|
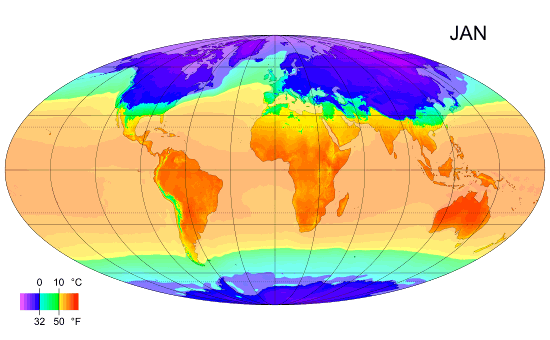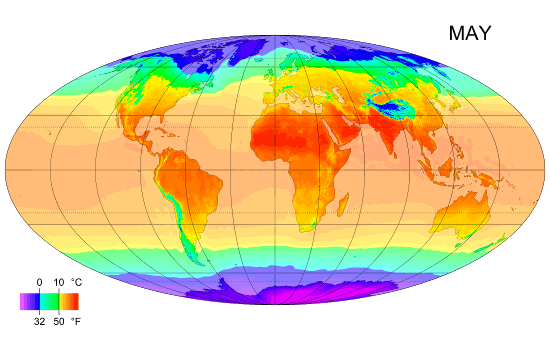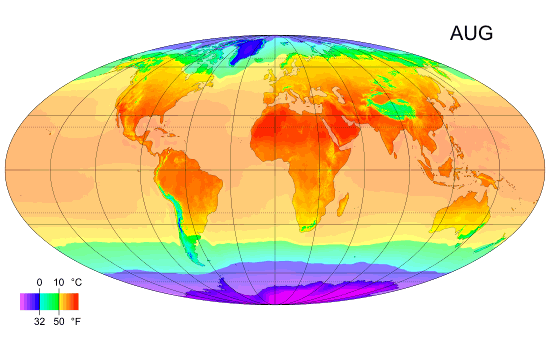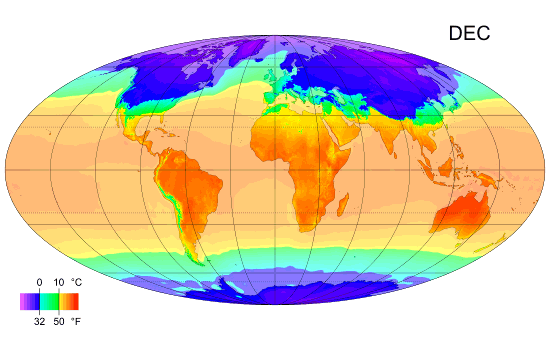
Climates
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoclimatologists
Paleoclimatology ( British spelling, palaeoclimatology) is the scientific study of climates predating the invention of meteorological instruments, when no direct measurement data were available. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important to understand natural variation and the evolution of the current climate. Paleoclimatology uses a variety of proxy methods from Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, boreholes, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells, and microfossils. Combined with techniques to date the proxies, the paleoclimate records are used to determine the past states of Earth's atmosphere. The scientific field of paleoclimatology came to maturity in the 20th century. Notable periods studied by paleoclimatologists include the frequent glaciations that Earth has undergone, rapid cooling events like the Younger Dryas, and the rapid warming durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Classification
Climate zones are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. The most used is the Köppen climate classification scheme first developed in 1884. There are several ways to classify climates into similar regimes. Originally, climes were defined in Ancient Greece to describe the weather depending upon a location's latitude. Modern climate classification methods can be broadly divided into ''genetic'' methods, which focus on the causes of climate, and ''empiric'' methods, which focus on the effects of climate. Examples of genetic classification include methods based on the relative frequency of different air mass types or locations within synoptic scale meteorology, synoptic weather disturbances. Examples of empirical, empiric classifications include climate zones defined by plant hardiness, evapotranspiration, or associations with certain biomes, as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornthwaite Climate Classification
The Thornthwaite climate classification is a climate classification system created by American climatologist Charles Warren Thornthwaite in 1931 and modified in 1948. 1931 classification Precipitation effectiveness Thornthwaite initially divided climates based on five characteristic vegetations: Rainforest, forest, grassland, steppe and desert. One of the main factors for the local vegetation is precipitation, but most importantly, precipitation effectiveness, according to Thornthwaite. Thornthwaite based the effectiveness of precipitation on an index (the P/E index), which is the sum of the 12 monthly P/E ratios. The monthly P/E ratio can be calculated using the formula: P/E \text = \frac Temperature efficiency Similarly to precipitation effectiveness, Thornthwaite also developed a T/E index to represent thermal efficiency. Featuring six climate provinces: Tropical, mesothermal, microthermal, taiga, tundra and frost. The T-E index is the sum of the 12 monthly T-E ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth. Weather is driven by atmospheric pressure, air pressure, temperature, and moisture differences between one place and another. These differences can occur due to the effect of Sun angle on climate, Sun's angle at any particular spot, which varies with latitude. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the largest scale atmospheric circulations: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Diversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than one-fifth of Earth's terrestrial area and contain about 50% of the world's species. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity for both marine and terrestrial taxa. Since life began on Earth, six major mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The Phanerozoic aeon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the Cambrian explosion. In this period, the majority of multicellular phyla first appeared. The next 400 million years included repeated, massive biodiversity loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at , and 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |