|
Cochin Jew
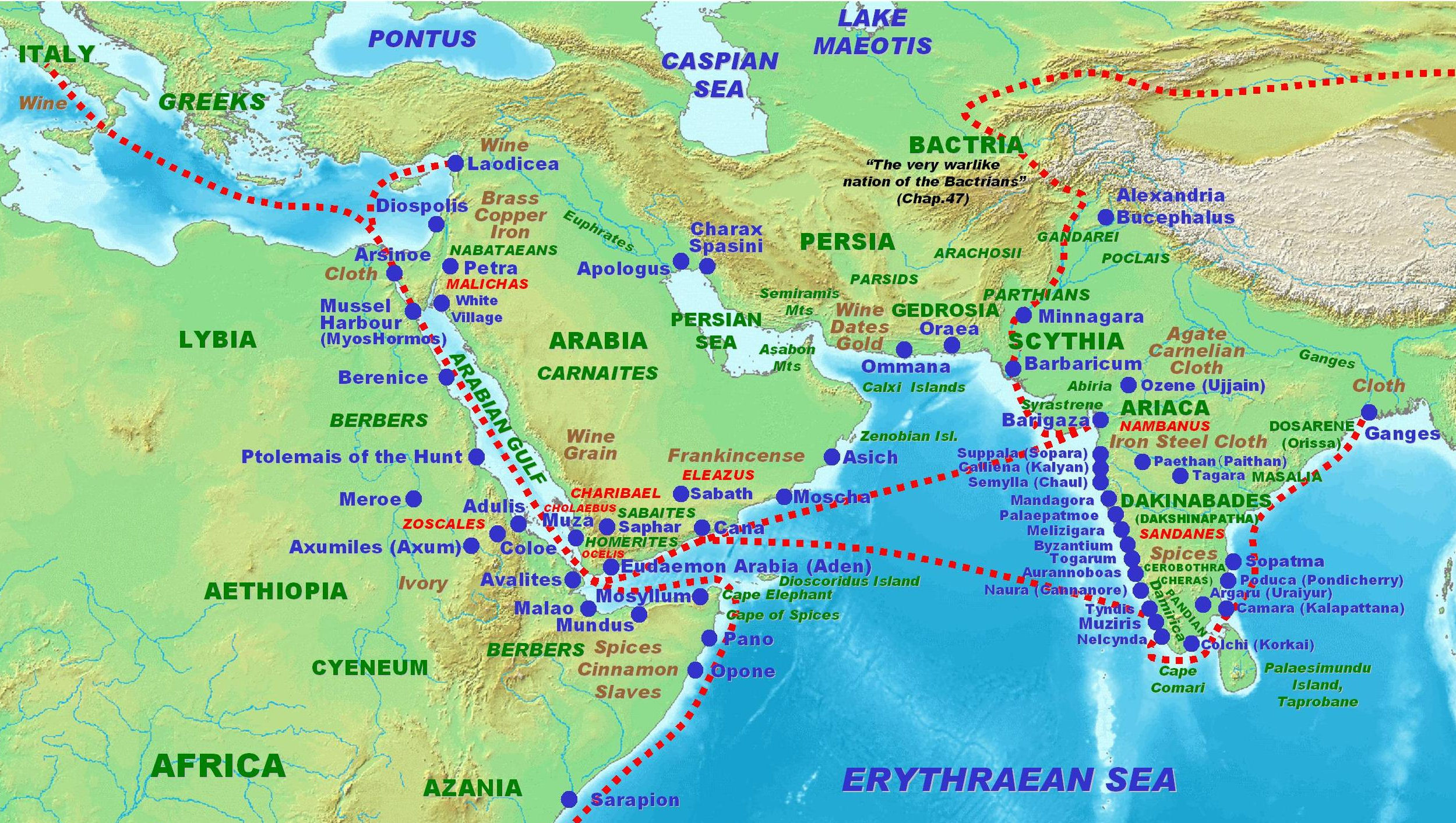
Cochin Jews (also known as Malabar Jews or Kochinim from ) are one of the oldest groups of Jews in India, with roots that are claimed to date back to the time of King Solomon. The Cochin Jews settled in the Kingdom of Cochin in South India, now part of the present-day state of Kerala. As early as the 12th century, mention is made of the Jews in southern India by Benjamin of Tudela. Following their expulsion from Iberia in 1492 by the Alhambra Decree, a few families of Sephardi Jews eventually made their way to Cochin in the 16th century. They became known as Paradesi Jews (or Foreign Jews). The European Jews maintained some trade connections to Europe, and their language skills were useful. Although the Sephardim spoke Ladino (Spanish or Judeo-Spanish), in India they learned Judeo-Malayalam from the Malabar Jews.Katz 2000; Koder 1973; Thomas Puthiakunnel 1973. The two communities retained their ethnic and cultural distinctions.Weil, Shalva. "The Place of Alwaye in Modern Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Jews In India
The history of the Jews in India dates back to ancient history, antiquity.''The Jews of India: A Story of Three Communities'' by Orpa Slapak. The Israel Museum, Jerusalem. 2003. p. 27. .Weil, Shalva. ''India's Jewish Heritage: Ritual, Art, and Life-Cycle''. Mumbai: Marg Publications [first published in 2002; 3rd edn.]. 2009. Judaism was one of the first foreign religions to arrive in the Indian subcontinent in recorded history. Rabbi Eliezer ben Jose of the 2nd-century AD mentions the Jewish people of India () in his work ''Mishnat Rabbi Eliezer'', saying that they are required to ask for rain in the summer months, during their regular rainy season, yet make use of the format found for winter in the Amidah, Standing Prayer, and to cite it in the blessing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradesi Jews
Paradesi Jews refer to Jewish immigrants to the Indian subcontinent during the 15th and 16th centuries following the expulsion of Jews from Spain and Portugal. ''Paradesi'' means ''foreign'' in Malayalam and Tamil language, Tamil. These Sephardic immigrants fled persecution and death by burning in the wake of the 1492 Alhambra Decree and Manuel I of Portugal, King Manuel's 1496 decree expelling Jews from Portugal. They are sometimes referred to as "White Jews", although that usage is generally considered pejorative or discriminatory and refers to relatively recent Jewish immigrants (end of the 15th century onward), predominantly Sephardim. During the 18th and 19th centuries, Paradesi Jews were Sephardi immigrants to the Indian subcontinent from Arab and Muslim countries fleeing forcible conversion, persecution, and antisemitism. The Paradesi Jews of Cochin traded in spices. They are a community of Sephardic Jews settled among the larger Cochin Jews, Cochin Jewish community loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Of Tudela
Benjamin of Tudela (), also known as Benjamin ben Jonah, was a medieval Jewish traveler who visited Europe, Asia, and Africa in the twelfth century. His vivid descriptions of western Asia preceded those of Marco Polo by a hundred years. With his broad education and vast knowledge of languages, Benjamin of Tudela is a major figure in medieval geography and Jewish history. ''The Travels of Benjamin'' is an important work not only as a description of the Jewish communities, but also as a reliable source about the geography and ethnography Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining ... of the Middle Ages. Some modern historians credit Benjamin with giving accurate descriptions of everyday life in the Middle Ages. Originally written in Hebrew, his itinerary was translated into Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chendamangalam Synagogue
The Chendamangalam Synagogue (; ) is a former Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Judaism, Jewish congregation and synagogue, located in Chendamangalam, a village in the Ernakulam district, Ernakulam district of the coastal state of Kerala, in India. Completed in 1420 Common Era, CE, the building was abandoned in 1950s, and was subsequently repurposed as a Jewish museum. History Established in 1100 CE, the congregation is one of the oldest known Jewish communities established by the Cochin Jews, Malabar Jews, though the synagogue structure itself dates from 1420, and was renovated in 1614, making it the oldest synagogue in the Commonwealth of Nations. A tombstone recovered from Kodungallur was stored in this synagogue and is on display in the front yard, with an inscription of Sarah Bat Israel, dating from 1269, making it the second oldest Jewish epitaph found in India. After the entire congregation made ''aliyah'' to Israel in the 1950s, the former synagogue was defunct for decades. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer Torah
file:SeferTorah.jpg, A Sephardic Torah scroll rolled to the first paragraph of the Shema file:Köln-Tora-und-Innenansicht-Synagoge-Glockengasse-040.JPG, An Ashkenazi Torah scroll rolled to the Decalogue file:Keneseth Eliyahoo Synagogue, Interior, Tora Cases.jpg, Torah cases at Knesset Eliyahoo, Knesset Eliyahoo Synagogue, Mumbai, India A Torah scroll (, , lit. "Book of Torah"; plural: ) is a manuscript, handwritten copy of the Torah, meaning the five books of Moses (the first books of the Hebrew Bible). The Torah scroll is mainly used in the ritual of Torah reading during Jewish prayers. At other times, it is stored in the holiest spot within a synagogue, the Torah ark, which is usually an ornate curtained-off cabinet or section of the synagogue built along the wall that most closely faces Jerusalem, the Mizrah, direction Jews face when Jewish prayer, praying. The text of the Torah is also commonly printed and bookbinding, bound in codex, book form for non-ritual functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadavumbhagam Ernakulam Synagogue
The Kadavumbhagham Ernakulam Synagogue is a Jewish congregation and synagogue, located in Kochi, in the Ernakulam district in the state of Kerala, India. Established in 1200 CE and restored several times on the same site, it is the oldest synagogue of the Malabar Jews with a Sefer Torah scroll and offering occasional services. The synagogue is modelled on the earliest synagogue of the Malabar Jews at Muziris (currently submerged due to rising sea levels), which date from the time of ancient sea trade between the Mediterranean and Kerala. Although the former Chendamangalam Synagogue, completed in 1166 CE, is the oldest surviving synagogue structure in Kerala and the Indian subcontinent, its Torah scrolls were taken to Israel by its congregation in 1952. Consequently, the Kadavumbhagham Ernakulam Synagogue is the oldest Malabar Jewish synagogue today (since its restoration in 2018) with a Torah scroll that is occasionally used for services. The Paradesi Sephardic Syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
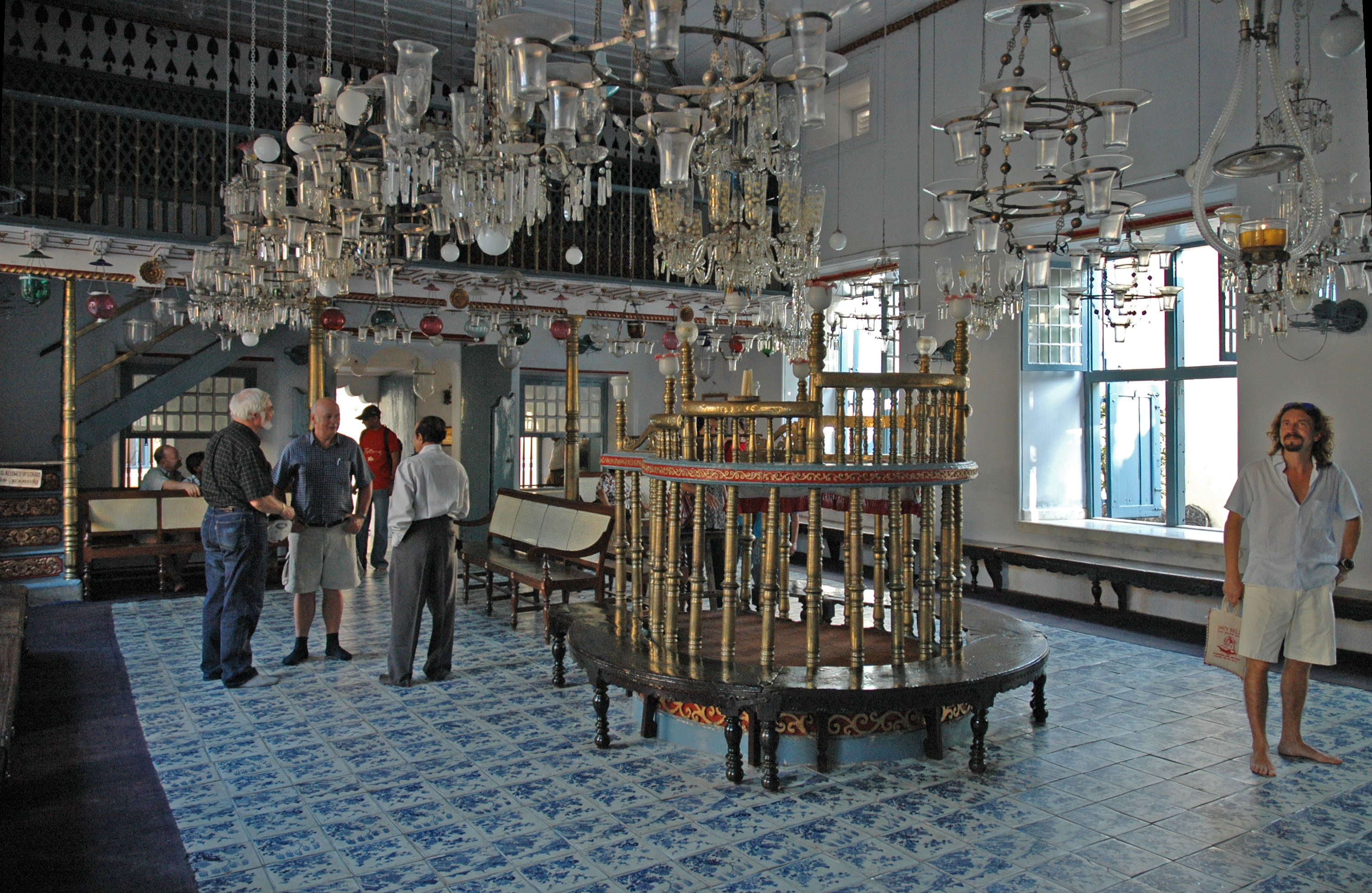
Paradesi Synagogue
The Paradesi Synagogue or the Mattancherry Synagogue () is a synagogue located in Mattancherry Jew Town, a suburb of the city of Kochi, Kerala, in India. It was built in 1568 A.D. by Samuel Castiel, David Belila, and Joseph Levi for the flourishing Paradesi Jewish community in Kochi. Cochin Jews were composed mainly of the much older Malabari Jews and the newly arrived Sephardic refugees from the Portuguese religious persecution of Jews in Spain and Portugal. It is the oldest active synagogue in the Commonwealth of Nations.The Paradesi Synagogue, Cochin, India Database of Jewish Communities, Museum of the Jewish People at Beit Hatfutsot. Accessed online 13 February 2007. ''Paradesi'' is a word used in several [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Synagogues In Kerala
There are at least eight known synagogues in Kerala in recorded history, even though most of them are not operating anymore. Seven of the synagogues are used by the Cochin Jews, with one used by the Paradesi Jews. Each of these is quite unique in its construction and architecture; nevertheless, they retain very similar aesthetics, blending in both the Jewish and Keralite traditions rarified over centuries.India’s Synagogue Variety: Architecture, History, and Context Jay A. Waronker, Café Dissensus, 31 December 2014 A synagogue was called "Beit Knesset" (; ) in Judeo-Malayalam or "Jootha Palli" () with ''joothan'' meaning Jew in Malayalam and -''palli'' a suffix added to prayer houses of the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic fait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indian people are a distinct minority group, minority community of mixed-race British and Indian ancestry. During the colonial period, their ancestry was defined as British paternal and Indian maternal heritage; post-independence, "Anglo-Indian" has also encompassed other European and Indian ancestries. Anglo-Indians' first language is usually English language, English. Prior to 1911, various designations like "Eurasian" or "Indo-Briton" were used to describe this community. The All India Anglo-Indian Association, founded in 1926, has long represented the interests of this ethnic group; it holds that Anglo-Indians are unique in that they are Christianity in India, Christians, speak Indian English, English as their mother tongue, and have a historical link to both the British Isles and the Indian sub-continent. During the period of Colonial India, British rule in India, children born to unions between British fathers and Indian mothers from the 17th century onwards form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territorial evolution of the British Empire, territories of the British Empire from which it developed. They are connected through their English in the Commonwealth of Nations, use of the English language and cultural and historical ties. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental relations, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member nations. Numerous List of Commonwealth organisations, organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah
''Aliyah'' (, ; ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel or the Palestine (region), Palestine region, which is today chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jerusalem in Judaism, Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action – emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel – is referred to in the Hebrew language as ''yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Knesset, Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of Jewish history, their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to Jewish militar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th century by modern Western geographers and was originally applied to the Ottoman Empire, but today has varying definitions within different academic circles. The term ''Near East'' was used in conjunction with the ''Middle East'' and the ''Far East'' (China and beyond), together known as the "three Easts"; it was a separate term from the ''Middle East'' during earlier times and official British usage. As of 2024, both terms are used interchangeably by politicians and news reporters to refer to the same region. ''Near East'' and ''Middle East'' are both Eurocentrism, Eurocentric terms. According to the National Geographic Society, the terms ''Near East'' and ''Middle East'' denote the same territories and are "generally accepted as comprisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |