|
Coelolepidae
Coelolepidae is an extinct family of thelodont vertebrate agnatha Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present ( cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclos ...ns that lived during the Silurian.Pander, C. H., 1856. Monographie der fossilen Fische des silurischen Systems der russisch-baltischen Gouvernments. Buchdruckerei der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften, St. Petersburg, 91 pp. References External links * Thelodonti Prehistoric jawless fish families Silurian jawless fish {{Silurian-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelolepis
''Coelolepis'' is an extinct genus of jawless fish of the Silurian.Pander, C. H., 1856. Monographie der fossilen Fische des silurischen Systems der russisch-baltischen Gouvernments. Buchdruckerei der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften, St. Petersburg, 91 pp. See also * List of prehistoric jawless fish genera This list of prehistoric jawless fish is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be jawless fish, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepte ... * List of thelodont genera References External links * Thelodonti genera Silurian jawless fish {{Silurian-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelodus
''Thelodus'' (from el, θηλή , 'nipple' and el, ὀδούς , 'tooth') is an extinct genus of thelodont agnathan that lived during the Silurian period. Fossils have been found in Europe, Asia and North America.''Thelodus'' at .org Unlike many thelodonts, species of ''Thelodus'' are known not only from scales, but from impressions in rocks. Some species, such as the Canadian ''T. inauditus'', are thought to be comparable in size to other thelodonts, i.e., from 5 to 15 centimeters in length.Märss, Tiiu, Mark VH Wilson, and Raymond Thorsteinsson. "New thelodont (Agnatha) and possible chondrichthyan (Gnathostomata) taxa established in the Silurian and Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loganellia
''Loganellia'' is a genus of jawless fish which lived between 430 and 370 million years ago, during the Silurian and Devonian periods of the Paleozoic. ''Loganellia'' belonged to the Thelodonti class and like other Thelodonts possessed scales instead of plate armor. ''Loganellia'' are thought to be more closely related to the crown group of gnathostomes than conodonts. They are noted for their denticle whorls - oropharyngeal denticles that lined their branchial bars - which are thought to be homologous with other, later gnathostome teeth. In this sense, ''Loganellia'' may possess the earliest known dental structures related to modern teeth, and would have evolved in the throat, rather than through dermal denticle A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as w ...s or jaws. Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
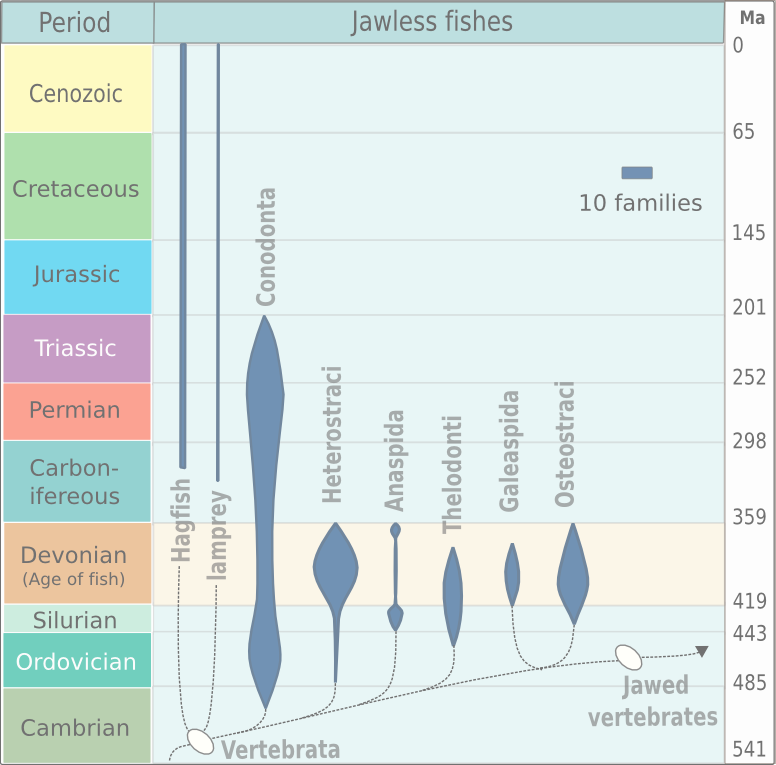
Thelodont
Thelodonti (from Greek: "feeble teeth")Maisey, John G., Craig Chesek, and David Miller. Discovering fossil fishes. New York: Holt, 1996. is a class of extinct jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor. There is much debate over whether the group of Palaeozoic fish known as the Thelodonti (formerly coelolepids) represent a monophyletic grouping, or disparate stem groups to the major lines of jawless and jawed fish. Thelodonts are united in possession of "thelodont scales". This defining character is not necessarily a result of shared ancestry, as it may have been evolved independently by different groups. Thus the thelodonts are generally thought to represent a polyphyletic group, although there is no firm agreement on this point. On the basis that they are monophyletic, they are reconstructed as being ancestrally marine and invading freshwater on multiple occasions. "Thelodonts" were morphologically very similar, and probably closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * Agnatha, jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * Gnathostomata, jawed vertebrates, which include: ** Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish (sharks, Batoidea, rays, and Chimaeriformes, ratfish) ** Euteleostomi, bony vertebrates, which include: *** Actinopterygii, ray-fins (the majority of living Osteichthyes, bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant taxon, Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatha
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present ( cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelodonti
Thelodonti (from Greek: "feeble teeth")Maisey, John G., Craig Chesek, and David Miller. Discovering fossil fishes. New York: Holt, 1996. is a class of extinct jawless fishes with distinctive scales instead of large plates of armor. There is much debate over whether the group of Palaeozoic fish known as the Thelodonti (formerly coelolepids) represent a monophyletic grouping, or disparate stem groups to the major lines of jawless and jawed fish. Thelodonts are united in possession of " thelodont scales". This defining character is not necessarily a result of shared ancestry, as it may have been evolved independently by different groups. Thus the thelodonts are generally thought to represent a polyphyletic group, although there is no firm agreement on this point. On the basis that they are monophyletic, they are reconstructed as being ancestrally marine and invading freshwater on multiple occasions. "Thelodonts" were morphologically very similar, and probably closely relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Jawless Fish Families
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |