|
Cohors VI Delmatarum Equitata
Cohors sexta Delmatarum equitata ("6th part-mounted Cohort of Dalmatae") was a Roman auxiliary mixed infantry and cavalry regiment. The Delmatae It is named after the Dalmatae, an Illyrian-speaking tribe that inhabited the Adriatic coastal mountain range of the eponymous Dalmatia. The ancient geographer Strabo describes these mountains as extremely rugged, and the Dalmatae as backward and warlike. He claims that they did not use money long after their neighbours adopted it and that they "made war on the Romans for a long time". He also criticises the Dalmatae, a nation of pastoralists, for turning fertile plains into sheep pasture. Indeed, the name of the tribe itself is believed to mean "shepherds", derived from the Illyrian word ''delme'' ("sheep"). The final time this people fought against Rome was in the Illyrian revolt of 6–9 AD. The revolt was started by Dalmatae auxiliary forces and soon spread all over Dalmatia and Pannonia. The resulting war was described by the Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
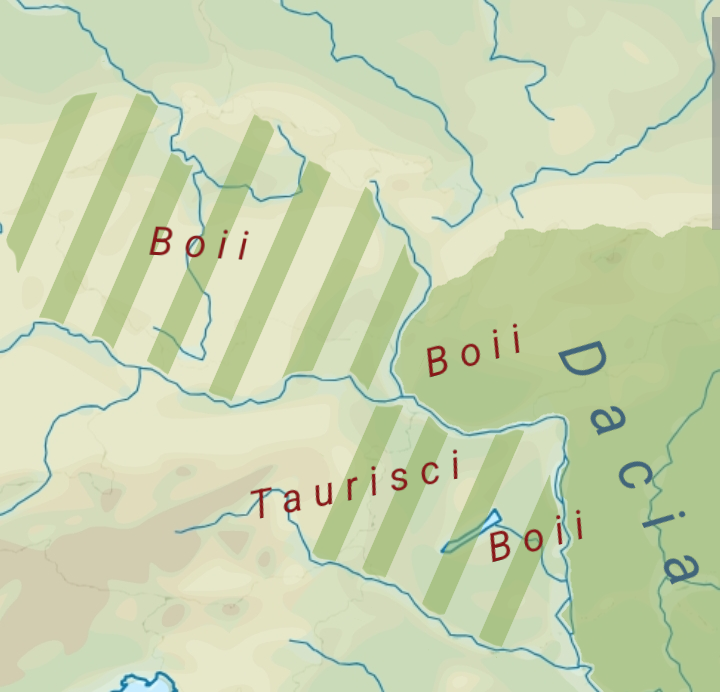
Dalmatia (Roman Province)
Dalmatia was a Roman province. Its name is derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, which lived in the central area of the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It encompassed the northern part of present-day Albania, much of Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Serbia, thus covering an area significantly larger than the current Croatian and Montenegrin region of Dalmatia. Originally this region was called Illyria (in Greek) or Illyricum (in Latin). The province of Illyricum was dissolved and replaced by two separate provinces: Dalmatia and Pannonia. Conquest The region which ran along the coast of the Adriatic Sea and extended inland on the Dinaric Alps was called Illyria by the Greeks. Originally, the Romans also called the area Illyria and later, Illyricum. The Romans fought three Illyrian Wars (229 BC, 219/8 BC and 168 BC) mainly against the kingdom of the Ardiaei to the south of the region. In 168 BC, they abolished this kingdom and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decurio
''Decurio'' was an official title in Ancient Rome, used in various connections: * Decurion (administrative), a member of the senatorial order in the Italian towns under the administration of Rome, and later in provincial towns organized on the Italian model. The number of ''decuriones'' varied in different towns, but was usually 100. The qualifications for the office were fixed in each town by a special law for that community (''lex municipalis''). Cicero (in Verr. 2. 49, 120) alludes to an age limit (originally thirty years, until lowered by Augustus to twenty-five), to a property qualification (cf. Pliny, Ep. i. 19. 2), and to certain conditions of rank. The method of appointment varied in different towns and at different periods. In the early municipal constitution ex-magistrates passed automatically into the Senate of their town; but at a later date this order was reversed and membership of the Senate became a qualification for the magistracy. Cicero (''loc. cit.'') speaks of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherchel
Cherchell () is a town on Algeria's Mediterranean coast, west of Algiers. It is the seat of Cherchell District in Tipaza Province. Under the names Iol and Caesarea, it was formerly a Roman colony and the capital of the kingdoms of Numidia and Mauretania. Names The town was originally known by a Phoenician and Punic name that included the element (), meaning "island". Yol is often attributed to the name of a local divinity of the sea as the word "''Ilel'' / ''Yelel" in local etymology'' meaning sea in Tamazight. This may have been , meaning "Island of Sand". The Punic name was hellenized as ''Iṑl'' (Greek language:Ἰὼλ) and latinized as Iol. The modern name Cherchel and Cherchell are French transcriptions of the berber word ''Šaršār'' (''Achercher'') to signify "Waterfall".. The modern name may have derived from the town's old Latin name Caesarea (Greek language: ἡ Καισάρεια, ''hē Kaisáreia''), the name given by the ruler Juba II. to honor h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Military Diploma
A Roman military diploma was a document inscribed in bronze certifying that the holder was honourably discharged from the Roman armed forces and/or had received the grant of Roman citizenship from the emperor as reward for service. The diploma was a notarised copy of an original ''constitutio'' (decree) issued by the emperor in Rome, listing by regiment (or unit) the eligible veterans. The ''constitutio'', recorded on a large bronze plate, was lodged in the military archive at Rome (none such has been found; presumably they were melted down in later times). History Diplomas were issued during the Principate period (52–284 AD) to retiring veterans who had served in those corps of the Roman armed forces which enlisted ''peregrini'', that is, inhabitants of the Roman empire who were not Roman citizens (the vast majority of the empire's population in the 1st and 2nd centuries). Such corps were: the ; Roman navy, the Praetorian Guard's cavalry (''equites singulares Augusti''); ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Roman Italy, Italy. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to an illness he suffered when young, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's assassination, at which point he was the last adult male of his family. Despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian Empire during the period 264 to 146BC. Three such wars took place, involving a total of forty-three years of warfare on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region, and a four-year-long Mercenary War, revolt against Carthage. The First Punic War broke out on the Mediterranean island of Sicily in 264BC as a result of Rome's expansionary attitude combined with Carthage's proprietary approach to the island. At the start of the war Carthage was the dominant power of the western Mediterranean, with an extensive maritime empire (a thalassocracy), while Rome was a rapidly expanding power in Roman Italy, Italy, with a strong Roman army of the mid-Republic, army but no navy. The fighting took place primarily on Sicily and its surrounding waters, as well as in North Africa, Corsica and Sardinia. It lasted twenty-three years, until 241BC, when the Carthaginians were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire. His most important surviving work is ''De vita Caesarum'', commonly known in English as '' The Twelve Caesars'', a set of biographies of 12 successive Roman rulers from Julius Caesar to Domitian. Other works by Suetonius concerned the daily life of Rome, politics, oratory, and the lives of famous writers, including poets, historians, and grammarians. A few of these books have partially survived, but many have been lost. Life Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus was probably born about AD 69, a date deduced from his remarks describing himself as a "young man" 20 years after Nero's death. His place of birth is disputed, but most scholars place it in Hippo Regius, a small north African town in Numidia, in modern-day Algeria. It is certain that Suetonius came from a family of moderate social position, that his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It included the modern regions western Hungary, western Slovakia, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia, and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. Background In the Early Iron Age, Transdanubia was inhabited by the Pannonians or Pannonii, a collection of Illyrians, Illyrian tribes. The Celts invaded in the Late Iron Age and Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman historian Pompeius Trogus writes that the Celts were met with heavy resistance from the locals and were not able to overrun the southern part of Transdanubia. Some tribes advanced as far as Delphi, with the Scordisci settling in Syrmia (279 BC) upon being forced to withdraw. The arrival of the Celts in Transdanubia disrupted the flow of amber from the Balti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrian Revolt
The (Latin for ''War of the Batos'') or Great Illyrian Revolt was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Romans. The Roman historian Suetonius described the uprising as the most difficult conflict faced by Rome since the Punic Wars two centuries earlier. The rebellion began among native peoples who had been recruited as auxiliary troops for the Roman army. They were led by Bato the Daesitiate, a chieftain of the Daesitiatae in the central part of present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, and were later joined by the Breuci, a tribe in Pannonia led by Bato the Breucian. Many other tribes in Illyria also joined the revolt. Velleius Paterculus called it the Pannonian and Dalmatian War because it involved both regions of Illyricum. The four-year war lasted from AD 6 to AD 9 and witnessed a large deployment of Roman forces i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Auxiliary
The (; ) were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen Roman legion, legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 27 BC. By the 2nd century, the contained the same number of infantry as the legions and, in addition, provided almost all of the Roman army's Roman cavalry, cavalry (especially light cavalry and horse archer, archers) and more specialised troops. The thus represented three-fifths of Rome's regular land forces at that time. Like their legionary counterparts, auxiliary recruits were mostly volunteers, not conscripts. The were mainly recruited from the ''peregrinus (Roman), peregrini'', free provincial subjects who did not hold Roman citizenship and constituted the vast majority of the population in the 1st and 2nd centuries (c. 90% in the early 1st century). In contrast to the legions, which only admitted Roman citizenship, Roman citizens, members of the could be recruited from territories outside of Roman contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |