|
Cogidubnus
Tiberius Claudius Cogidubnus (or Togidubnus, Togidumnus or similar; see naming difficulties) was a 1st-century king of the Regni or Regnenses tribe in early Roman Britain. Chichester and the nearby Roman villa at Fishbourne, believed by some to have been Cogidubnus' palace, were probably part of the territory of the Atrebates tribe before the Roman conquest of Britain in AD 43. Cogidubnus may therefore have been an heir of Verica, the Atrebatic king whose overthrow prompted the emperor Claudius to invade. After the conquest, the area formed part of the civitas of the Regnenses / Regni, possibly Cogidubnus' kingdom before being incorporated into the Roman province. The public baths, amphitheatre and forum in Silchester were probably built in Cogidubnus' time. Sources In Tacitus's ''Agricola'', published 98, where his name appears as "Cogidumnus" in most manuscripts although they can be considered as copies, and "Togidumnus" in one, X�AVCTORITAT ·TI�CLAVD· OIDVBNI·R G·M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
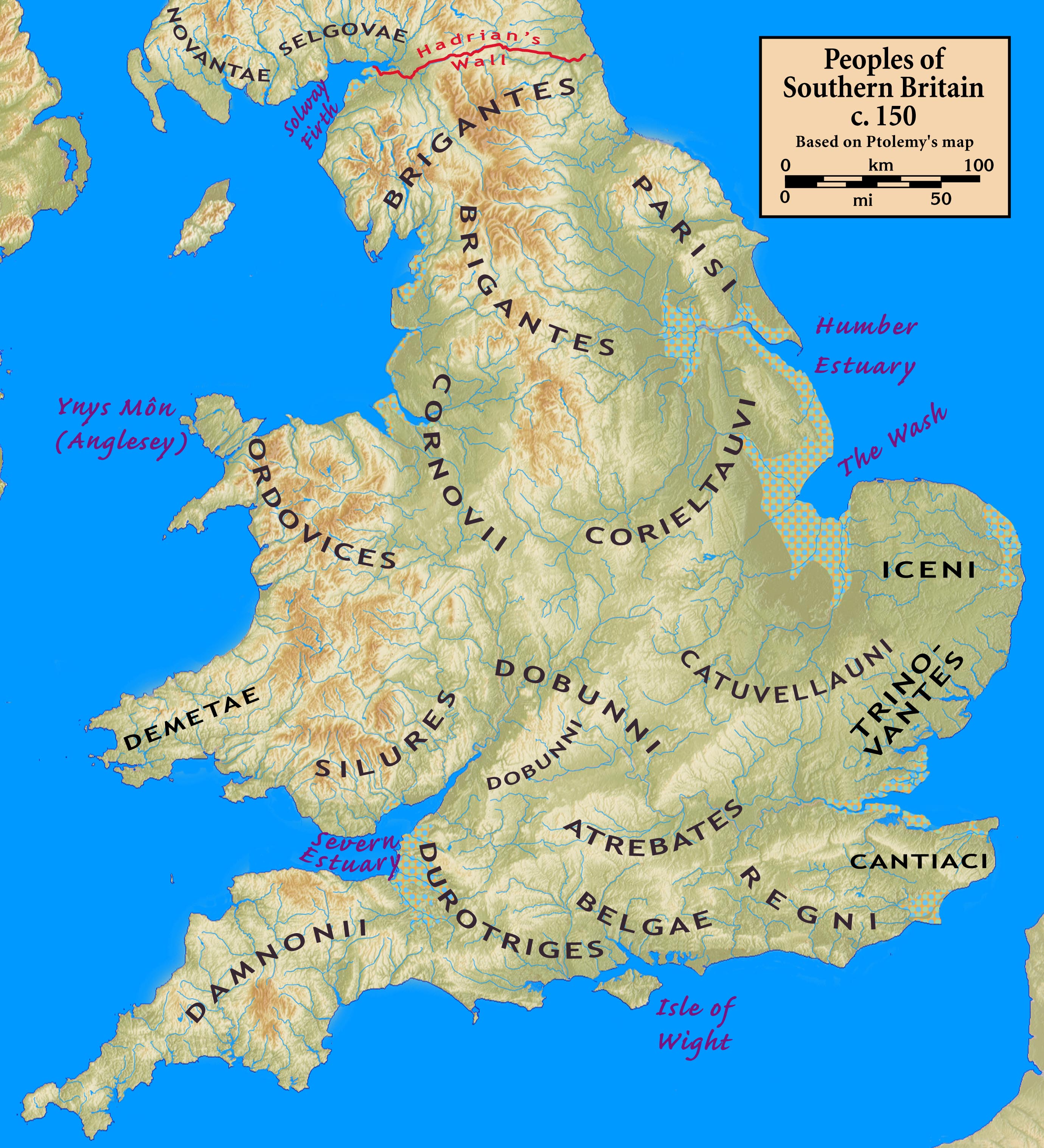
Regni
The Regni (also the Regini or the Regnenses) were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman Conquest, and later a civitas or canton of Roman Britain. They lived in what is now Sussex, as well as small parts of Hampshire, Surrey and Kent, with their tribal heartland at Noviomagus Reginorum (modern Chichester). Territory It is generally accepted that the Regni broadly occupied the region that later became Sussex. Surrey is sometimes included within Regni territory and sometimes within the territory of the Atrebates to the north. However the archeological record north of the Weald shows significant differences to the south and so it would appear Surrey was not normally included in the Regni tribal area. The tribe was surrounded on the west by the Belgae, on the north by the Atrebates, and on the east by the Cantiaci. To the south and east across the ''Oceanus Britannicus'' or ''Oceanus Gallicus'' (the present day English Channel) lay Gaul and the trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishbourne Roman Palace
Fishbourne Roman Palace or Fishbourne Villa is in the village of Fishbourne, West Sussex, Fishbourne, near Chichester in West Sussex. The palace is the largest known Roman residence north of the Alps, and has an unusually early date of 75 AD, around thirty years after the Roman conquest of Britain. Much of the palace has been excavated and is preserved, along with an on-site museum. The rectangular palace surrounded formal gardens, the northern parts of which have been reconstructed. Extensive alterations were made in the second and third centuries AD, when many of the original black and white mosaics were overlaid with more sophisticated coloured work, including the perfectly preserved Dolphin mosaic in the north wing. More alterations were in progress when the palace burnt down in around 270 AD, after which it was abandoned. Discovery and excavation The site was accidentally discovered in 1805, during the construction of a new home on the grounds of the ancient R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrebates
The Atrebates (Gaulish: *''Atrebatis'', 'dwellers, land-owners, possessors of the soil') were a Belgic tribe of the Iron Age and the Roman period, originally dwelling in the Artois region. After the tribes of Gallia Belgica were defeated by Caesar in 57 BC, 4,000 Atrebates participated in the Battle of Alesia in 53, led by their chief Commius. They revolted again in 51 BC, after which they maintained a friendly relationship with Rome, as Commius received sovereignty over the neighbouring Morini. The quality of their woollens is still mentioned in 301 AD by Diocletian's Price Edict. An offshoot of the Belgic tribe probably entered Britain before 54 BC, where it was successively ruled by kings Commius, Tincommius, Eppillus and Verica. After 43 AD, only parts of the area were still controlled by king Claudius Cogidubnus, after which they fell under Roman power. Name They are mentioned as ''Atrebates'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Atrebátioi'' (Ἀ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Client Kingdoms In Britain
The Roman client kingdoms in Britain were native tribes which chose to align themselves with the Roman Empire because they saw it as the best option for self-preservation or for protection from other hostile tribes. Alternatively, the Romans created (or enlisted) some client kingdoms when they felt influence without direct rule was desirable. Client kingdoms were ruled by client kings. In Latin these kings were referred to as ''rex sociusque et amicus'', which translates to "king, ally, and friend". The type of relationships between client kingdoms and Rome was reliant on the individual circumstances in each kingdom. The beginnings of the system are to be found in Caesar's re-enthroning of Mandubracius as king of the Trinovantes, who had been dethroned by Cassivellaunus and then aided Caesar's second invasion of Britain in 54 BC. The system further developed in the following hundred years, particularly under Augustus's influence, so that by the time of the Roman invasion in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verica
Verica (early 1st century AD) was a British client king of the Roman Empire in the years preceding the Claudian invasion of 43 AD. From his coinage, he appears to have been king of the probably Belgic Atrebates tribe and a son of Commius. The distribution of his coins also shows that Verica's kingdom was centred on modern Sussex and east Hampshire, and its capital would have been in or close to what became the Roman Noviomagus Reginorum (modern Chichester). He succeeded his elder brother Eppillus as king in about 15 AD, and may also have reigned over the northern Atrebatic kingdom at Calleva Atrebatum, today called Silchester. He was recognised as '' rex'' by Rome and appears to have had friendly trade and diplomatic links with the empire. His territory was pressed from the east by the Catuvellauni, led by Epaticcus, brother of Cunobelinus, who conquered Calleva in about 25 AD. After Epaticcus's death ca. 35 AD Verica regained some territory, but Cunobelinus's son Carat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Conquest Of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain was the Roman Empire's conquest of most of the island of Great Britain, Britain, which was inhabited by the Celtic Britons. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain (most of what is now called England and Wales) by AD 87, when the Stanegate was established. The conquered territory became the Roman Roman Britain, province of Britannia. Following Julius Caesar's invasions of Britain in 54 BC, some southern British chiefdoms had become Roman client kingdoms in Britain, allies of the Romans. The exile of their ally Verica gave the Romans a pretext for invasion. The Roman army was recruited in Roman Italy, Italia, Hispania, and Gaul and used the newly-formed fleet ''Classis Britannica''. Under their general Aulus Plautius, the Romans pushed inland from the southeast, defeating the Britons in the Battle of the Medway. By AD 47, the Romans held the lands southeast of the Fosse Way. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chichester
Chichester ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parish in the Chichester District, Chichester district of West Sussex, England.OS Explorer map 120: Chichester, South Harting and Selsey Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton B2 edition. Publishing Date:2009. It is the only city in West Sussex and is its county town. It was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Anglo-Saxon settlement and a major market town from those times through Norman dynasty, Norman and medieval times to the present day. It is the seat of the Church of England Diocese of Chichester and is home to a 12th-century cathedral. The city has two main watercourses: the Chichester Canal and the River Lavant, West Sussex, River Lavant. The Lavant, a Winterbourne (stream), winterbourne, runs to the south of the city walls; it is hidden mostly in culverts when close to the city centre. History Roman period There is no recorded evidence that Chichester was a settlement of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cultural practices. There existed several different types of citizenship, determined by one's gender, class, and political affiliations, and the exact duties or expectations of a citizen varied throughout the history of the Roman Empire. History The oldest document currently available that details the rights of citizenship is the Twelve Tables, ratified 449 BC. Much of the text of the Tables only exists in fragments, but during the time of Ancient Rome the Tables would be displayed in full in the Roman Forum for all to see. The Tables detail the rights of citizens in dealing with court proceedings, property, inheritance, death, and (in the case of women) public behavior. Under the Roman Republic, the government conducted a census every fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Philology
Classics, also classical studies or Ancient Greek and Roman studies, is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, ''classics'' traditionally refers to the study of Ancient Greek and Roman literature and their original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics may also include as secondary subjects Greco-Roman philosophy, history, archaeology, anthropology, architecture, art, mythology, and society. In Western civilization, the study of the Ancient Greek and Roman classics was considered the foundation of the humanities, and they traditionally have been the cornerstone of an elite higher education. Etymology The word ''classics'' is derived from the Latin adjective '' classicus'', meaning "belonging to the highest class of citizens." The word was originally used to describe the members of the Patrician (ancient Rome), Patricians, the highest class in ancient Rome. By the 2nd century AD the word was used in literary criticism to describe writers of the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |