|
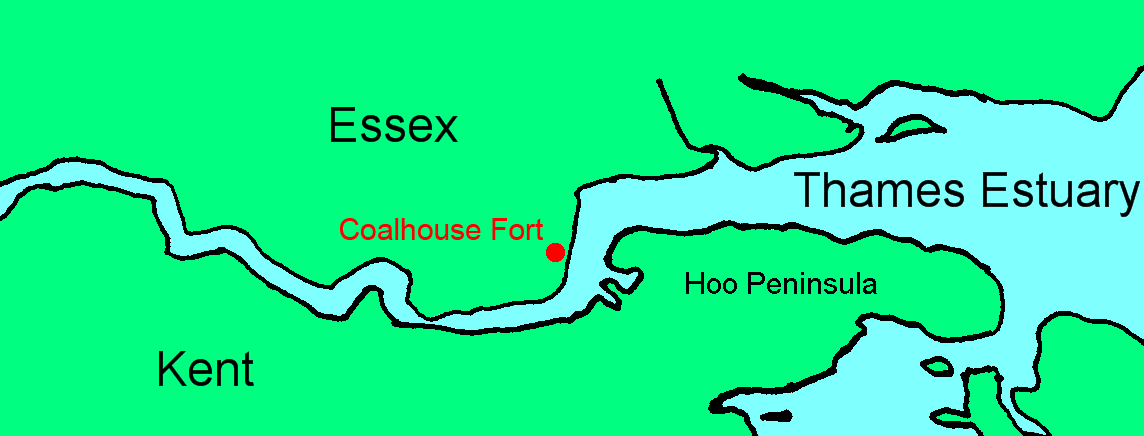
Coalhouse Fort
Coalhouse Fort is an artillery fort in the eastern English county of Essex. It was built in the 1860s to guard the lower Thames from seaborne attack. It stands at Coalhouse Point on the north bank of the river, at a location near East Tilbury which was vulnerable to raiders and invaders. It was the last in a series of fortifications dating back to the 15th century and was the direct successor to a smaller mid-19th century fort built on the same site. Constructed during a period of tension with France, its location on marshy ground caused problems from the start and led to a lengthy construction process. The fort was equipped with a variety of large-calibre artillery guns and the most modern defensive facilities of the time, including shell-proof casemates protected by granite facing and cast-iron shields. Its lengthy construction and the rapid pace of artillery development at the time meant that it was practically obsolete for its original purpose within a few years of its comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Tilbury
East Tilbury is a village and former civil parish in the unitary authority of Thurrock borough, Essex, England, and one of the traditional List of traditional (Church of England) parish churches in Thurrock, Church of England parishes in Thurrock. In 2011 the ward had a population of 6,363. History In Saxon times, the location on which St Catherine's Church (right) now stands was surrounded by tidal marshland. This is the probable location for the minster church established by St Cedd at ''Tilaburg,'' which is mentioned in Bede's ''History of the English Church and People''. In the 1860s, Coalhouse Fort was constructed on the bank of the Thames, close to the parish church. This fort was an active part of the defences of London up to and including World War II, having originally been developed as a precaution against French Ironclad warship, ironclads approaching London up the Thames it was refortified with new armaments as threats changed over the years. From 1894 to 1936 East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Reformation: various religious and political movements that affected both the practice of Christianity in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe and relations between church and state. The English Reformation began as more of a political affair than a theological dispute. In 1527 Henry VIII requested an annulment of his marriage, but Pope Clement VII refused. In response, the English Reformation Parliament, Reformation Parliament (1529–1536) passed laws abolishing papal authority in England and declared Henry to be Supreme Head of the Church of England, head of the Church of England. Final authority in doctrinal disputes now rested with the monarch. Though a religious traditionalist hims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device Forts
The Device Forts, also known as Henrician castles and blockhouses, were a series of artillery fortifications built to defend the coast of England and Wales by Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII. Traditionally, the Crown had left coastal defences in the hands of local lords and communities but the threat of French and Spanish invasion led the King to issue an order, called a "device", for a major programme of work between 1539 and 1547. The fortifications ranged from large stone castles positioned to protect The Downs (ship anchorage), the Downs anchorage in Kent, to small blockhouses overlooking the entrance to Milford Haven in Pembrokeshire, and earthwork Bastion, bulwarks along the Essex coast. Some forts operated independently, others were designed to be mutually reinforcing. The Device programme was hugely expensive, costing a total of £376,000 (estimated as between £2 and £82 billion in today's money); much of this was raised from the proceeds of the Dissolution of the Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive strong point against any enemy that does not possess siege equipment or, in modern times, artillery, air force or cruise missiles. A fortification intended to resist these weapons is more likely to qualify as a fortress or a redoubt, or in modern times, be an underground bunker. However, a blockhouse may also refer to a room within a larger fortification, usually a battery or redoubt. Etymology The term '' blockhouse'' is of uncertain origin, perhaps related to Middle Dutch '' blokhus'' and 18th-century French '' blocus'' (blockade). In ancient Greece Blockhouses existed in ancient Greece, for example the one near Mycenae. Early blockhouses in England Early blockhouses were designed solely to protect a particular area by the use of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement with Pope Clement VII about such an annulment led Henry to initiate the English Reformation, separating the Church of England from papal authority. He appointed himself Supreme Head of the Church of England and dissolution of the monasteries, dissolved convents and monasteries, for which he was List of people excommunicated by the Catholic Church, excommunicated by the pope. Born in Greenwich, Henry brought radical changes to the Constitution of England, expanding royal power and ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings in opposition to papal supremacy. He frequently used charges of treason and heresy to quell dissent, and those accused were often executed without a formal trial using bills of attainder. He achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart (fortification)
In fortification architecture, a rampart is a length of Embankment (earthworks), embankment or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, Human settlement, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth and/or masonry.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 241. Darvill, Timothy (2008). ''Oxford Concise Dictionary of Archaeology'', 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, p. 376. . Types The composition and design of ramparts varied from the simple mounds of earth and stone, known as dump ramparts, to more complex earth and timber defences (box ramparts and timberlaced ramparts), as well as ramparts with stone revetments. One particular type, common in Central Europe, used earth, stone and timber posts to form a ''Pfostenschlitzmauer'' or "post-slot wall". Vitrified ramparts were composed of stone that was subsequently fired, possibly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive government specifically or only to the monarch and their Viceroy, direct representatives. The term can be used to refer to the rule of law; or to the functions of executive (government), executive (the Crown-King-in-Council, in-council), legislative (the Crown-in-parliament), and judicial (the Crown on the bench) governance and the civil service. The concept of the Crown as a corporation sole developed first in the Kingdom of England as a separation of the physical crown and property of the kingdom from the person and personal property of the monarch. It spread through English and later British colonisation and developed into an imperial crown, which rooted it in the legal lexicon of all 15 Commonwealth realms, their various dependencies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoo Peninsula
The Hoo Peninsula is a peninsula in Kent, England, separating the estuaries of the rivers Thames and Medway. It is dominated by a line of chalk, clay and sand hills, surrounded by an extensive area of marshland composed of alluvial silt. The name ''Hoo'' is a Saxon word believed to mean 'spur of land' or refers to the 'distinct heel-shape of the ridge of hills' through Hoo. Hoo features in the Domesday Book.''The Place Names of Kent'', Judith Glover, 1976, Batsford. The peninsula is home to internationally and nationally protected wildlife sites as well as industrial facilities and energy industries. History The Romans have been credited with the first two attempts at building a sea wall. The subsequent draining of the marshes created pastureland to support sheep. The area is rich in archaeology. Bronze Age implements and Jutish cemeteries have been found on the peninsula, and Roman pottery at Cooling. It was once the point of departure across the ancient Saxon fording ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooling Castle
Cooling Castle is a 14th-century quadrangular castle in the village of Cooling, Kent on the Hoo Peninsula about north of Rochester. It was built in the 1380s by the Cobham family, the local lords of the manor, to guard the area against French raids into the Thames Estuary. The castle has an unusual layout, comprising two walled wards of unequal size next to each other, surrounded by moats and ditches. It was the earliest English castle designed for the use of gunpowder weapons by its defenders. Despite this distinction, the use of gunpowder weapons ''against'' the castle proved devastating. It was captured after only eight hours when Sir Thomas Wyatt besieged it in January 1554 during his unsuccessful rebellion against Queen Mary. His attack badly damaged the castle, and it was subsequently abandoned and allowed to fall into disrepair. A farmhouse and outbuildings were constructed among the ruins a century later. Today the farmhouse is the home of the musician Jools Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War (1369–89)
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of England and France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces. The Hundred Years' War was a significant conflict in the Middle Ages. During the war, five generations of kings from two rival dynasties fought for the throne of France, then the wealthiest and most populous kingdom in Western Europe. The war had a lasting effect on European history: both sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |