the second half of the 17th century. Royal reform of 1666 In 1666, the ''Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso'' underwent one of the most comprehensive institutional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
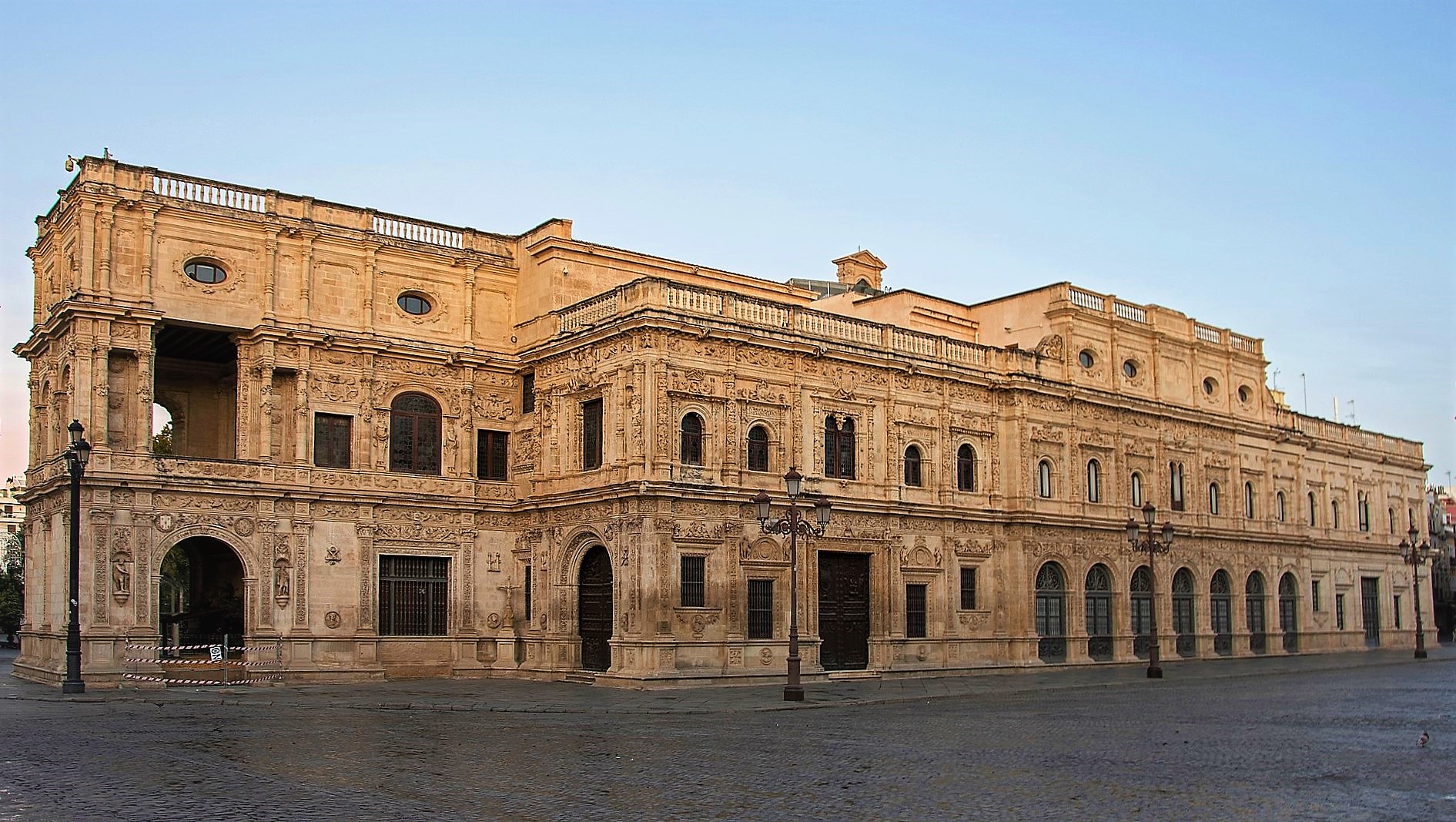
Alcalá De Henares
Alcalá de Henares () is a Spanish municipality of the Community of Madrid. Housing is primarily located on the right (north) bank of the Henares River, Henares. , it has a population of 193,751, making it the region's third-most populated Municipalities in Spain, municipality. Predated by earlier hilltop settlements (''oppidum, oppida'') and the primitive ''Complutum'' on the left bank of the Henares, the new Roman settlement of ''Complutum'' was founded in the mid 1st century on the right bank (north) river meadow, becoming a bishopric seat in the 5th century. One of the several Muslim citadels in the Central March, Middle March of al-Andalus (hence the name ''Alcalá'', a derivative of the Arabic term for citadel) was established on the left bank, while, after the Christian conquest culminated , the bulk of the urban nucleus returned to the right bank. For much of the late middle-ages and the early modern period before becoming part of the province of Madrid, Alcalá de Henares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip IV Of Spain
Philip IV (, ; 8 April 160517 September 1665), also called the Planet King (Spanish: ''Rey Planeta''), was King of Spain from 1621 to his death and (as Philip III) King of Portugal from 1621 to 1640. Philip is remembered for his patronage of the arts, including such artists as Diego Velázquez, and his rule over Habsburg Spain, Spain during the Thirty Years' War. By the time of his death, the Spanish Empire had reached approximately 12.2 million square kilometres (4.7 million square miles) in area but in other aspects was in Decline of Spain, decline, a process to which Philip contributed with his inability to achieve successful domestic and military reform. He was succeeded on his death by his young son Charles II of Spain, Charles II as King of Spain and in 1640 (with the collapse of the Iberian Union) by John IV of Portugal, John IV as King of Portugal. Personal life Philip IV was born in the Royal Palace of Valladolid, and was the eldest son of Philip III of Spai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateresque Architecture In The Community Of Madrid
Plateresque, meaning "in the manner of a silversmith" (''plata'' being silver in Spanish), was an artistic movement, especially architectural, developed in Spain and its territories, which appeared between the late Gothic and early Renaissance in the late 15th century and spread over the next two centuries. It is a modification of Gothic spatial concepts and an eclectic blend of Mudéjar, Flamboyant, Gothic, and Lombard decorative components, as well as Renaissance elements of Tuscan origin.Bozal, Valeriano; ''Art history in Spain: From the origins to the Enlightenment'', pp. 157, 165. Ed Akal (1978). . Examples of this syncretism are the inclusion of shields and pinnacles on façades, columns built in the Renaissance neoclassical manner, and façades divided into three parts (in Renaissance architecture they are divided into two). It reached its peak during the reign of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor,Arellano, Fernando; ''The Hispanic American Art'', pp. 13–14. Ed. Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In The Community Of Madrid
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to Spain and the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy, also known as the Rex Catholicissimus, Catholic Monarchy, in the period from 1516 to 1700 when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. In this period the Spanish Empire was at the zenith of its influence and power. During this period, Spain held many territories, including American continental holdings and the Spanish West Indies, West Indies; European territories like the Habsburg Netherlands, Low Countries, Council of Italy, Italian territories, Iberian Union, Portugal and parts of County of Burgundy, France; and the Captaincy General of the Philippines, Philippines and other possessions in Southeast Asia. The period of Spanish history has also been referred to as the "Age of Discovery, Age of Expansion". The Habsburg name was not always used by the family members, who often emphasized their more prestigious princely titles. The dynasty was long known as the "House of Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Castile
The Council of Castile (), known earlier as the Royal Council (), was a ruling body and key part of the domestic government of the Crown of Castile, second only to the monarch himself. It was established under Isabella I in 1480 as the chief body dealing with administrative and judicial matters of the realm. With the 1516 ascension of Charles I (later Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor) to the throne of both Castile and Aragon, the Royal Council came to be known as the Council of Castile because Charles was king of many dominions other than Castile, while the Council retained responsibility only over Castile. During periods in which there was no monarch, an absent monarch, or an incompetent monarch, the Royal Council would rule as a regency council in his place. The Council weakened in the 19th century, where it was abolished and re-established several times before being dissolved permanently. History Origins The earliest form of the Royal Council was created at the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Reform Of The Colegio Mayor De San Ildefonso
The royal reform of the ''Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso'' (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Reales estatutos hechos por Su Majestad para el gobierno del Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso'') also known as the reform of García de Medrano was a comprehensive institutional reorganization of the principal college of the University of Alcalá, University of Alcalá de Henares, formally enacted on 4 November 1666 by direct order of the Crown of Castile, Spanish Crown following a Decree, royal decree issued on 27 August 1665. The reform was designed and implemented by García de Medrano y Álvarez de los Ríos, a Doctor of Canons and professor of canon law at the University of Salamanca, and a senior jurist of the Royal Council of Castile, who was appointed by King Philip IV of Spain to address the college's declining academic standards, administrative disorder, and lax discipline. The resulting body of legislation—consisting of 82 detailed statutes—regulated all aspects of college life, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
García De Medrano Y Álvarez De Los Ríos
García de Medrano y Álvarez de los Ríos, Lord of San Gregorio (Valladolid, 20 July 1604 – 3 September 1683) was a prominent Spanish Nobility, nobleman, Politician, statesman and jurist from the House of Medrano, holding numerous high-ranking positions throughout his career. He served as regent and interim viceroy of the Kingdom of Navarre, ''Fiscal'' (prosecutor), mayor and regent of Seville, and professor at the University of Salamanca. In 1657, he presided over the Hall of Mayors of Castile and led significant reforms of the colleges in Spain, including a Royal reform of the Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso, royal reform of the ''Colegio Mayor de San Ildefonso'' at the University of Alcalá in 1666. He was also a Knight of the Order of Santiago, perpetual ''regidor'' of Soria and procurator in the ''Cortes'', crime prosecutor of the ''Real Audiencia, Royal Audiencia and Chancery'' of Valladolid, auditor of Valladolid, auditor of the Council of Finance and the Council of the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decree
A decree is a law, legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state, judge, monarch, royal figure, or other relevant Authority, authorities, according to certain procedures. These procedures are usually defined by the constitution, Legislative Law, Legislative laws, or customary laws of a government. Belgium In Belgium, a decree is a law of a Communities, regions and language areas in Belgium, community or regional parliament, e.g. the Flemish Parliament. Catholic Church A decree (Ecclesiastical Latin, Latin: ''decretum'') in the usage of the canon law (Catholic Church), canon law of the Catholic Church has various meanings. Any papal bull, papal brief, brief, or motu proprio is a decree inasmuch as these documents are legislative acts of the pope. In this sense, the term is quite ancient. The Roman Congregations were formerly empowered to issue decrees in matters which come under their particular jurisdiction but were forbidden from continuing to do so under Pope Benedic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform
Reform refers to the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The modern usage of the word emerged in the late 18th century and is believed to have originated from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement, which identified "Parliamentary Reform" as its primary aim. Reform is generally regarded as antithetical to revolution. Developing countries may implement a range of reforms to improve living standards, often with support from international financial institutions and aid agencies. This can involve reforms to macroeconomic policy, the civil service, and public financial management. In politics, there is debate over what constitutes reform vs. revolution, and whether all changes labeled "reform" actually represent progress. For example, in the United States, proponents of term limits or rotation in office consider it a revolutionary method (advocated as early as the Articles of Confederation) for rooting out government corruption by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |