|
Coagulation Factor XIa
Factor XI, or plasma thromboplastin antecedent, is the zymogen form of factor XIa, one of the enzymes involved in coagulation. Like many other coagulation factors, it is a serine protease. In humans, factor XI is encoded by ''F11'' gene. Function Factor XI (FXI) is produced by the liver and circulates as a homo-dimer in its inactive form. The plasma half-life of FXI is approximately 52 hours. The zymogen factor is activated into ''factor XIa'' by factor XIIa (FXIIa), thrombin, and FXIa itself; due to its activation by FXIIa, FXI is a member of the "contact pathway" (which includes HMWK, prekallikrein, factor XII, factor XI, and factor IX). Factor XIa activates factor IX by selectively cleaving arg- ala and arg- val peptide bonds. Factor IXa, in turn, forms a complex with Factor VIIIa (FIXa-FVIIIa) and activates factor X. Physiological inhibitors of factor XIa include protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI, a member of the serine protease inhibitor/serpin class of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zymogen
In biochemistry, a zymogen (), also called a proenzyme (), is an inactive precursor of an enzyme. A zymogen requires a biochemical change (such as a hydrolysis reaction revealing the active site, or changing the configuration to reveal the active site) to become an active enzyme. The biochemical change usually occurs in Golgi bodies, where a specific part of the precursor enzyme is cleaved in order to activate it. The inactivating piece which is cleaved off can be a peptide unit, or can be independently-folding domains comprising more than 100 residues. Although they limit the enzyme's ability, these N-terminal extensions of the enzyme or a "prosegment" often aid in the stabilization and folding of the enzyme they inhibit. The pancreas secretes zymogens partly to prevent the enzymes from digesting proteins in the cells where they are synthesised. Enzymes like pepsin are created in the form of pepsinogen, an inactive zymogen. Pepsinogen is activated when chief cells release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Z-dependent Protease Inhibitor
Protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI) is a protein circulating in the blood which inhibits factors Xa and XIa of the coagulation cascade. It is a member of the class of the serine protease inhibitors (serpins). Its name implies that it requires protein Z, another circulating protein, to function properly, but this only applies to its inhibition of factor X. It is about 72 kDa heavy and 444 amino acids large. It is produced by the liver. Role in disease Water ''et al.'' found deficiency of ZPI in 4.4% of a cohort of patients with thrombophilia (a tendency to thrombosis). History Han ''et al.'' first described ZPI in 1998. The same group further characterised it in 2000. References External links * The MEROPS MEROPS is an online database for peptidases (also known as proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes) and their inhibitors. The classification scheme for peptidases was published by Rawlings & Barrett in 1993, and that for protein inhibito ... online data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asundexian
Asundexian is a Factor XIa inhibitor developed by Bayer to prevent stroke. Clinical trial(s) Asundexian efficacy and safety in patients have been evaluated in two clinical trial programs: phase IIb PACIFIC and phase III OCEANIC. In the phase IIb PACIFIC clinical trial programs, asundexian consistently showed no difference in bleeding rate compared with placebo and reduced the risk of bleeding compared with apixaban Apixaban, sold under the brand name Eliquis, is an anticoagulant medication used to treat and prevent blood clots and to prevent stroke in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation through directly inhibiting factor Xa. It is used as an al .... All three trials in the programs were not powered to show efficacy of asundexian. However, a phase III trial, OCEANIC-AF, demonstrated a hazard ratio of 3.8 for stroke or systemic embolism with asundexian vs apixaban, so it was stopped due to a "lack of efficacy." The remaining active study OCEANIC-STROKE was recomme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus. Thrombosis can cause serious conditions such as stroke and heart attack. Thrombosis may occur in veins (venous thrombosis) or in arteries (arterial thrombosis). Venous thrombosis (sometimes called DVT, deep vein thrombosis) leads to a blood clot in the affected part of the body, while arterial thrombosis (and, rarely, severe venous thrombosis) affects the blood supply and leads to damage of the tissue supplied by that artery (ischemia and necrosis). A piece of either an arterial or a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
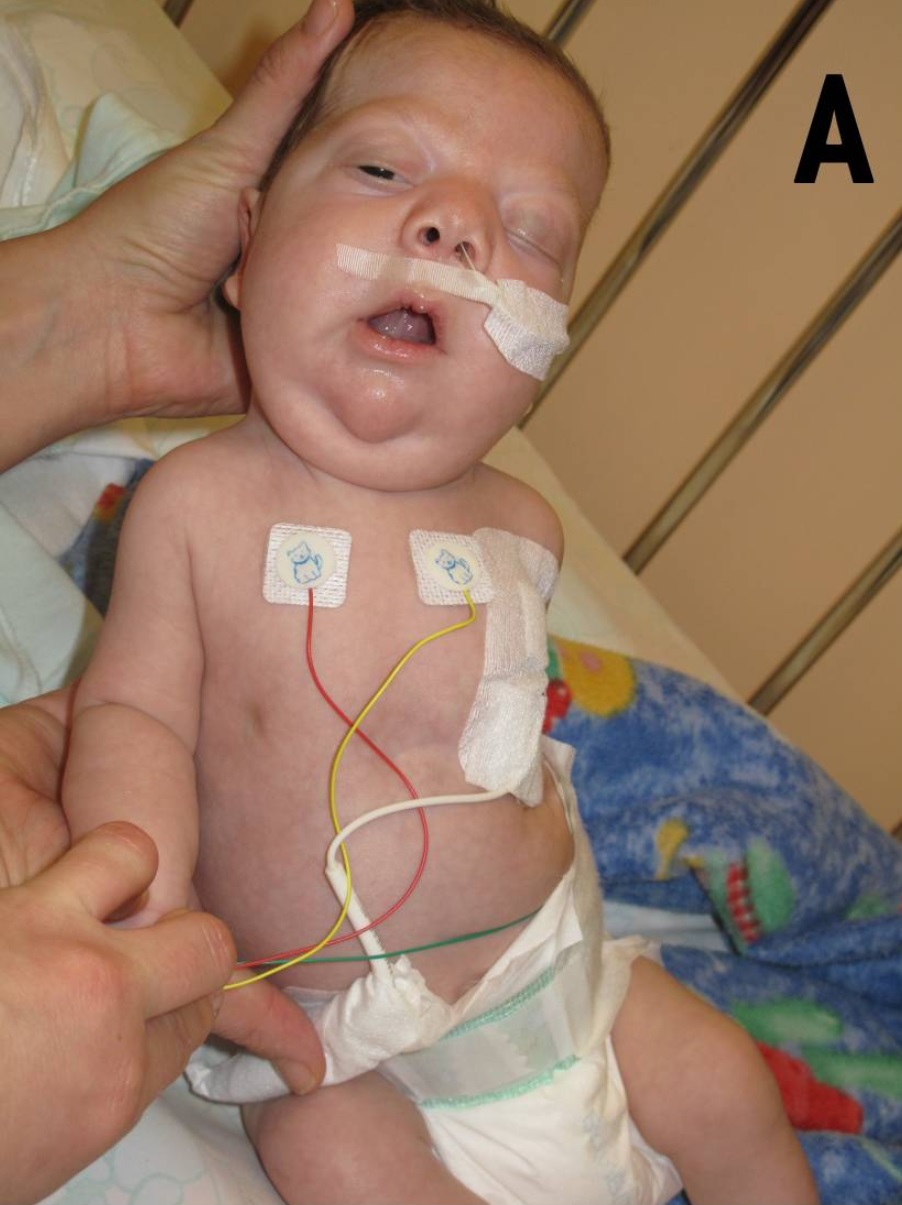
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. Some of NS' symptoms are shared with Watson syndrome, a related genetic condition. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves sustained activation of the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having Heterozygosity, two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or Heredity, inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that Ethnogenesis, emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium Common era, CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language that originated in the 9th century, and largely migrated towards Northern Europe#UN geoscheme classification, northern and eastern Europe during the late Middle Ages due to Antisemitism in Europe, persecution. Hebrew was primarily used as a Literary language, literary and sacred language until its 20th-century Revival of the Hebrew language, revival as a common language in Israel. Ashkenazim adapted their traditions to Europe and underwent a transformation in their interpretation of Judaism. In the late 18th and 19th centuries, Jews who remained in or returned to historical German lands experienced a cultural reorientation. Under the influence of the Haskalah and the struggle for emancipation, as well as the intellec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemophilia C
Haemophilia C (also known as plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA) deficiency or Rosenthal syndrome) is a mild form of haemophilia affecting both sexes, due to factor XI deficiency. It predominantly occurs in Ashkenazi Jews. It is the fourth most common coagulation disorder after von Willebrand's disease and haemophilia A and B. In the United States, it is thought to affect 1 in 100,000 of the adult population, making it 10% as common as haemophilia A. Signs and symptoms In terms of the signs/symptoms of haemophilia C, unlike individuals with Haemophilia A and B, people affected by it are not ones to bleed spontaneously. In these cases, haemorrhages tend to happen after a major surgery or injury. However, people affected with haemophilia C might experience symptoms closely related to those of other forms of haemophilia such as the following: Cause Haemophilia C is caused by a deficiency of coagulation factor XI and is distinguished from haemophilia A and B by the fact it doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide Bond
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups. In inorganic chemistry, the anion appears in a few rare minerals, but the functional group has tremendous importance in biochemistry. Disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Compounds of the form are usually called '' persulfides'' instead. Organic disulfides Structure Disulfides have a C–S–S–C dihedral angle approaching 90°. The S–S bond length is 2.03 Å in diphenyl disulfide, similar to that in elemental sulfur. Disulfides are usually symmetric but they can also be unsymmetric. Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organosulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (; symbol Cys or C) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine enables the formation of Disulfide, disulfide bonds, and often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. Cysteine is chiral, but both D and L-cysteine are found in nature. LCysteine is a protein monomer in all biota, and D-cysteine acts as a signaling molecule in mammalian nervous systems. Cysteine is named after its discovery in urine, which comes from the urinary bladder or cyst, from Ancient Greek, Greek κύστις ''kýstis'', "bladder". The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide bond, disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. When used as a food additive, cysteine has the E number E920. Cysteine is Genetic code, encoded by the codo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein Ib
Glycoprotein Ib (GPIb), also known as CD42, is a component of the GPIb-V-IX complex on platelets. The GPIb-V-IX complex binds von Willebrand factor, allowing platelet adhesion and platelet plug formation at sites of vascular injury. Glycoprotein Ibα (GPIbα) is the major ligand-binding subunit of the GPIb-V-IX complex. GPIbα is heavily glycosylated. It is deficient in the Bernard–Soulier syndrome. A gain-of-function mutation causes platelet-type von Willebrand disease. Autoantibodies against Ib/IX can be produced in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Components include GP1BA and GP1BB Glycoprotein Ib (platelet), beta polypeptide (GP1BB) also known as CD42c (Cluster of Differentiation 42c), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BB gene. Function Platelet glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) is a heterodimeric transmembrane prot .... It complexes with Glycoprotein IX. References External links * Glycoproteins {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
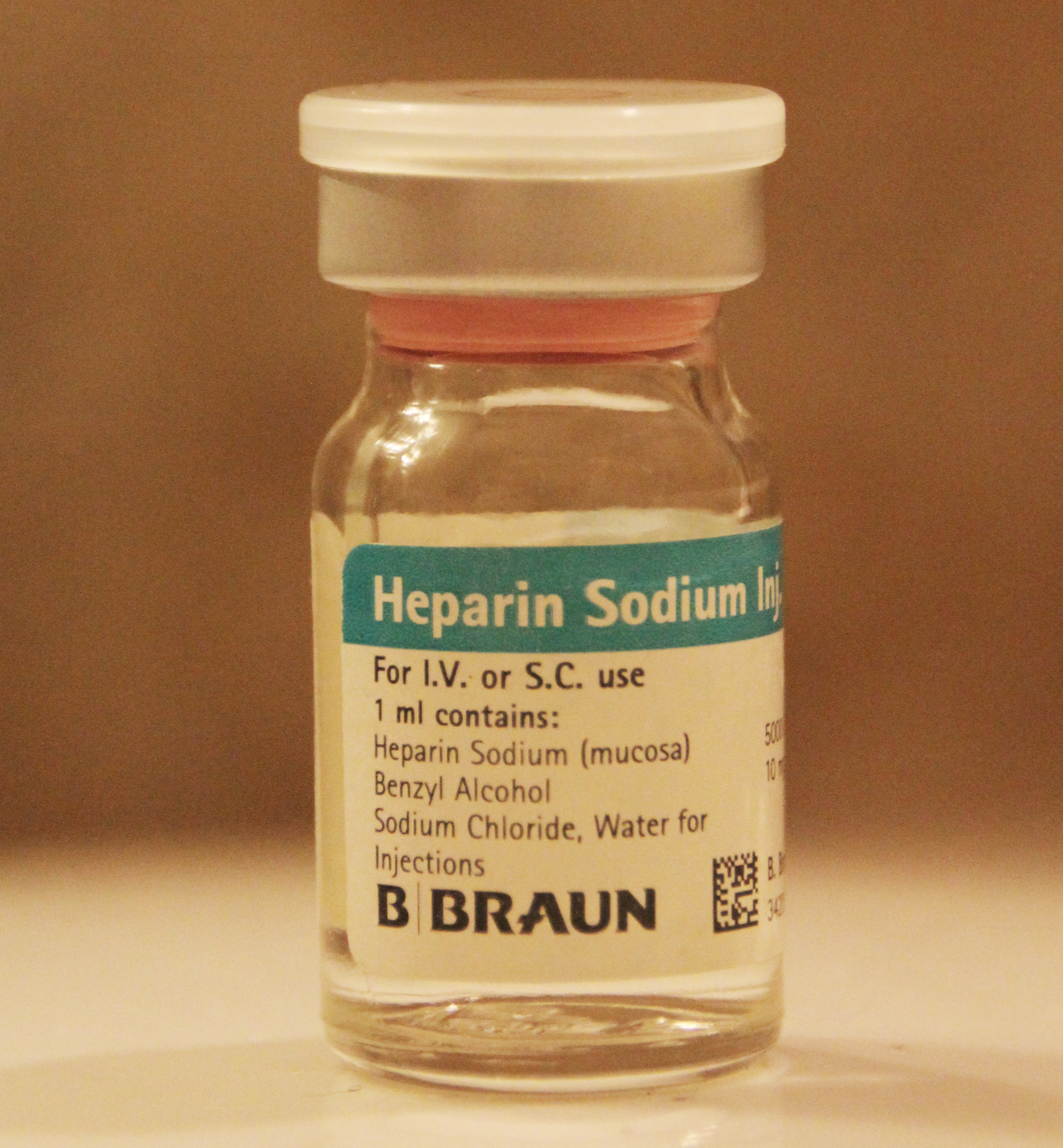
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood anticoagulant that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of myocardial infarction, heart attacks and unstable angina. It can be given intravenously or by subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin. Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of Post-vaccination embolic and thrombotic events, vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |