|
Clionoidea
Clionoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of sea slugs, specifically naked (i.e. unshelled) pteropods, marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusks in the clade Gymnosomata. They are sometimes called "sea angels" or "naked sea butterflies" along with the other superfamily in the Gymnosomata. They can be found anywhere from the surface to a depth of 350 meters. They are transparent and small, with the largest of the species being up to 5 cm. Common ''Clione'' Some species of sea angel feed only on sea butterflies. The angels have terminal mouths with the radula common to mollusks, and tentacles to grasp their prey, sometimes with suckers similar to cephalopods. Their "wings" allow sea angels to swim much faster than the larger (usually fused) wings of sea butterflies. Gymnosomes slowly beat their wing-like parapodia in a rowing motion to propel their perfectly-streamlined bodies through the upper 20 meters of the water column. Although usually slow moving, beating their wings once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy Of The Gastropoda (Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005)
The taxonomy of the Gastropoda as it was revised in 2005 by Philippe Bouchet and Jean-Pierre Rocroi is a system for the scientific classification of gastropod mollusks. (Gastropods are a taxonomic class of animals which consists of snails and slugs of every kind, from the land, from freshwater, and from saltwater.) The paper setting out this taxonomy was published in the journal '' Malacologia''. The system encompasses both living and extinct groups, as well as some fossils whose classification as gastropods is uncertain. The Bouchet & Rocroi system was the first complete gastropod taxonomy that primarily employed the concept of clades, and was derived from research on molecular phylogenetics; in this context a clade is a "natural grouping" of organisms based upon a statistical cluster analysis. In contrast, most of the previous overall taxonomic schemes for gastropods relied on morphological features to classify these animals, and used taxon ranks such as order, superorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosomata
Sea angels (clade Gymnosomata) are a large group of small free-swimming sea slugs, not to be confused with Cnidarians (Jellyfish and other similar creatures), classified into six different families. They are pelagic opisthobranchs in the clade Gymnosomata within the larger mollusc clade Heterobranchia. Sea angels were previously referred to as a type of pteropod. Sea angels are also sometimes known as "cliones" but this is potentially misleading because the family Clionidae is just one of the families within this clade. Recent molecular data suggest the Gymnosomata form a sister group to the Thecosomata (other planktonic, weakly or nonmineralized gastropods), but this long-standing hypothesis has also had some recent detractors. Fossils of the group go back to the Middle Frasnian stage of the Late Devonian period. Distribution These organisms have a wide geographic range, from polar regions, under sea ice, to equatorial (tropic) seas. Description In this clade, the foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clione Limacina
''Clione limacina'', known as the naked sea butterfly, sea angel, and common clione, is a sea angel (pelagic sea slug) found from the surface to greater than depth.Gofas, S. (2012). ''Clione limacina''. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=139178 on 2012-07-23 It lives in the Arctic Ocean and cold regions of the North Atlantic Ocean. It was first described by Friderich Martens in 1676 and became the first gymnosomatous (without a shell) " pteropod" to be described. Subspecies * ''Clione limacina australis'' ( Bruguière, 1792)Gofas, S. (2011). ''Clione limacina''. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=139178 on 2011-01-29 * ''Clione limacina limacina'' (Phipps, 1774) Distribution ''Clione limacina'' is found in cold waters of the Arctic Ocean and North Atlantic Ocean, ranging south at least to the Sargasso Sea. There are three oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notobranchaeidae
The Notobranchaeidae, or "naked sea butterflies", are a taxonomic family of floating sea slugs, specifically under the subclass Opistobranchia, also called "sea angels". Similar to other Pteropods, these pelagic marine heterobranch gastropod mollusks are holoplanktonic. Morphology While they are not particularly strong swimmers, the foot of these organisms is modified into wing-like structures, called parapodia that they employ for locomotion. Additionally, like other Pteropods of the order Gymnosomata, Notobrachaeidae lack shells entirely as adults.Pierrot-Bults, Annelies & Peijnenburg, K. (2015). Pteropods. Encyclopedia of marine geosciences. 1-10. However, they do possess a shell earlier on in their lives. They are also defined by how they possess a posterior gill, strong jaws, grasping tentacles that frequently possess suckers resembling those of cephalopods, and usually buccal cones as well. Behavior Like other members of the clade Gymnosomata, Notobrachaeidae are highly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliopsidae
The Cliopsidae, common name sea angels, are a taxonomic family of small, free-swimming sea slugs, pelagic marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusks in the order Opisthobranchia. As is the case in all gymnosome pteropods, these sea angels lack a shell except during an early embryonic stage. The small lateral wing-like flaps (parapoda) are used in a slow swimming mode. The foot is reduced to three small median lobes. Genera and species Genera and species within the family Cliopsidae include: Genus ''Cliopsis'' Troschel, 1854 * ''Cliopsis krohnii'' Troschel, 1854 Troschel, Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Pteropoden, Archiv f. Naturgesch., Jáhrg. xx. p. 222, p1. x. figs. 2-4. Genus ''Pruvotella'' * ''Pruvotella danae'' Pruvot-Fol, 1942 ** Distribution : Bermuda ) , anthem = "God Save the King" , song_type = National song , song = "Hail to Bermuda" , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , mapsize2 = , map_caption2 = , subdivision_type = Sovereign s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clionidae
The Clionidae are a family of sea angels, which are a group of pelagic marine gastropods. They resemble angels, complete with flapping "wings", hence their common name. They are gelatinous, mostly transparent pteropods, and they only have shells in their embryonic stage. They are mostly very small, with the largest species (''Clione limacina'') reaching . External anatomy The Clionidae use winglike flaps for rhythmical locomotion, as if flying in the sea. These "wings" are attached to the anterior part of the body. The posterior part is gelatinous and mostly transparent. The orange visceral sac is confined to the anterior part. Life habits Mating is carried out ventrally for mutual fertilization. The following spring, this results in a free-floating, gelatinous egg mass. Taxonomy Clionidae d'Orbigny, 1851 is unfortunately also the name of a family of sponges in the order Hadromerida, class Demospongiae. Within the ICZN there has been a proposed emendation of spelling to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms (such as grass or algae which produce their own food via photosynthesis) and ending at an apex predator species (like grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivores (like earthworms or woodlice), or decomposer species (such as fungi or bacteria). A food chain also shows how organisms are related to each other by the food they eat. Each level of a food chain represents a different trophic level. A food chain differs from a food web because the complex network of different animals' feeding relations are aggregated and the chain only follows a direct, linear pathway of one animal at a time. Natural interconnections between food chains make it a food web. Food chains were first introduced by the Arab scientist and philosopher Al-Jahiz in the 10th century and later popularized in a book published in 1927 by Charles Elton, which also introduced the food web concept. A common metric used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem. By way of his voyages in the 1770s, James Cook proved that waters encompassed the southern latitudes of the globe. Since then, geographers have disagreed on the Southern Ocean's northern boundary or even existence, considering the waters as various parts of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, instead. However, according to Commodore John Leech of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), recent oceanographic research has discovered the importance of Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
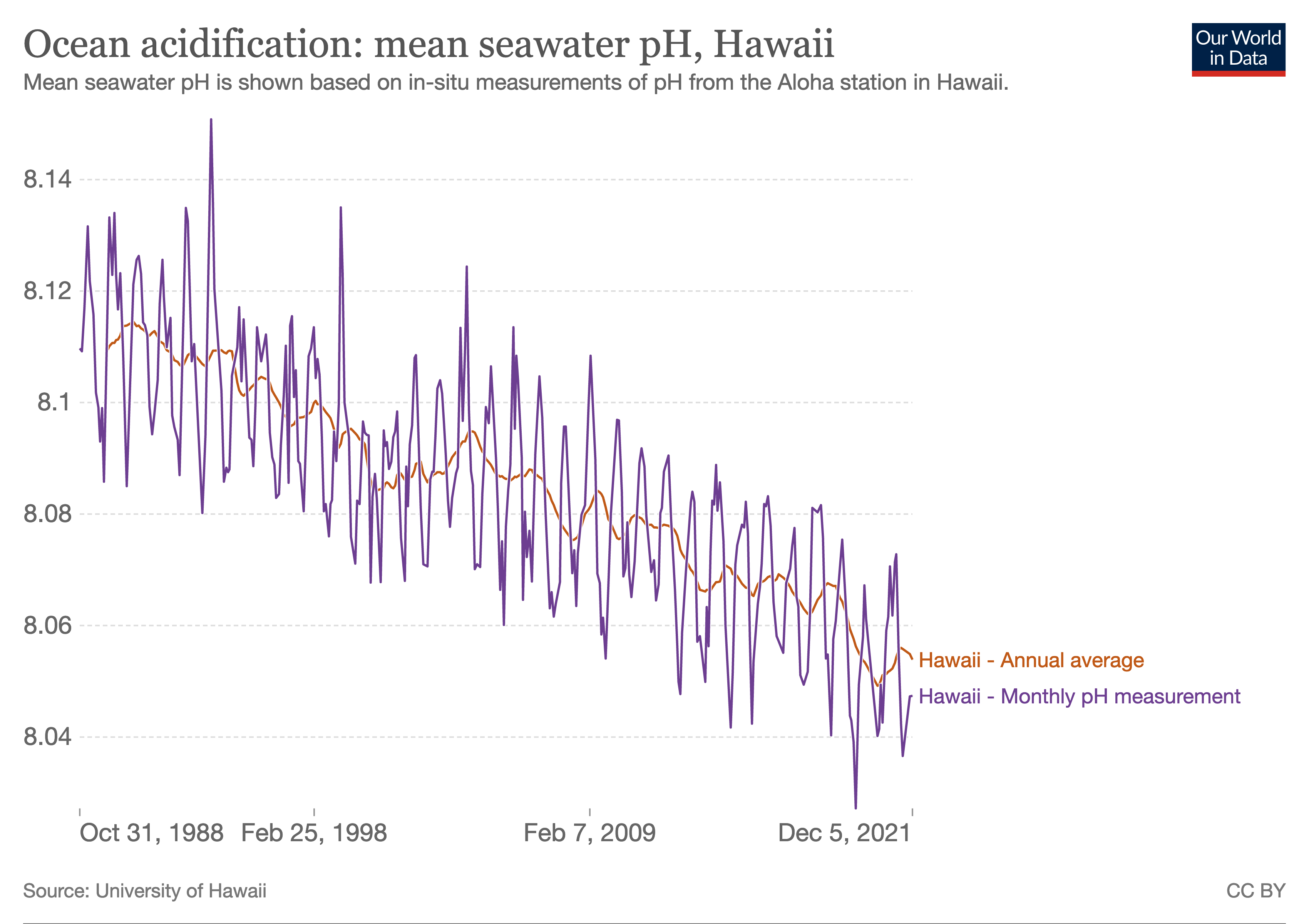
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxide emissions from human activities which have led to atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels of more than 410 ppm (in 2020). The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. This leads to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (H+). The free hydrogen ions (H+) decrease the pH of the ocean, therefore increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). A decrease in pH corresponds to a decrease in the concentration of carbonate ions, which are the main building block for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells and skeletons. Marine calcifying organisms, like mollusks, oysters and corals, are particularly affected by this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusks
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPCC
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts to prepare IPCC reports. It draws the experts from nominations by governments and observer organisations. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC informs governments about the state of knowledge of climate change. It does this by examining all the relevant scientific literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |