|
Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease of the intestinal tract of animals caused by coccidian protozoa. The disease spreads from one animal to another by contact with infected feces or ingestion of infected tissue. Diarrhea, which may become bloody in severe cases, is the primary symptom. Most animals infected with coccidia are asymptomatic, but young or immunocompromised animals may suffer severe symptoms and death. While coccidia can infect a wide variety of animals, including humans, birds, and livestock, they are usually species-specific. One well-known exception is toxoplasmosis caused by '' Toxoplasma gondii''. Humans may first encounter coccidia when they acquire a dog, cat or bird that is infected. Other than ''T. gondii'', the infectious organisms are canine and feline-specific and are not contagious to humans, unlike the zoonotic diseases. Coccidia in dogs Puppies are frequently infected with coccidia from the feces of their mother, and are more likely to develop cocc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidia
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an animal cell. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals, and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa. Infection with these parasites is known as coccidiosis. Coccidia can infect all mammals, some birds, some fish, some reptiles, and some amphibians. Most species of coccidia are species-specific in their host. An exception is '' Toxoplasma gondii'', which can infect all mammals, although it can only undergo sexual reproduction in cats. Depending on the species of coccidia, infection can cause fever, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, and nervous system effects and changes to behavior, and may lead to death. Healthy adults may recover without medication—but those who are immunocompromised or young almost certainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eimeria
''Eimeria'' is a genus of apicomplexan parasites that includes various species capable of causing the disease coccidiosis in animals such as cattle, poultry and smaller ruminants including sheep and goats. ''Eimeria'' species are considered to be monoxenous because the life cycle is completed within a single host, and stenoxenous because they tend to be host specific, although a number of exceptions have been identified. Species of this genus infect a wide variety of hosts. Thirty-one species are known to occur in bats (Chiroptera), two in turtles, and 130 named species infect fish. Two species (''E. phocae'' and ''E. weddelli'') infect seals. Five species infect llamas and alpacas: ''E. alpacae'', ''E. ivitaensis'', ''E. lamae'', ''E. macusaniensis'', and ''E. punonensis''. A number of species infect rodents, including ''E. couesii'', ''E. kinsellai'', ''E. palustris'', ''E. ojastii'' and ''E. oryzomysi''. Others infect poultry (''E. necatrix'' and ''E. tenella''), rabbits ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eimeria Zuernii
''Eimeria zuernii'' is a species of the parasite ''Eimeria'' that causes diarrheic disease known as eimeriosis in cattle (''Bos taurus''), and mainly affects younger animals. The disease is also commonly referred to as coccidiosis. The parasite can be found in cattle around the globe. Description ''Eimeria zuernii'' is a very host specific parasite that only infects cattle. Cattle gets infected by ingesting food, water or surfaces contaminated with infective (sporulated) oocysts (fecal-oral-route). After the oocyst hatch in the gut of the animal it releases 8 zoites that undergo two asexual cycles (schizogony). The first cycle happens inside the lamina propria cells and produces many small schizonts. The second generation of schizonts target epithelial cells in the cecum and colon. The second generation of schizonts undergo a sexual cycle (gametogony) which is also the time when clinical signs of the disease can be observed. The release of new oocysts destroys mucosal cells which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toltrazuril
Toltrazuril is an antiparasitic medication used primarily to treat coccidiosis in animals. Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease caused by coccidia, which are microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. Mechanism of action Toltrazuril works by interfering with the protozoa's ability to reproduce. It disrupts the division of the protozoal nucleus and damages the cell membrane of the parasites. This action results in the destruction of the coccidia at all stages of their life cycle. Use in veterinary medicine Toltrazuril is widely used in veterinary medicine Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, management, medical diagnosis, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in non-human animals. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all a ... to treat coccidiosis in various animals, including poultry, pigs, cattle, sheep, and compani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amprolium
Amprolium is the organic compound sold as a coccidiostat used in poultry. It has many International Nonproprietary Names. __TOC__ Uses in coccidiosis treatment in poultry The drug is a thiamine analogue and blocks the thiamine transporter of ''Eimeria'' species. By blocking thiamine uptake it prevents carbohydrate synthesis. Despite only moderate efficacy it is well favoured due to few resistance issues and is commonly used in the United States in conjunction with sulfonamides prophylactically in chickens and cattle as a coccidiostat. Synthesis Condensation of ethoxymethylenemalononitrile (1) with acetamidine (2) affords the substituted pyrimidine (4). The reaction may well involve conjugate addition of the amidine nitrogen to the malononitrile followed by loss of ethoxide (3); addition of the remaining amidine nitrogen to one of the nitriles will then lead to the pyrimidine (4). Reduction of the nitrile gives the corresponding aminomethyl compound (5). Exhaustive methylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Leukemia Virus
Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) is a retrovirus that infects cats. FeLV can be transmitted from infected cats when the transfer of saliva or nasal secretions is involved. If not defeated by the animal's immune system, the virus weakens the cat's immune system, which can lead to diseases which can be lethal. Because FeLV is cat-to-cat contagious, FeLV+ cats should only live with other FeLV+ cats. FeLV is categorized into four subgroups, A, B, C and T. An infected cat has a combination of FeLV-A and one or more of the other subgroups. Symptoms, prognosis and treatment are all affected by subgroup. FeLV+ cats often have a shorter lifespan, but can still live "normal", healthy lives. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of infection with feline leukemia virus are quite varied and include loss of appetite, poor coat condition, anisocoria (uneven pupils), infections of the skin, bladder, and respiratory tract, oral disease, seizures, lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes), skin le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Distemper
Canine distemper (CDV) (sometimes termed "footpad disease") is a viral disease that affects a wide variety of mammal families, including domestic and wild species of dogs, coyotes, foxes, pandas, wolves, ferrets, skunks, raccoons, and felines, as well as pinnipeds, some primates, and a variety of other species. CDV does not affect humans. In canines, CDV affects several body systems, including the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts, the spinal cord, and the brain. Common symptoms include high fever, eye inflammation and eye/nose discharge, labored breathing and coughing, vomiting and diarrhea, loss of appetite and lethargy, and hardening of the nose and footpads. The viral infection can be accompanied by secondary bacterial infections and can eventually present serious neurological symptoms. Canine distemper is caused by a single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Paramyxoviridae'' (the same family of viruses that causes measles, mumps, and bronchiolitis in humans). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptosporidium Hominis
''Cryptosporidium hominis'', along with '' Cryptosporidium parvum'', is among the medically important ''Cryptosporidium'' species. It is an obligate parasite of humans that can colonize the gastrointestinal tract resulting in the gastroenteritis and diarrhea characteristic of cryptosporidiosis. Unlike ''C. parvum'', which has a rather broad host range, ''C. hominis'' is almost exclusively a parasite of humans. As a result, ''C. hominis'' has a low zoonotic potential compared to ''C. parvum''. It is spread through the fecal-oral route usually by drinking water contaminated with oocyst laden feces. There are many exposure risks that people can encounter in affected areas of the world. Cryptosporidium infections are large contributors of child death and illness in heavily affected areas, yet low importance has been placed on both identifying the species and finding more treatment options outside of nitazoxanide for children and AIDS patients. Characteristics ''Cryptosporidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptosporidium Muris
''Cryptosporidium muris'' is a species of coccidium, first isolated from the gastric glands of the common mouse. ''Cryptosporidium'' does originate in common mice, specifically laboratory mice. However, it also has infected cows, dogs, cats, rats, rabbits, lambs, and humans and other primates. General characteristics ''Cryptosporidium muris'' infects dogs, rabbits, lambs, cats, humans, and non-human primates. This type of ''cryptosporidium'' infects people and animals by the oocyst acquired in water. If people or animals drink the water, then they could become infected and then complete the cycle by passing oocysts. People and animals can also become infected by being in water that has the oocysts present. The area where ''Cryptosporidium muris'' most commonly occurs is in Kenya, France, Thailand, and Indonesia. It also occurs in the western hemisphere but to a far lower amount. Diagnostics and prevention The current diagnostics for ''Cryptosporidium muris'' are Polymerase Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
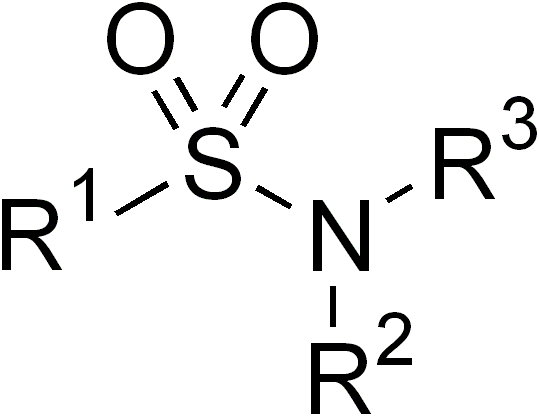
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of medication, drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the Sulfonamide (chemistry), sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Drug allergy, Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by ''Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the ileum, distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tract in both immunocompetent (i.e., individuals with a normal functioning immune system) and immunocompromised (e.g., persons with HIV/AIDS or autoimmune disorders) individuals, resulting in diarrhea, watery diarrhea with or without an unexplained cough. In immunosuppressed individuals, the symptoms are particularly severe and can be fatal. It is primarily spread through the fecal-oral route, often through contaminated water; recent evidence suggests that it can also be transmitted via fomites contaminated with respiratory secretions. ''Cryptosporidium'' is commonly isolated in HIV-positive patients presenting with diarrhea. The organism was first described in 1907 by Tyzzer, who recognised it was a coccidian. On January 8, 2025, a group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |