|
Clipstone Miners Welfare F
Clipstone is a village in the Newark and Sherwood district of Nottinghamshire, England. The population of the civil parish was 3,469 at the 2001 census, increasing to 4,665 at the 2011 census, and substantially more so to 6,185 at the 2021 census. The village was formally based on mining as part of the Industrial Revolution. Clipstone Colliery Headlocks History Clipstone is very close to the village of Kings Clipstone. The earliest historical reference to the settlement is in the Domesday Book of 1086, where the village is mentioned as "Clipestune". Subsequent written sources use the forms "Clipestone", "Clippeston", "Clipiston". The place-name Clipstone seems to contain an Old Norse personal name, ''Klyppr'', with ''tun'' (Old English), an enclosure or farmstead, so 'Klyppr's farm or settlement'. Prehistoric period The earliest date-able material from Clipstone is from the Bronze Age. These pieces of material were a spearheadNottinghamshire Historic Environment Record, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated ''Notts.'') is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. The county is bordered by South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. The largest settlement is the city of Nottingham (323,632), which is also the county town. The county has an area of and a population of 1,154,195. The latter is concentrated in the Nottingham Urban Area, Nottingham built-up area in the south-west, which extends into Derbyshire and has a population of 729,997. The north-east of the county is more rural, and contains the towns of Worksop (44,733) and Newark-on-Trent (27,700). For Local government in England, local government purposes Nottinghamshire comprises a non-metropolitan county, with seven districts, and the Nottingham Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area. The East Midlands Combined County Authority includes Nottinghamshire County Council and Nottingham City Council. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Ditch
In archaeology, a ring ditch is a trench of circular or penannular plan, cut into bedrock. They are usually identified through aerial photography either as soil marks or cropmarks. When excavated, ring ditches are usually found to be the ploughed‐out remains of a round barrow where the barrow mound has completely disappeared, leaving only the infilled former quarry ditch. Both Neolithic and Bronze Age ring ditches have been discovered. The term is most often used as a generic description in cases where there is no clear evidence for the function of the site: for instance where it has been ploughed flat and is known only as a cropmark or a geophysical anomaly. The two most frequent monument types represented by ring ditches are roundhouses (where the 'ditch' is actually a foundation slot or eaves drip gully) and round barrows. The term is not normally used for larger features than these. Larger features would instead be described as 'circular enclosures'. Also related to ring dit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayman Rooke
Major Hayman Rooke (1723–1806) was an English antiquarian and British Army soldier who discovered the Major Oak tree in Sherwood Forest and two Roman Villas near Mansfield Woodhouse, Nottinghamshire. The Major Oak is named after him. Biography Hayman Rooke was born on 20 February 1723 and baptised at St Martin-in-the-Fields in City of Westminster on 19 March of the same year.Major Oak Day accessed October 2011 After a modest military career, in which he achieved the rank of in the 30th Regiment of Foot, Hayman Rooke retired to |
Villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house that provided an escape from urban life. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity, sometimes transferred to the Church for reuse as a monastery. They gradually re-evolved through the Middle Ages into elegant upper-class country homes. In the early modern period, any comfortable detached house with a garden near a city or town was likely to be described as a villa; most surviving villas have now been engulfed by suburbia. In modern parlance, "villa" can refer to various types and sizes of residences, ranging from the suburban semi-detached double villa to, in some countries, especially around the Mediterranean, residences of above average size in the countryside. Roman Roman villas included: * the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marching Camp
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English language, English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". Scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large Roman legion, legionary fortresses, smaller forts for Cohort (military unit), cohorts or for auxiliary forces, military camp, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. Etymology ''Castrum'' appears in Oscan language, Oscan and Umbrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
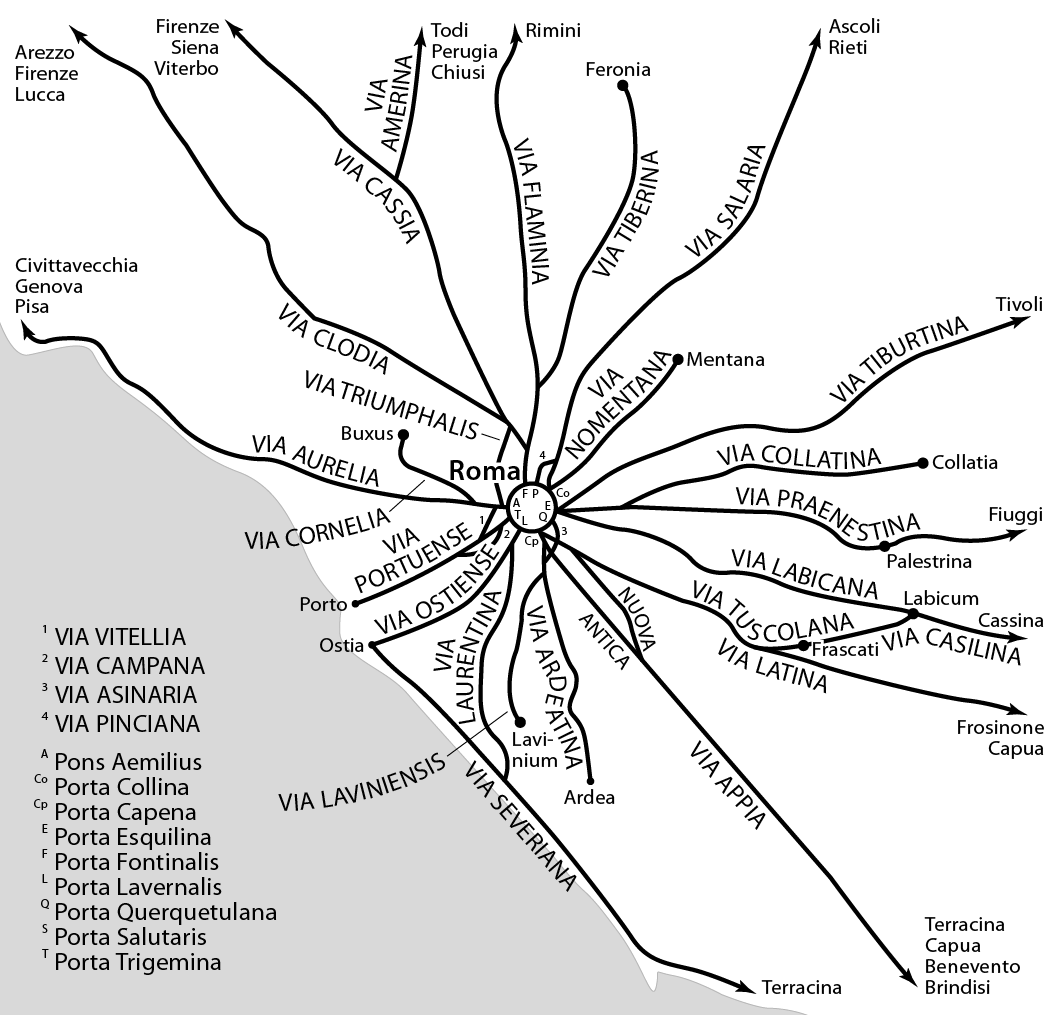
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coin Hoard
A hoard or "wealth deposit" is an archaeological term for a collection of valuable objects or artifacts, sometimes purposely buried in the ground, in which case it is sometimes also known as a cache. This would usually be with the intention of later recovery by the hoarder; hoarders sometimes died or were unable to return for other reasons (forgetfulness or physical displacement from its location) before retrieving the hoard, and these surviving hoards might then be uncovered much later by metal detector hobbyists, members of the public, and archaeologists. Hoards provide a useful method of providing dates for artifacts through association as they can usually be assumed to be contemporary (or at least assembled during a decade or two), and therefore used in creating chronologies. Hoards can also be considered an indicator of the relative degree of unrest in ancient societies. Thus conditions in 5th and 6th century Britain spurred the burial of hoards, of which the most famous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Rahtz
Philip Arthur Rahtz (11 March 1921 – 2 June 2011) was a British archaeologist. Rahtz was born in Bristol. After leaving Bristol Grammar School, he became an accountant before serving with the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. During war service, Rahtz became friends with the archaeologist Ernest Greenfield, the excavator of Great Witcombe Roman Villa, Gloucestershire and Lullingstone Castle, Kent. This friendship sparked a personal interest in archaeology and a professional career, which began with excavations at Chew Valley Lake (north Somerset) in 1953. A wide range of excavations in the area followed including Old Sarum in 1957, Glastonbury Tor in 1964–1966 and a Romano-Celtic Temple at Pagans Hill, Chew Stoke, from 1958. He also excavated at Bordesley Abbey, Worcestershire. Rahtz later ran summer school excavations for the University of Birmingham. He achieved his first permanent job as a lecturer at that university in 1963, and in 1978 he was appoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other flight, airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography. Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs or "drones"), balloon (aircraft), balloons, blimps and dirigibles, rockets, pigeon photography, pigeons, kite aerial photography, kites, or using action cameras while skydiving or wingsuiting. Handheld cameras may be manually operated by the photographer, while mounted cameras are usually remote operation, remotely operated or triggered automatically. Aerial photography typically refers specifically to bird's-eye view images that focus on landscapes and Earth surface, surface objects, and should not be confused with air-to-air photography, where one or more aircraft are used as chase planes that "chase" and photograph other aircraft in flight. Elevated photography can also produce b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |